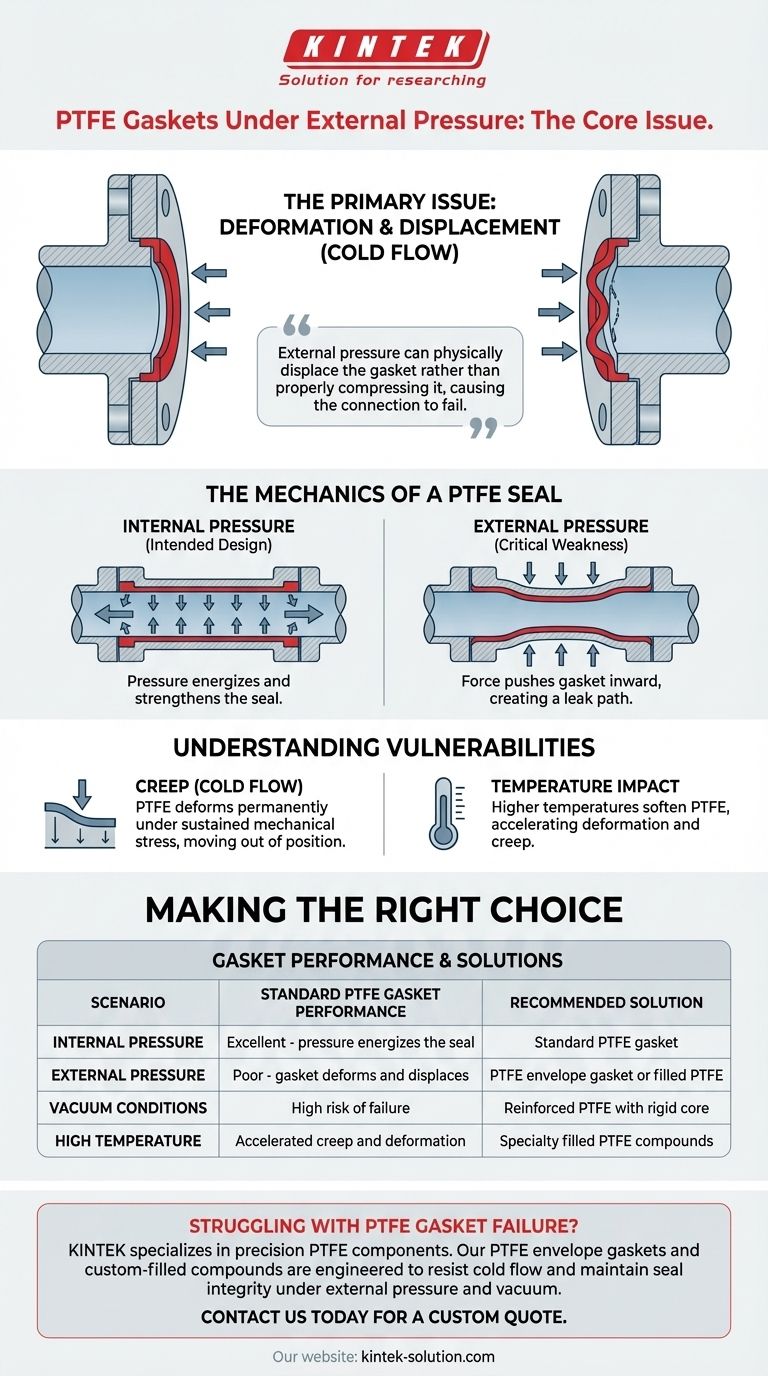
The primary issue with standard PTFE gaskets under external pressure is their tendency to deform and be pushed out of place. This deformation, often called shaping or cold flow, directly compromises the gasket's integrity and leads to a loss of the seal.
While PTFE excels at using internal pressure to strengthen a seal, it lacks the structural rigidity to resist external forces. This core weakness means external pressure can physically displace the gasket rather than properly compressing it, causing the connection to fail.

The Mechanics of a PTFE Seal
To understand the problem, you must first understand how a PTFE gasket is designed to function. Its effectiveness is fundamentally tied to the direction of the pressure it is sealing against.
Internal Pressure: The Intended Design
PTFE gaskets work exceptionally well when sealing against internal pressure. The pressure from the fluid or gas inside the pipe pushes outward on the soft gasket material.
This force presses the PTFE more firmly against the flange faces, effectively using the system's own pressure to energize and strengthen the seal. This is due to the material's rebound characteristics.
External Pressure: The Critical Weakness
When external pressure is applied, this mechanism works in reverse and becomes a liability. The force pushes the gasket inward, away from the sealing surfaces.
Instead of being compressed into the flange, the soft PTFE material can be deformed or squeezed into the bore of the pipe. This displacement creates a direct path for leakage, causing the seal to fail completely.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The unique properties that make PTFE an excellent sealing material in some conditions also create its primary vulnerabilities. The key is understanding its tendency to "creep."
The Problem of Creep (Cold Flow)
PTFE is a relatively soft polymer known for creep, or cold flow. This is the tendency of the material to slowly and permanently deform when under a sustained mechanical stress.
External pressure provides the exact kind of sustained stress that encourages creep. Over time, the gasket will slowly move out of position, even if the initial seal was good, leading to an eventual failure.
The Impact of Temperature
While PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, higher temperatures soften the material further. This makes it even more susceptible to deformation and creep when subjected to external pressure, accelerating potential failure.
Not All PTFE is Equal
It is crucial to distinguish between standard PTFE and specialized variants. For instance, PTFE envelope gaskets, which have a rigid core material wrapped in a thin PTFE layer, offer a much better solution.
The rigid insert resists the deformative force of external pressure, while the PTFE exterior provides the necessary chemical resistance and sealing surface. Similarly, filled or modified PTFE can offer improved creep resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching the material's properties to the specific pressure dynamics of your system.
- If your primary focus is sealing standard internal pressure: A standard PTFE gasket is often an excellent and cost-effective choice, leveraging the system's pressure to maintain a strong seal.
- If your application involves external pressure or vacuum conditions: A standard PTFE gasket is a high-risk choice; you should specify a PTFE envelope gasket with a rigid insert or a specially filled PTFE compound designed to resist creep.
- If you are troubleshooting a leak in a low-pressure system: Investigate if any external loading or vacuum cycles could be causing the gasket to deform and compromise the seal over time.
Ultimately, understanding the direction of pressure is the critical first step in specifying the right gasket for the job.
Summary Table:
| Scenario | Standard PTFE Gasket Performance | Recommended Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Pressure | Excellent - pressure energizes the seal | Standard PTFE gasket |
| External Pressure | Poor - gasket deforms and displaces | PTFE envelope gasket or filled PTFE |
| Vacuum Conditions | High risk of failure | Reinforced PTFE with rigid core |
| High Temperature | Accelerated creep and deformation | Specialty filled PTFE compounds |
Struggling with PTFE gasket failure under external pressure? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components that solve these exact challenges. Our PTFE envelope gaskets with rigid cores and custom-filled PTFE compounds are engineered to resist cold flow and maintain seal integrity under external pressure and vacuum conditions. Whether you're in semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial applications, we provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact us today to discuss your specific sealing requirements and let our experts provide a reliable solution. Get a Custom Quote
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What design considerations are important for custom PTFE parts? Design for Performance & Reliability
- What factors should be considered when choosing between Nylon and PTFE? Select the Right Material for Your Application



















