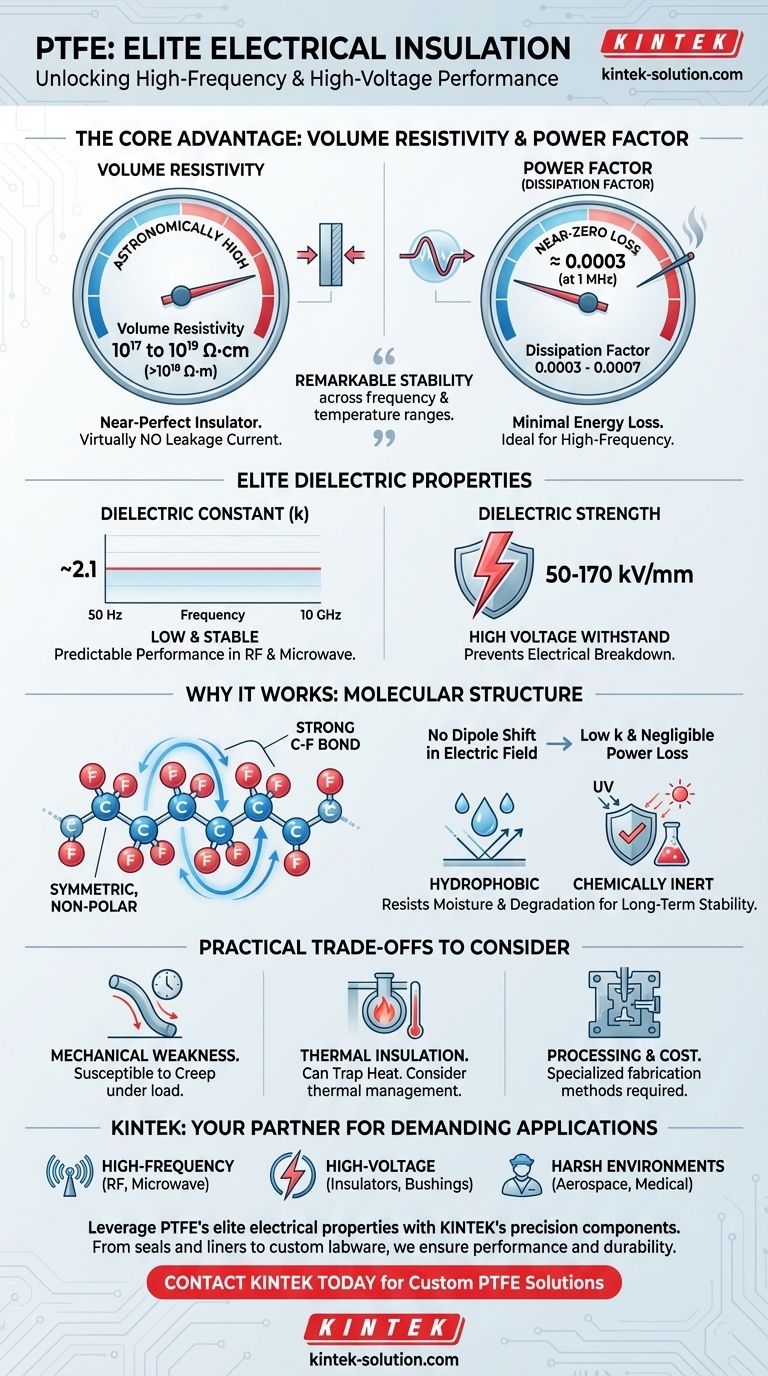
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is one of the highest-performing electrical insulators available. Its volume resistivity is exceptionally high, typically cited in the range of 10¹⁷ to 10¹⁹ Ω·cm (or >10¹⁸ Ω·m). The power factor is so low that it is considered negligible for most applications, with a dissipation factor around 0.0003 at 1 MHz, indicating minimal energy loss.
The true value of PTFE isn't just its excellent individual electrical properties, but their remarkable stability across wide ranges of frequency and temperature. This reliability makes it a definitive choice for demanding high-frequency and high-voltage applications where performance cannot be compromised.
Deconstructing PTFE's Electrical Performance
To understand why PTFE is specified for critical applications, we must look beyond the numbers and understand what they mean in practice. The material's electrical behavior is a direct result of its unique, highly symmetric molecular structure.
Exceptionally High Volume Resistivity
Volume resistivity measures a material's inherent resistance to the flow of electrical current through its bulk.
PTFE's value of 10¹⁷ to 10¹⁹ Ω·cm is astronomical. This indicates that it is an almost perfect insulator, allowing virtually no leakage current to pass through the material itself under a DC voltage.
Near-Zero Power Factor (Dissipation Factor)
For a superior insulator like PTFE, the power factor and dissipation factor are practically interchangeable. This value represents how much electrical energy is lost, usually as heat, when the material is subjected to an alternating electric field.
PTFE’s dissipation factor is incredibly low, around 0.0003 to 0.0007. This means an extremely small fraction of energy is wasted, which is critical for preventing heat buildup and signal degradation in high-frequency circuits.
Elite Dielectric Properties
Two other properties cement PTFE's status as a top-tier insulator: dielectric strength and dielectric constant.
The dielectric strength (50-170 kV/mm) is the maximum voltage the material can withstand before electrical breakdown occurs. PTFE's high value makes it suitable for high-voltage applications.
The dielectric constant (~2.1) is a measure of a material's ability to store electrical energy. PTFE's value is not only low but, more importantly, extremely stable across a vast frequency spectrum (from 50 Hz to 10 GHz). This stability ensures predictable, consistent performance in RF and microwave circuits.
Why PTFE Is Such a Superior Insulator
The material's elite performance is not an accident. It stems directly from its molecular structure and chemical composition.
The Molecular Structure Advantage
PTFE consists of a long chain of carbon atoms completely shielded by fluorine atoms. This carbon-fluorine bond is exceptionally strong and the symmetric arrangement of the fluorine atoms creates an electrically stable, non-polar molecule.
This structure prevents molecular dipoles from shifting in an electric field, which is the primary reason for its low dielectric constant and negligible power loss.
Immunity to Environmental Factors
PTFE exhibits extremely low surface tension, making it hydrophobic (water-repellent). Unlike many other insulators, it does not absorb moisture from the air, which would otherwise degrade its electrical properties.
Furthermore, its chemical inertness means it resists degradation from oils, chemicals, and UV light, ensuring long-term stability in harsh operating environments.
Understanding the Practical Trade-offs
No material is perfect for every situation. While its electrical properties are world-class, PTFE has mechanical and thermal limitations that must be considered.
Mechanical Weakness
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to creep, meaning it can slowly deform over time when under a constant load, especially at elevated temperatures. It is not suitable for applications requiring high structural strength or abrasion resistance.
Thermal Insulation Can Be a Downside
While PTFE has an impressively wide operating temperature range, it is an excellent thermal insulator. This means it does not dissipate heat well.
In applications where an insulated component generates significant heat, that heat can become trapped, potentially leading to premature failure of the component itself.
Processing and Cost
PTFE can be more difficult and costly to process compared to common engineering plastics. Techniques like bonding it to other surfaces or injection molding require specialized methods, which can add to the total cost of a component.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting PTFE should be a deliberate decision based on specific performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency performance: PTFE is an ideal choice for RF connectors, microwave circuits, and high-speed data cables due to its low, stable dielectric constant and near-zero dissipation factor.
- If your primary focus is high-voltage insulation: Its combination of immense volume resistivity and high dielectric strength makes it a top-tier material for high-voltage wire insulation, bushings, and standoffs.
- If your primary focus is reliability in harsh environments: PTFE's chemical inertness and resistance to moisture ensure its electrical properties will not degrade over time, making it perfect for critical aerospace, chemical processing, and medical applications.
By understanding these elite electrical characteristics and their practical trade-offs, you can confidently leverage PTFE for the most demanding insulation challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Typical Value for PTFE | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Resistivity | 10¹⁷ – 10¹⁹ Ω·cm | Near-perfect insulator, minimal leakage current |
| Dissipation/Power Factor | 0.0003 – 0.0007 | Minimal energy loss, ideal for high-frequency use |
| Dielectric Constant | ~2.1 | Low and stable across a wide frequency range |
| Dielectric Strength | 50 – 170 kV/mm | High voltage withstand capability |
Leverage PTFE's Elite Electrical Properties for Your Most Demanding Applications
Do you need reliable, high-performance insulation that won't compromise under extreme conditions? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with custom fabrication capabilities, from prototypes to high-volume orders, to ensure your components meet the highest standards of electrical performance and durability.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and let our expertise in PTFE solutions power your next project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the common quality control methods for PTFE products? Ensure Performance and Reliability
- What is the volume resistivity of PTFE and why is it significant? Unlock Superior Electrical Insulation
- What are the advantages of RPTFE over standard PTFE? Superior Strength and Durability for Demanding Applications
- What is the role of valves in industrial piping systems? Ensure Safety, Control, and Efficiency
- What are the main properties of Teflon material? Unrivaled Chemical Resistance & Non-Stick Performance
- What are the key electrical properties of PTFE? Essential for High-Frequency & High-Voltage Electronics
- What is PTFE and what are its basic properties? The Ultimate Guide to the High-Performance Polymer
- How was PTFE accidentally discovered? The Serendipitous Story of Teflon's Invention



















