At its core, a PTFE heat press sheet is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer, a material most people recognize by its common brand name, Teflon. Its unique chemical structure is what gives it the exceptional properties required for high-temperature applications like heat pressing.
While the material is simply Polytetrafluoroethylene, its true value comes from a unique combination of non-stick, heat-resistant, and durable properties. This makes it an indispensable protective barrier for both your project and your equipment in any heat transfer process.
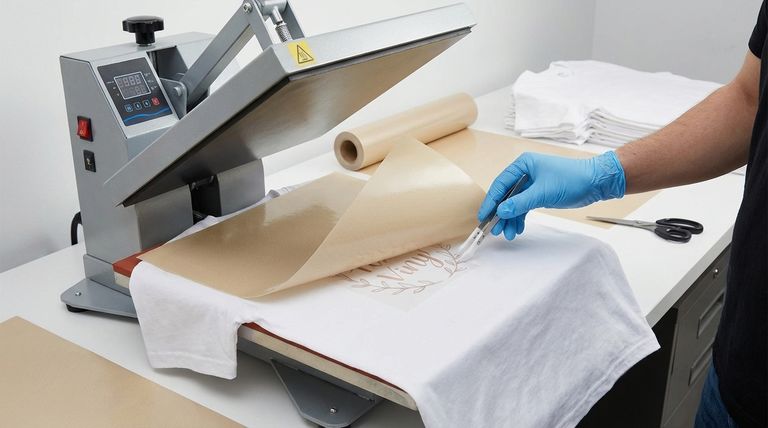
Why PTFE is the Ideal Material for Heat Pressing
The selection of PTFE is not accidental; its fundamental characteristics are perfectly suited for the demands of heat transfer applications. It solves several critical problems that arise when applying heat and pressure to textiles, vinyl, and sublimation inks.
Exceptional Heat Resistance
PTFE can withstand the high temperatures required for heat transfer vinyl (HTV) and sublimation without melting or degrading. This stability ensures it remains a reliable barrier press after press.
Superior Non-Stick Surface
This is perhaps its most crucial feature. The non-stick surface prevents inks, adhesives, and melted vinyl from sticking to the upper platen of your heat press, ensuring a clean transfer and easy cleanup.
High Chemical Resistance
The material is inert and does not react with the vast majority of chemicals, including the inks and dyes used in sublimation and other printing methods. This prevents contamination and ensures the sheet's longevity.
Durability and Reusability
A single PTFE sheet can be used for hundreds or even thousands of presses. Its durable nature makes it a highly cost-effective tool for both hobbyists and professional operations.
The Practical Role of a PTFE Sheet in Your Workflow
Understanding the material's properties is one thing; knowing its function in practice is what elevates your results. A PTFE sheet serves as a critical intermediary with two primary protective roles.
Protecting Your Garment
Placing a sheet over your design shields the fabric from direct, harsh contact with the heated metal platen. This helps prevent scorching or yellowing on sensitive materials like polyester.
Protecting Your Heat Press
The sheet acts as a guard for the upper platen. It catches any excess ink from sublimation or adhesive that might ooze from heat transfer vinyl, keeping your expensive equipment clean and free of residue that could ruin future projects.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
While highly effective, PTFE sheets are not without their operational nuances. Understanding their limitations is key to using them correctly and avoiding common mistakes.
Wrinkles Can Transfer
Any crease, wrinkle, or fold in the PTFE sheet can potentially be imprinted onto your final design under heat and pressure. Always ensure the sheet is completely flat before use.
It Is a Heat Barrier
The sheet is an insulator, not a conductor. It can slightly reduce the temperature that reaches your design. You may need to perform test presses and marginally increase your temperature or dwell time to compensate.
Contaminants Must Be Cleaned
The non-stick surface is easy to clean, but it must be done. Any stray bits of vinyl, lint, or ink residue left on the sheet from a previous job will be permanently pressed into your next one.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Using this knowledge effectively depends entirely on your specific goal. A PTFE sheet is a versatile tool that adapts to different heat transfer methods.
- If your primary focus is protecting your heat press: Use the sheet on every single press to prevent the slow buildup of adhesive and ink residue on your platen.
- If your primary focus is a clean vinyl (HTV) transfer: Place the sheet over your design to shield it from direct heat, preventing scorching and creating a smoother finish.
- If your primary focus is vibrant sublimation printing: Always use the sheet as a protective barrier to prevent ink blow-out or ghosting from contaminating your heat platen or press pads.
Understanding the properties of your PTFE sheet transforms it from a simple accessory into a critical tool for achieving consistent, professional-quality results.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Heat Pressing |
|---|---|
| Exceptional Heat Resistance | Withstands high temps without degrading, ensuring reliability. |
| Superior Non-Stick Surface | Prevents inks and vinyl from sticking, ensuring clean transfers. |
| High Chemical Resistance | Inert to inks and dyes, preventing contamination and extending life. |
| Durability & Reusability | Cost-effective for hundreds or thousands of presses. |
Achieve Flawless Heat Transfers with Precision PTFE Components from KINTEK
Understanding the critical role of high-quality PTFE is the first step. The next is ensuring you have a reliable supplier for the components that protect your projects and equipment.
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components—including custom heat press sheets, seals, liners, and labware. We serve the specialized needs of the industrial, laboratory, and textile printing industries.
Partner with KINTEK for:
- Consistent Performance: Our PTFE components offer the exact non-stick and heat-resistant properties you rely on.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototype sheets to high-volume orders, we tailor solutions to your specific requirements.
- Uncompromising Quality: Precision production ensures every component delivers durability and reliability, press after press.
Stop letting material limitations affect your results. Let KINTEK provide the high-performance PTFE components that safeguard your investments and elevate your output.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your custom PTFE needs!
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE control valves important in chemical industries? Ensure Safety and Reliability in Harsh Environments
- What are some variations of control valve designs? A Guide to Linear vs. Rotary Motion Valves
- How should one choose the right type of PTFE gasket? A Guide to Optimal Seal Performance
- What control options are available for PTFE/PFA lined ball valves? Choose the Right Actuation Method
- How are PTFE coated fasteners beneficial in the automotive sector? Enhance Reliability and Simplify Maintenance
- Can you provide an example of a large-scale PTFE application? The Metrodome's 20-Acre PTFE Roof
- What industries are particularly suited for PTFE with fillers? Enhance Performance in Demanding Applications
- What design considerations are important for PTFE slide bearing implementation? Achieve Long-Lasting, Low-Friction Performance



















