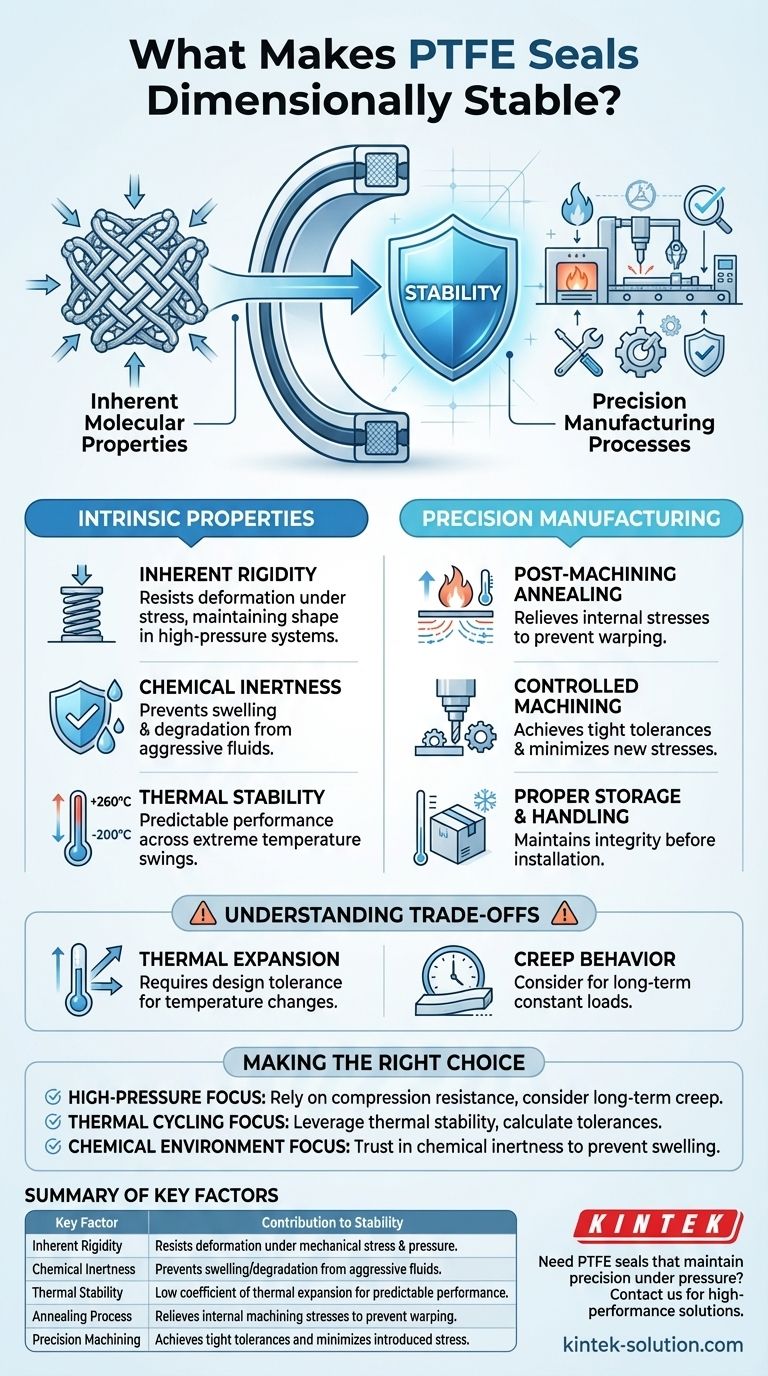
At its core, the dimensional stability of a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) seal is a result of two key factors: its inherent molecular properties and the precision manufacturing processes used to create it. PTFE's molecular structure provides exceptional rigidity and resistance to compression, while specialized techniques like post-machining annealing relieve internal stresses, ensuring the final part holds its exact shape under operational pressure and temperature.
The crucial insight is that PTFE's stability isn't just a raw material property. It is the outcome of a deliberate engineering process where the material's natural strengths are refined and its weaknesses, like thermal expansion, are managed through precise fabrication and design.

The Intrinsic Properties of PTFE
The foundation of PTFE's stability lies in its unique chemical and physical characteristics. These properties make it a default choice for demanding sealing applications where maintaining dimensions is non-negotiable.
Inherent Rigidity and Compression Resistance
PTFE’s structure gives it a natural rigidity that resists deformation under mechanical stress. This ensures the seal maintains its intended shape and sealing force, which is critical for consistent performance in high-pressure systems.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is nearly inert to almost all industrial chemicals due to its strong carbon-fluorine bonds. This resistance prevents the seal from swelling, softening, or degrading when exposed to aggressive fluids, which would otherwise cause significant dimensional changes.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE operates effectively across a vast temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). Its relatively low coefficient of thermal expansion for a polymer means it expands and contracts less than other materials, making it more predictable and stable during thermal cycling.
The Role of Precision Manufacturing
A raw block of PTFE is not enough to guarantee a stable seal. The manufacturing process plays an equally important role in locking in the final dimensions and ensuring reliability.
Post-Machining Annealing
This is a critical step. After machining, internal stresses are introduced into the material. Annealing is a controlled heating and cooling process that relieves these residual stresses, preventing the part from warping or changing shape over time.
Controlled Machining Techniques
Achieving tight tolerances requires specialized machining. Using extremely sharp tools, controlled cutting parameters, and proper workholding techniques minimizes the cutting forces and heat generated, preventing the introduction of new stresses into the part.
Proper Storage and Handling
Even after fabrication, stability can be compromised. Storing PTFE seals in environments free from high temperatures or excessive humidity is essential to prevent any unintended material changes before installation.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's limitations is key to using it effectively and avoiding design failures. Understanding these factors allows for proper compensation in the design phase.
Thermal Expansion and Contraction
While PTFE has a low thermal expansion coefficient for a polymer, it still expands and contracts with temperature changes. For applications with extreme temperature swings, these dimensional changes must be calculated and accounted for in the design tolerances to maintain a proper seal.
The Behavior of "Creep"
Under a constant load over a long period, PTFE can exhibit creep, which is a slow, minor deformation. This means under sustained stress, a seal might experience very small dimensional changes. This behavior must be considered in static, high-load applications to ensure long-term reliability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To ensure dimensional stability, you must align the material's properties and manufacturing considerations with your specific application demands.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure performance: Rely on PTFE's inherent compression resistance but design for potential long-term creep if the load is constant.
- If your primary focus is thermal cycling: Leverage PTFE's excellent thermal stability but always incorporate calculated tolerances to account for expansion and contraction.
- If your primary focus is aggressive chemical environments: Trust in PTFE's chemical inertness to prevent dimension-altering swelling or degradation.
Ultimately, selecting a PTFE seal is a decision based on understanding how its engineered stability will perform within your specific operational constraints.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Contribution to Dimensional Stability |
|---|---|
| Inherent Rigidity | Resists deformation under mechanical stress and pressure. |
| Chemical Inertness | Prevents swelling or degradation from aggressive fluids. |
| Thermal Stability | Low coefficient of thermal expansion for predictable performance. |
| Annealing Process | Relieves internal machining stresses to prevent warping. |
| Precision Machining | Achieves tight tolerances and minimizes introduced stress. |
Need PTFE seals that maintain precision under pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production process, from custom prototypes to high-volume orders, ensures your seals are dimensionally stable and reliable, even in the most demanding environments.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are O-rings and why are they commonly used? A Guide to Simple, Reliable Sealing
- Why are PTFE seals preferred over traditional rubber seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What factors should be considered when selecting a PTFE butterfly valve? Ensure Peak Performance & Reliability
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What do the ratings A, B, and C indicate in the chemical resistance table for Filled PTFE? A Guide to Material Safety
- What safety precautions are needed when machining Teflon? A Guide to Preventing Toxic Fumes
- What types of Teflon backup rings are available and their uses? Ensure Sealing Integrity in High-Pressure Systems
- What are the limitations of machining Teflon (PTFE)? Overcome Challenges for Precision Parts



















