At its core, Teflon's exceptional chemical resistance stems directly from its unique molecular structure. The bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms are among the strongest known in organic chemistry, creating a remarkably stable and non-reactive material that aggressive chemicals simply cannot break down.
The key to understanding Teflon's resilience is to see it as a molecular fortress. Its carbon backbone is completely shielded by a tightly packed sheath of fluorine atoms, held together by powerful bonds, making it inert to nearly all chemical attacks.
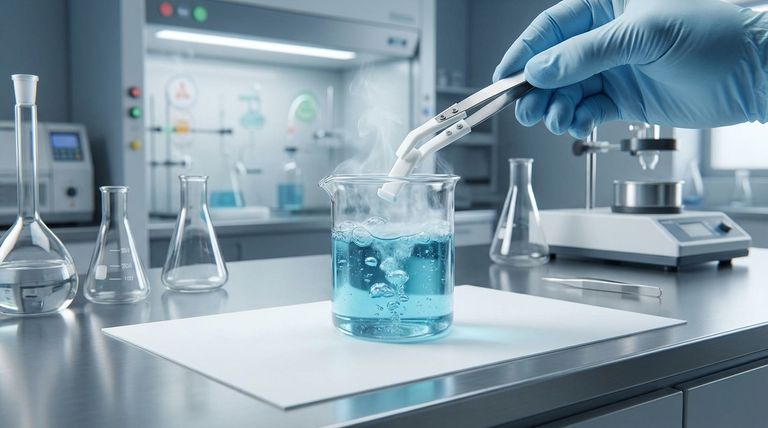

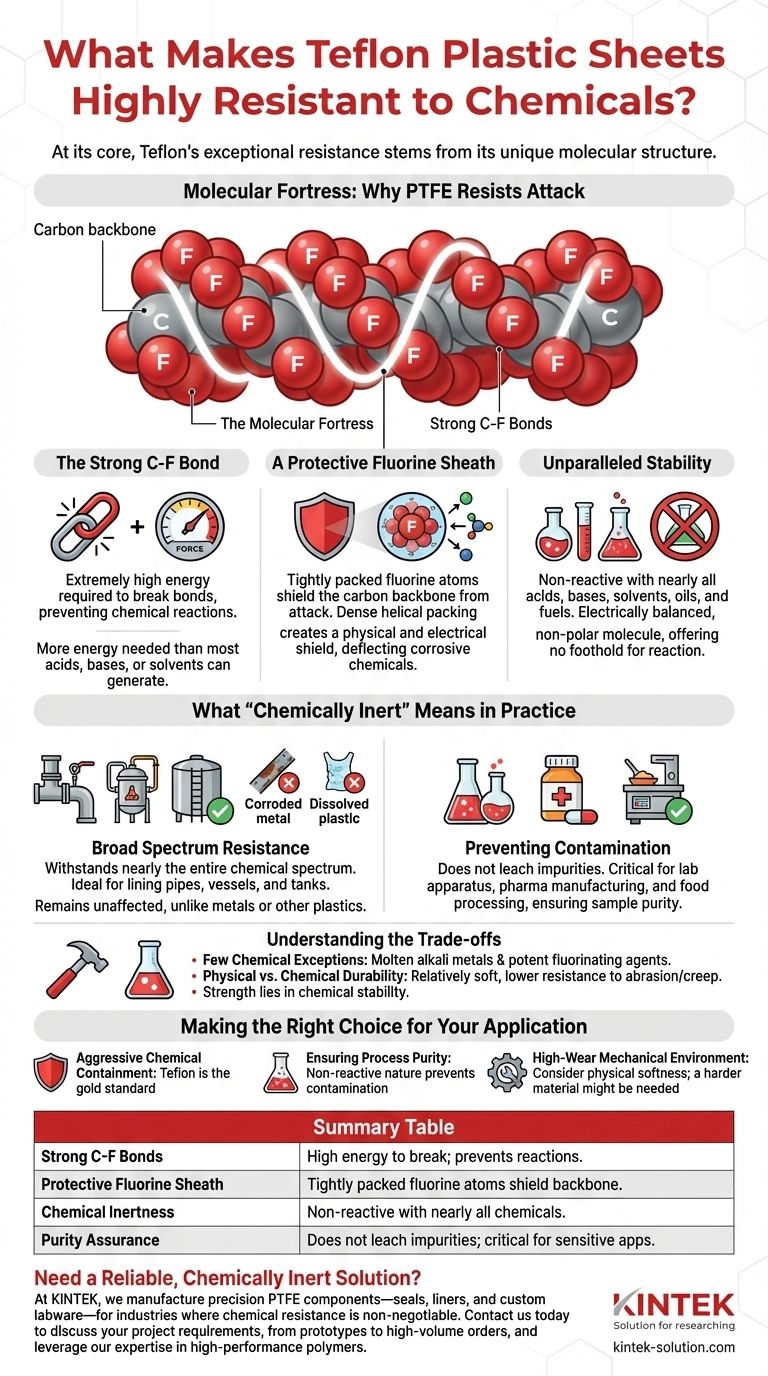
The Molecular Fortress: Why PTFE Resists Attack
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), the chemical name for Teflon, has a simple but incredibly robust structure. This structure is the source of its legendary chemical inertness.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The single bond between a carbon atom and a fluorine atom is extraordinarily strong. It requires a tremendous amount of energy to break, far more than what most acids, bases, or solvents can generate.
This inherent strength means that when a chemical comes into contact with a Teflon sheet, it lacks the power to initiate a reaction and break the material apart.
A Protective Fluorine Sheath
The fluorine atoms in the PTFE molecule are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to. They arrange themselves in a tight helix around the carbon chain backbone.
This dense helical packing creates a physical and electrical shield. It effectively prevents corrosive chemicals from even reaching the more vulnerable carbon backbone, deflecting them before they have a chance to react.
Unparalleled Stability
Because of this structure, Teflon is inert to a vast array of substances. It does not react with acids, bases, solvents, oils, fuels, or even highly reactive chemicals. The molecule is electrically balanced and non-polar, offering no foothold for a chemical reaction to begin.
What "Chemically Inert" Means in Practice
Understanding the molecular principle is one thing; seeing its impact in real-world applications is another. Teflon's inertness makes it a cornerstone material in demanding industries.
Broad Spectrum Resistance
Teflon sheets reliably withstand exposure to nearly the entire chemical spectrum. This makes them the material of choice for lining pipes, reaction vessels, and chemical storage tanks.
Unlike metals that corrode with acids or plastics that dissolve in solvents, PTFE remains completely unaffected.
Preventing Contamination
Because Teflon does not react with the substances it touches, it does not leach or release impurities. This property is critical in laboratory apparatus, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and food processing, where sample purity is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical resistance is nearly absolute, it's crucial to distinguish it from its physical properties. No material is without its limitations.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
In extremely rare and highly specialized conditions, PTFE can be attacked. These exceptions include molten alkali metals (like sodium) and some of the most potent fluorinating agents. For over 99% of applications, however, this is not a practical concern.
Physical vs. Chemical Durability
Teflon's chemical inertness does not make it indestructible. It is a relatively soft material with lower resistance to abrasion, creep, and cutting compared to metals or harder plastics. Its strength lies in its chemical stability, not its mechanical toughness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right material requires matching its properties to your primary goal.
- If your primary focus is containing aggressive chemicals: Teflon is the default gold standard, providing unwavering performance against nearly all acids, bases, and organic solvents.
- If your primary focus is ensuring process purity: Teflon's non-reactive nature prevents it from contaminating sensitive materials, making it ideal for laboratory, medical, or food-grade applications.
- If your primary focus is a high-wear mechanical environment: You must consider Teflon's physical softness and evaluate if a harder material is needed, even if it means sacrificing some chemical resistance.
Ultimately, relying on Teflon for chemical containment is a decision backed by the fundamental principles of chemistry.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters for Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|
| Strong C-F Bonds | Extremely high energy required to break these bonds, preventing chemical reactions. |
| Protective Fluorine Sheath | Tightly packed fluorine atoms shield the carbon backbone from attack. |
| Chemical Inertness | Non-reactive with nearly all acids, bases, solvents, oils, and fuels. |
| Purity Assurance | Does not leach impurities, critical for labs, pharmaceuticals, and food processing. |
Need a Reliable, Chemically Inert Solution?
At KINTEK, we manufacture precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for industries where chemical resistance is non-negotiable. Whether you're in semiconductor manufacturing, medical device production, or specialized laboratory research, our custom fabrication ensures your materials can withstand aggressive environments without contamination.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements, from prototypes to high-volume orders, and leverage our expertise in high-performance polymers.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is PTFE considered an ideal substitute for other plastics in high-temperature applications? Superior Thermal Stability & Performance
- How does PTFE contribute to durability and longevity in industrial applications? Enhance Equipment Lifespan with PTFE
- How is Expanded PTFE (EPTFE) material constructed? A Deep Dive into the Microporous Transformation
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What are the characteristics of polyimide-filled PTFE? Unlock Low Friction for Delicate Surfaces
- What are some common fillers used with PTFE and their benefits? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- What are the applications of PTFE laminated fabric in special apparel? A Guide to Advanced Protection & Comfort
- How does PTFE's low friction property benefit mechanical engineering applications? Achieve Efficiency and Reliability



















