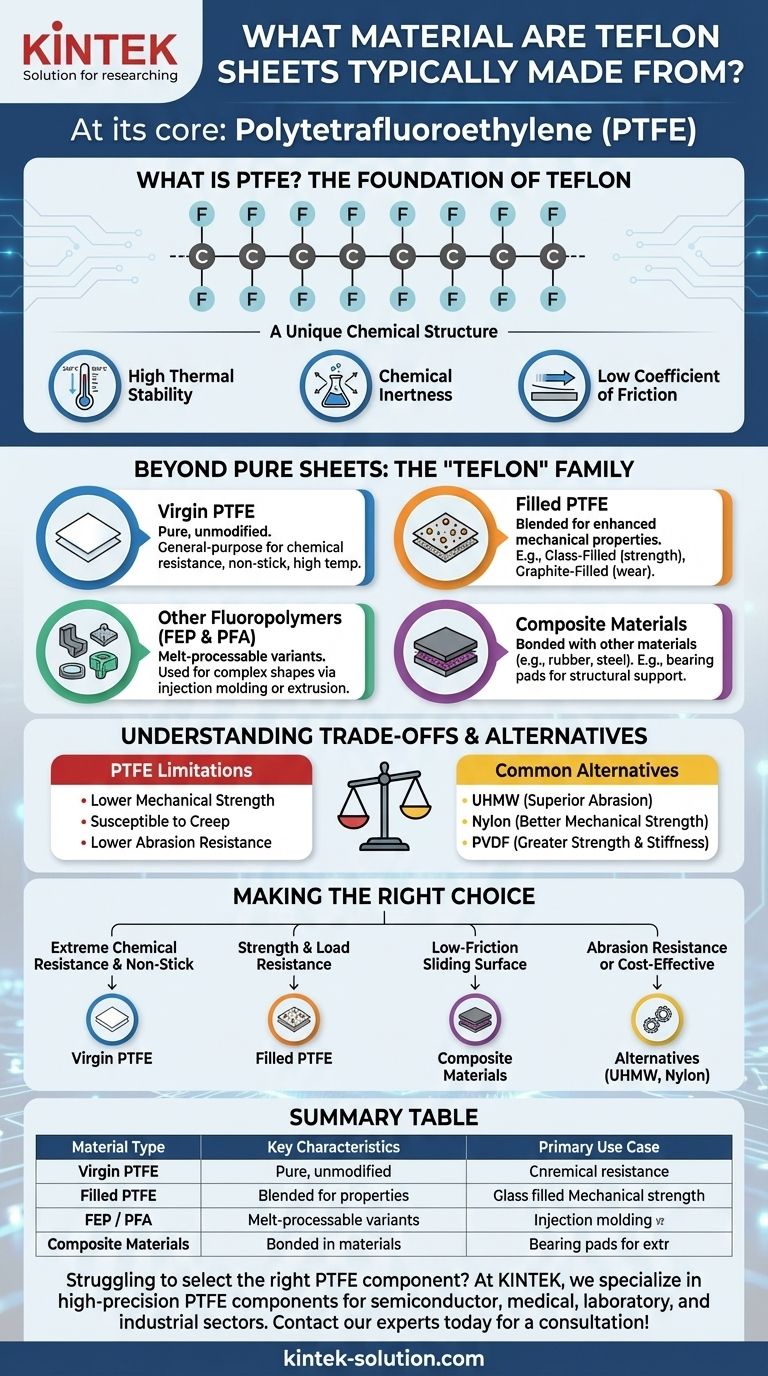
At its core, a Teflon sheet is made from a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer known as polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This material, part of a larger family of fluorocarbons, consists exclusively of carbon and fluorine atoms. Its unique molecular structure is the source of its celebrated properties, including exceptional heat resistance and a famously non-stick surface.
While PTFE is the foundational material, the term "Teflon" often serves as a brand name for a family of related materials. Understanding that pure sheets, filled compounds, and composite systems all exist under this umbrella is critical to solving your specific engineering challenge.

What is PTFE? The Foundation of Teflon
To understand Teflon, you must first understand its primary component, PTFE. This is not an ordinary plastic; it is a high-performance polymer engineered for extreme conditions.
A Unique Chemical Structure
PTFE is a fluorocarbon, meaning it's composed of a long chain of carbon atoms completely surrounded by fluorine atoms. The carbon-fluorine bond is one of the strongest in organic chemistry.
This incredibly stable and tightly bonded structure is directly responsible for the material's signature characteristics. It creates a chemically inert and low-friction surface at a molecular level.
Key Performance Properties
The structure of PTFE gives rise to three defining properties that make it invaluable across industries:
- High Thermal Stability: PTFE can withstand a wide range of temperatures, from cryogenic levels up to approximately 260°C (500°F), without degrading.
- Chemical Inertness: It is resistant to almost all chemicals and solvents, making it ideal for use in corrosive environments.
- Low Coefficient of Friction: PTFE has one of the lowest friction values of any known solid, which is why it is used for non-stick coatings and low-wear bearings.
Beyond Pure Sheets: The "Teflon" Family
While "Teflon sheet" often implies pure PTFE, the term is frequently used to describe a broader category of materials tailored for specific applications. The base PTFE is often modified to enhance certain properties.
Virgin PTFE
This is the pure, unmodified form of polytetrafluoroethylene. It is used for general-purpose applications where chemical resistance, high-temperature performance, and a non-stick surface are the primary requirements.
Filled PTFE
To improve mechanical properties, PTFE is often blended with fillers. For example:
- Glass-Filled PTFE: Increases compressive strength and dimensional stability.
- Graphite-Filled PTFE: Enhances wear resistance and thermal conductivity.
These compounds are chosen when pure PTFE might be too soft or prone to deforming under load.
Other Fluoropolymers (FEP & PFA)
The Teflon brand also includes other, similar fluoropolymers like FEP (fluorinated ethylene propylene) and PFA (perfluoroalkoxy). These materials share many of PTFE's benefits but can be melt-processed using conventional injection molding and extrusion techniques.
Composite Materials
In many applications, Teflon is not used alone but as a critical component in a larger system. For instance, structural bearing pads are often made by bonding a dimpled Teflon plate to a laminated rubber and steel pad, combining flexibility and load-bearing capacity with a low-friction sliding surface.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Alternatives
No material is perfect for every situation. While PTFE offers remarkable performance, it's essential to understand its limitations and when an alternative might be more suitable.
Limitations of PTFE
The primary trade-off with pure PTFE is its relatively low mechanical strength. It can be susceptible to "creep" or cold flow, where the material slowly deforms under sustained pressure. It also has lower abrasion resistance compared to harder engineering plastics.
Common Alternatives
Depending on the specific need, other polymers may be a better fit:
- UHMW (Ultra-High-Molecular-Weight Polyethylene): Offers superior abrasion resistance and impact strength at a lower cost, but with less heat and chemical resistance.
- Nylon: Provides better mechanical strength and wear resistance in certain applications but lacks the thermal and chemical stability of PTFE.
- PVDF (Polyvinylidene Fluoride): Another fluoropolymer that offers greater strength and stiffness than PTFE but with a narrower temperature range.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires matching your primary goal to the material's strengths.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance and non-stick performance: Virgin PTFE is the definitive choice.
- If your primary focus is strength and resistance to deformation under load: A glass-filled or other filled PTFE compound is likely necessary.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction sliding surface on a structural element: A composite material, such as a Teflon-bonded bearing pad, is the solution.
- If your primary focus is abrasion resistance or cost-effectiveness in a less demanding environment: Consider alternatives like UHMW or Nylon.
By looking beyond the brand name, you can select the precise fluoropolymer variant that ensures the success and longevity of your project.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Key Characteristics | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin PTFE | High chemical resistance, non-stick, excellent thermal stability | General-purpose applications requiring inertness and non-stick properties |
| Filled PTFE | Enhanced strength, improved wear resistance, better dimensional stability | Applications needing increased mechanical performance under load |
| FEP / PFA | Melt-processable, similar chemical/thermal properties to PTFE | Applications requiring complex shapes via injection molding or extrusion |
| Composite Materials | Combines PTFE with other materials (e.g., rubber, steel) for structural support | Low-friction sliding surfaces on structural elements like bearing pads |
Struggling to select the right PTFE component for your demanding application? At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need a prototype or a high-volume order, our expertise ensures you get a solution that delivers superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and performance. Let's solve your material challenge together—contact our experts today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE reducing flanges an excellent choice for piping systems? Achieve Superior Corrosion Resistance and Reliability
- What is FEP and how does it differ from PTFE? Key Differences in Performance & Manufacturing
- What are the advantages of using PTFE combined with glass fiber aggregates? Achieve Superior Strength & Durability
- What are the key properties of PTFE for lip seals? Master Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What temperature limits should be considered for Teflon FEP and PFA encapsulated O-rings? Ensure Seal Integrity in High-Temp Applications
- Why is PTFE an ideal material for butterfly valves? Superior Sealing and Chemical Resistance
- What advantages do PTFE rotary shaft seals offer in high-speed applications? Unlock Superior Speed and Reliability
- How is PTFE used in football protective gear? Enhancing Performance and Safety



















