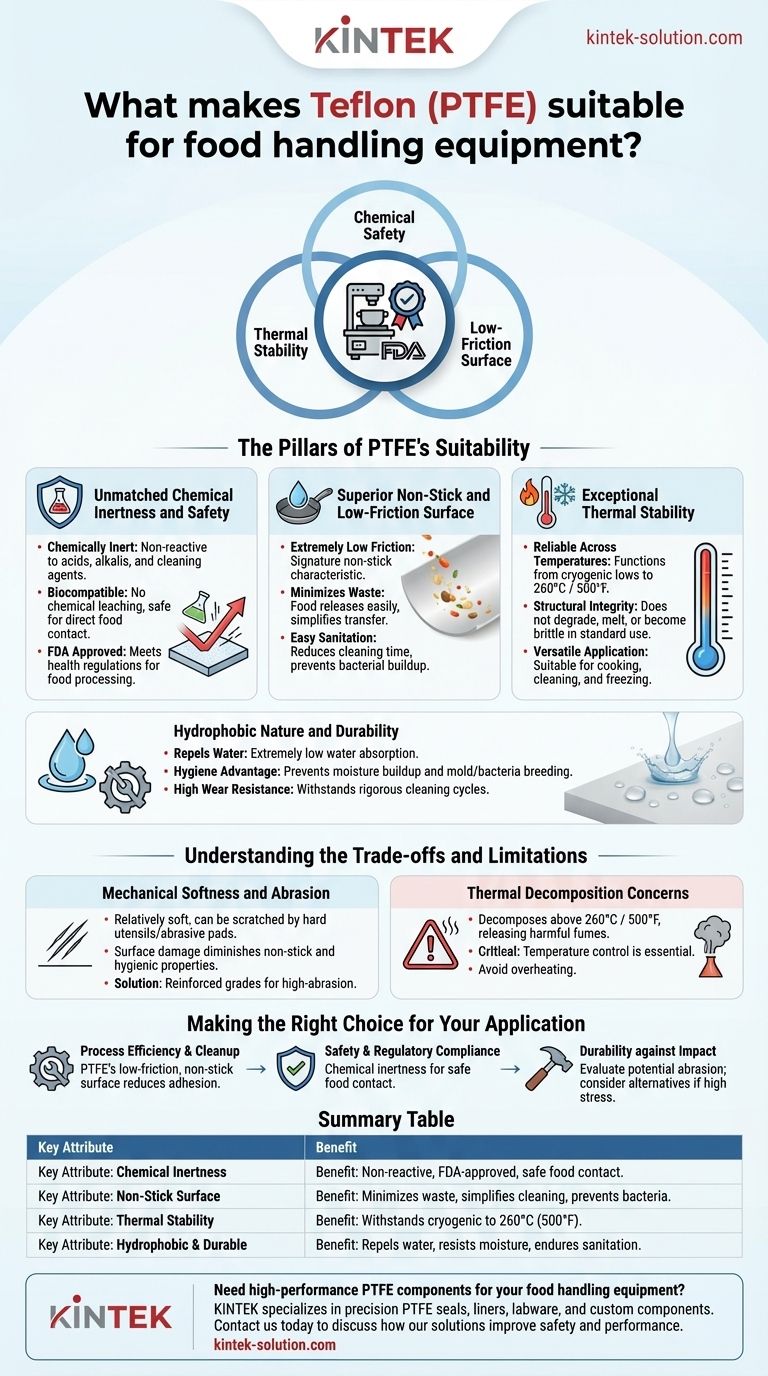
The suitability of Teflon (PTFE) for food handling stems from a unique combination of three core attributes: chemical safety, thermal stability, and an exceptionally low-friction surface. This trifecta ensures that equipment is not only compliant with health regulations like those from the FDA but also highly efficient and easy to sanitize, making it a cornerstone material in the food processing industry.
The core reason PTFE is trusted in food handling is not just its famous non-stick quality. It is the material's fundamental inability to react with food, cleaning agents, or extreme temperatures, which guarantees safety, purity, and operational performance.
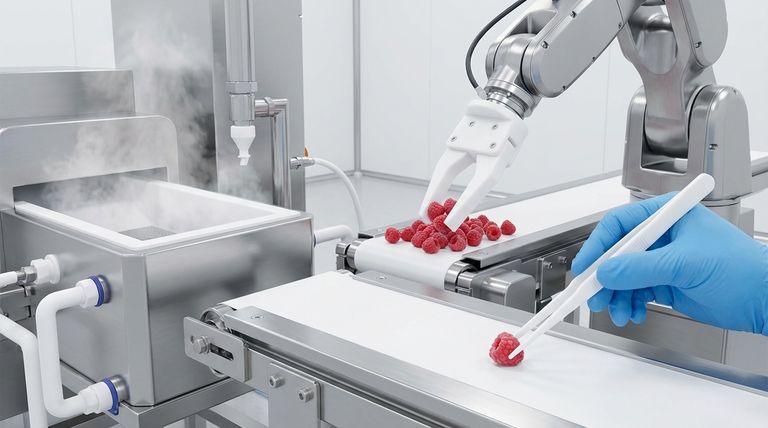

The Pillars of PTFE's Suitability in Food Handling
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a synthetic fluoropolymer engineered with properties that directly solve the primary challenges of food processing: safety, efficiency, and hygiene. Each attribute contributes to its widespread adoption and regulatory approval.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness and Safety
One of PTFE's most critical properties is that it is chemically inert. It does not react with acids, alkalis, or aggressive cleaning solutions commonly found in food production environments.
This inertness is the foundation for its biocompatibility. Because PTFE doesn't leach chemicals into its surroundings, it is safe for direct contact with food products, which is a prerequisite for gaining FDA approval and USDA certification.
Superior Non-Stick and Low-Friction Surface
PTFE is famous for its extremely low coefficient of friction, giving it its signature "non-stick" characteristic. This is not just a convenience; it is a major process advantage.
Food materials release easily from PTFE surfaces, which minimizes product waste and simplifies transfer between processing stages. This property also drastically reduces the time and effort required for cleaning and sanitation, preventing the buildup of food residue that could harbor bacteria.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
Food processing often involves a wide range of temperatures, from flash-freezing to baking and sterilization. PTFE performs reliably across this spectrum.
It maintains its structural integrity and properties at very high temperatures (up to 260°C / 500°F) and remains flexible at cryogenic lows. This thermal resistance ensures the material will not degrade, melt, or become brittle during standard cooking, cleaning, or freezing cycles.
Hydrophobic Nature and Durability
PTFE is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. Its rate of water absorption is extremely low, which is a critical feature for hygiene.
This resistance to moisture prevents the material from becoming a breeding ground for mold and bacteria. Combined with its high wear resistance, PTFE components can withstand repeated, rigorous cleaning cycles and maintain a sanitary surface over time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE is not without its limitations. Acknowledging these trade-offs is crucial for proper material selection and equipment design.
Mechanical Softness and Abrasion
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be scratched or damaged by hard metal utensils, abrasive cleaning pads, or sharp-edged food products like bone fragments.
Once the surface is compromised, its non-stick and hygienic properties can be diminished. In high-abrasion applications, reinforced grades of PTFE or alternative hard-coatings may be more appropriate.
Thermal Decomposition Concerns
Although it has excellent heat resistance, PTFE can begin to decompose at extremely high temperatures (generally above 260°C / 500°F). When overheated, it can release polymer fumes that are potentially harmful.
This is not a concern during normal food processing operations but highlights the importance of temperature control in applications like industrial ovens or direct-heat surfaces.
Cost and Fabrication
Compared to other polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene, virgin PTFE is a more expensive material. It also requires specialized techniques for molding and machining, which can add to the final cost of a component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on the specific demands of your equipment and process.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and easy cleanup: PTFE's low-friction, non-stick surface is its greatest asset for reducing product adhesion and simplifying sanitation protocols.
- If your primary focus is safety and regulatory compliance: The material's chemical inertness and resulting FDA approval make it a default choice for any surface in direct contact with food.
- If your primary focus is durability against physical impact: Carefully evaluate the potential for abrasion and consider if a softer material like PTFE can withstand the mechanical stress of your specific application.
Ultimately, understanding both the exceptional strengths and the practical limitations of PTFE empowers you to use it effectively and safely.
Summary Table:
| Key Attribute | Benefit in Food Handling |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive, FDA-approved for safe food contact; resistant to acids, alkalis, and cleaning agents. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Minimizes product waste, simplifies cleaning, and prevents bacterial buildup. |
| Thermal Stability | Withstands temperatures from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F) without degrading. |
| Hydrophobic & Durable | Repels water, resists moisture-related contamination, and endures rigorous sanitation cycles. |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your food handling equipment?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the food processing, semiconductor, medical, and laboratory industries. Our expertise ensures your equipment meets strict FDA and hygiene standards while enhancing operational efficiency.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specific requirements.
Contact us today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can improve the safety and performance of your food handling systems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How are PTFE gaskets and O-rings used in industrial and marine operations? Ensure Leak-Proof Sealing in Harsh Environments
- Why are PTFE extruded rods suitable for sealing applications? The Ultimate Guide to High-Performance Seals
- What are the temperature resistance properties of PTFE O-rings? Withstand -200°C to 260°C Extremes
- How do you install a PTFE coating thrust washer in a fishing reel? A Simple Upgrade for Smoother Casting & Longer Distance
- What are PTFE seals and why are they considered a reliable solution for extreme environments? Engineered for Harsh Conditions
- What industries commonly use PTFE components? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- Why is expanded PTFE considered superior for demanding applications? Unlock Superior Sealing Performance
- What are the main applications of rotary shaft seals? From Automotive to Pharma, Ensure Zero Leaks



















