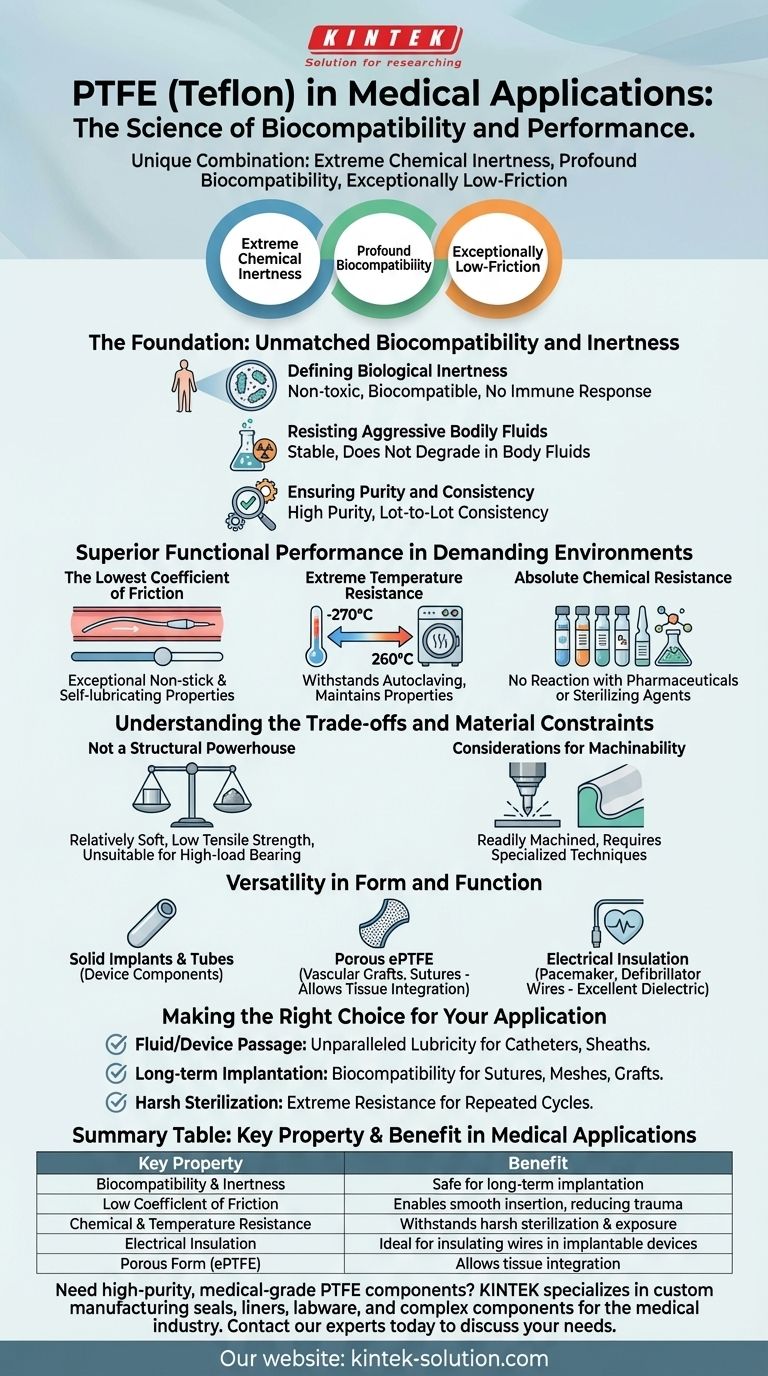
The fundamental reason PTFE (Teflon) is suitable for medical applications is its unique combination of three core properties: extreme chemical inertness, profound biocompatibility, and an exceptionally low-friction surface. This trio of characteristics allows it to perform reliably and safely when in direct contact with the human body, a requirement few other materials can meet.
The true value of PTFE in medicine isn't just one single feature, but its rare ability to be simultaneously ignored by the body's immune system while providing a functional, non-stick surface that improves device performance and patient outcomes.
The Foundation: Unmatched Biocompatibility and Inertness
For any material to be used inside the human body, its primary requirement is to go unnoticed. PTFE excels at this by being almost completely inert, meaning it does not react with its environment.
Defining Biological Inertness
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, which means it does not cause adverse reactions or trigger an immune response when it comes into contact with biological tissues or fluids. The body simply does not recognize it as a foreign invader.
Resisting Aggressive Bodily Fluids
This inertness extends to its chemical behavior. PTFE remains stable and does not degrade when exposed to the complex and often corrosive environment of the human body, ensuring the material's integrity over the long term for implants and devices.
Ensuring Purity and Consistency
Medical-grade PTFE is manufactured to high standards of purity and lot-to-lot consistency. This reliability is critical for medical devices, where even minor variations in material composition could have significant consequences.
Superior Functional Performance in Demanding Environments
Beyond simply being safe, PTFE offers functional advantages that make it a high-performance choice for specific medical tasks.
The Lowest Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it exceptional non-stick and self-lubricating properties. This is crucial for applications like catheters or guide wires, allowing them to glide smoothly through blood vessels with minimal tissue damage.
Extreme Temperature Resistance
With an enormous working thermal range (from -270°C to 260°C), PTFE can easily withstand common sterilization methods like autoclaving (steam heat). This resistance to heat ensures that devices made from PTFE can be made sterile without compromising their physical properties.
Absolute Chemical Resistance
This property makes PTFE invaluable for handling and delivering a wide range of pharmaceuticals and for use in components that must be cleaned with aggressive sterilizing agents. It will not react with or contaminate the substances it touches.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Material Constraints
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to using it effectively.
Not a Structural Powerhouse
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It lacks the high tensile strength and rigidity of metals or other high-performance polymers, making it unsuitable for high-load-bearing structural implants like artificial joints on its own.
Considerations for Machinability
While PTFE is readily machined, its softness requires specialized techniques to achieve tight tolerances without deforming the material. This can impact the complexity and cost of manufacturing certain components.
Versatility in Form and Function
PTFE's properties allow it to be adapted into a wide variety of medical products, serving different roles within the body and in external equipment.
From Solid Implants to Porous Grafts
PTFE can be machined from solid rods and tubes for device components or processed into a porous structure (ePTFE). This porous form is famously used in vascular grafts and sutures, as it allows the body's own tissues to grow into it, promoting integration.
Essential Electrical Insulation
As an excellent dielectric insulator, PTFE is used to insulate fine wires in pacemakers, defibrillators, and other implantable electronic devices where electrical signals must be precisely controlled and contained.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE should be based on a clear understanding of its strengths in the context of your specific medical goal.
- If your primary focus is fluid or device passage: PTFE's unparalleled lubricity makes it the ideal choice for catheters, sheaths, and guide wires to ensure smooth and safe navigation.
- If your primary focus is long-term implantation: Its biocompatibility and chemical inertness make it a foundational material for sutures, surgical meshes, and vascular grafts.
- If your primary focus is device components requiring harsh sterilization: PTFE's extreme resistance to both heat and chemicals ensures it will maintain its integrity through repeated sterilization cycles.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of biological safety and high-end functional performance makes it a foundational material in modern medical innovation.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit in Medical Applications |
|---|---|
| Biocompatibility & Inertness | Non-toxic, does not trigger immune response; safe for long-term implantation. |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Enables smooth insertion of catheters and guide wires, reducing tissue trauma. |
| Chemical & Temperature Resistance | Withstands harsh sterilization (autoclaving) and exposure to bodily fluids/drugs. |
| Electrical Insulation | Ideal for insulating wires in pacemakers and implantable electronic devices. |
| Porous Form (ePTFE) | Allows tissue integration in vascular grafts and surgical meshes. |
Need high-purity, medical-grade PTFE components for your device? KINTEK specializes in custom manufacturing PTFE seals, liners, labware, and complex components for the medical, semiconductor, and laboratory industries. From prototypes to high-volume orders, we ensure precision and consistency for critical applications. Contact our experts today to discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your medical device performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What is the chemical name for Teflon? Unpacking PTFE's Versatile Properties
- What is ePTFE and how is it produced? Unlock the Power of Microporous PTFE
- What are the key properties of PTFE plastic? Harness Extreme Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the medical applications of PTFE? Critical Uses in Implants and Instruments
- What food-related substances are compatible with PTFE? Ensure Safe, Non-Reactive Food Processing
- What is PTFE and what are its notable characteristics? A Guide to Its Unique Properties and Uses
- What are the dielectric properties of PTFE products? Ensure Stable, High-Performance Electrical Insulation
- What is the electrical insulation capability of PTFE? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications



















