The primary lining materials for this valve type are, by definition, PTFE and PFA. These fluoropolymers are selected for their exceptional chemical inertness, making them suitable for handling a wide range of aggressive and corrosive media. The specific choice between PTFE and PFA hinges on the precise operational demands of your system, particularly temperature, pressure, and the need to minimize fluid permeation.
While both PTFE and PFA provide outstanding corrosion resistance, the decision is not arbitrary. The choice depends on a trade-off between the proven performance and cost-effectiveness of PTFE versus the enhanced temperature capabilities and lower permeability of PFA for more demanding applications.

Why Lining is Essential for Corrosive Service
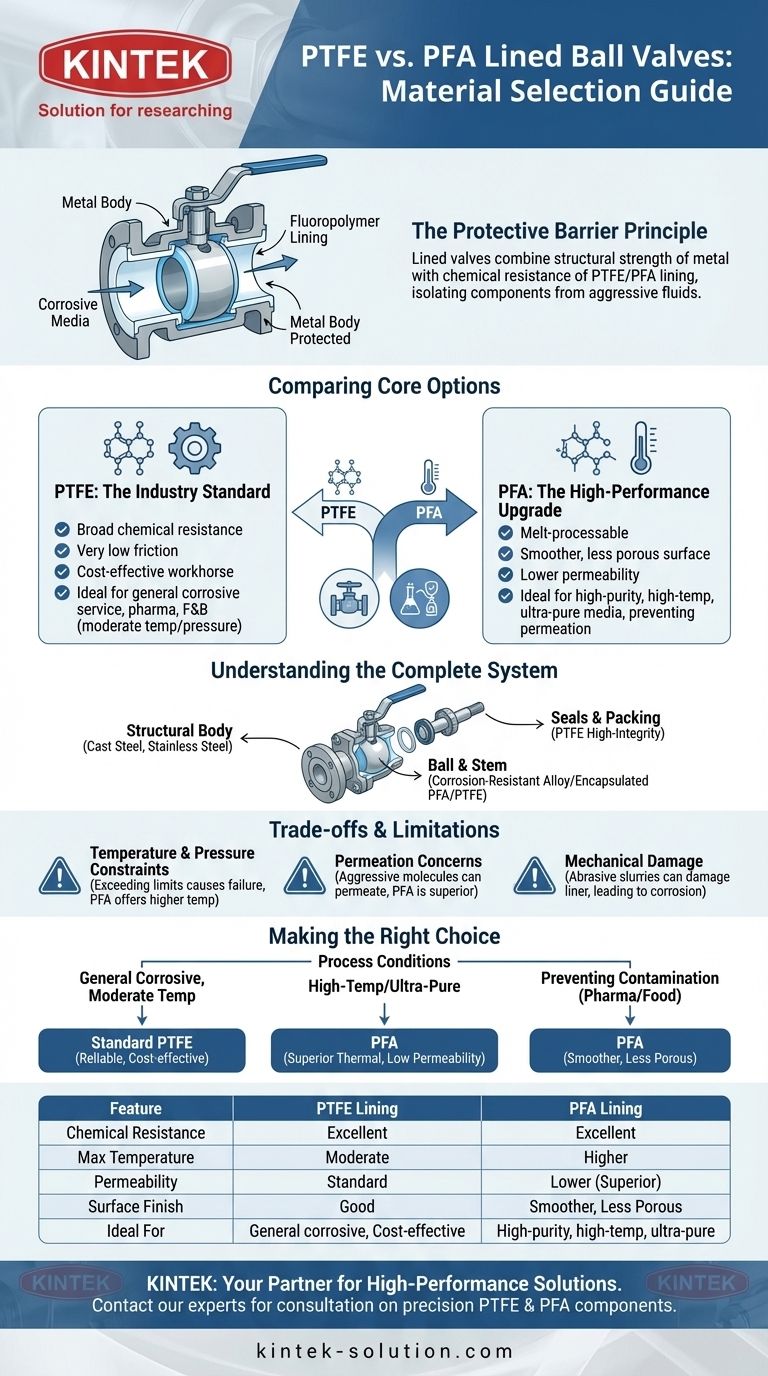
Lined valves are a composite construction designed to combine the structural strength of metal with the chemical resistance of a polymer. This design is fundamental to safely and reliably handling aggressive fluids.
The Protective Barrier Principle
The fluoropolymer lining (PTFE or PFA) is molded to the interior of a standard metal valve body, typically made of cast steel, ductile iron, or stainless steel. This lining completely isolates the metal components from the process fluid.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Both PTFE and PFA are resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals, including strong acids, bases, salts, and organic solvents. This prevents the chemical attack and corrosion that would quickly destroy an unlined metal valve.
Extending Valve Lifespan and Safety
By preventing corrosion, the lining drastically extends the valve's operational life, reduces maintenance costs, and enhances system safety by maintaining the structural integrity of the pressure-containing body.
Comparing the Core Lining Options: PTFE vs. PFA
Understanding the subtle but critical differences between these two materials is key to proper valve specification.
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene): The Industry Standard
PTFE is the most common lining material for these valves. It is known for its broad chemical resistance and very low coefficient of friction, which aids in smooth valve operation.
It serves as the reliable workhorse for a vast range of chemical processing, pharmaceutical, and food and beverage applications under moderate temperature and pressure conditions.
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy Alkane): The High-Performance Upgrade
PFA can be considered a premium version of PTFE. It is melt-processable, which results in a smoother, less porous, and non-permeable surface finish compared to standard PTFE.
This makes PFA the superior choice for high-purity applications, services with higher operating temperatures, or situations where preventing the permeation of tiny molecules (like chlorine gas) through the liner is critical.
Understanding the Complete Material System
A lined valve's performance depends on more than just the body lining. All wetted components must be compatible with the process fluid.
The Structural Body
The outer body provides the mechanical strength and pressure containment for the valve. The choice of cast steel versus stainless steel often depends on external environmental conditions, not the internal fluid.
The Ball and Stem
The ball, which controls the flow, is a primary wetted part. It is typically made from solid corrosion-resistant metal alloys or is itself encapsulated in PFA or PTFE to ensure complete protection.
Seals and Packing
High-integrity seals are critical for preventing leaks. Materials like PTFE are commonly used for valve seats and stem packing to provide a reliable, chemically resistant seal against both the process fluid and the atmosphere.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, lined valves have operational boundaries that must be respected to ensure reliable service.
Temperature and Pressure Constraints
Both PTFE and PFA have maximum temperature limits (typically higher for PFA). Exceeding these limits can cause the liner to soften, deform, or fail, compromising the protective barrier.
Permeation Concerns
While excellent, fluoropolymer liners are not absolutely impervious. Highly aggressive, small-molecule substances can slowly permeate the liner over time, especially at elevated temperatures. PFA generally offers significantly lower permeability than PTFE.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
Liners can be damaged by abrasive slurries, high-velocity solids, or improper installation and maintenance. Any scratch or gouge that exposes the underlying metal can lead to rapid localized corrosion and valve failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct lining material is a function of your specific process conditions and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is general corrosive service with moderate temperatures: Standard PTFE lining offers a proven, reliable, and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature applications or handling ultra-pure media: PFA is the superior choice due to its higher thermal rating and lower permeability.
- If your primary focus is preventing contamination in pharmaceutical or food-grade processes: The smoother, less porous surface of a PFA liner is often the preferred and specified material.
By matching the specific properties of the liner material to your operational demands, you ensure the long-term reliability and safety of your most critical processes.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Lining | PFA Lining |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent |
| Max Temperature | Moderate | Higher |
| Permeability | Standard | Lower (Superior) |
| Surface Finish | Good | Smoother, Less Porous |
| Ideal For | General corrosive service, cost-effective solutions | High-purity, high-temperature, ultra-pure media |
Need a Lined Ball Valve for a Demanding Application?
Choosing between PTFE and PFA is critical for your system's performance and longevity. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE and PFA components, including custom ball valve liners.
We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, providing solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you select or fabricate the perfect lining material for your specific needs. Contact our experts today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key features of Teflon balls? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Environments
- What size range do PTFE balls come in? A Guide from 3mm to 100mm
- What are the common applications of PTFE balls? Leverage Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What are PTFE balls made of and what are their key properties? Unlock Superior Chemical & Thermal Performance
- What makes PTFE balls ideal for chemical applications? Unmatched Inertness for Demanding Environments



















