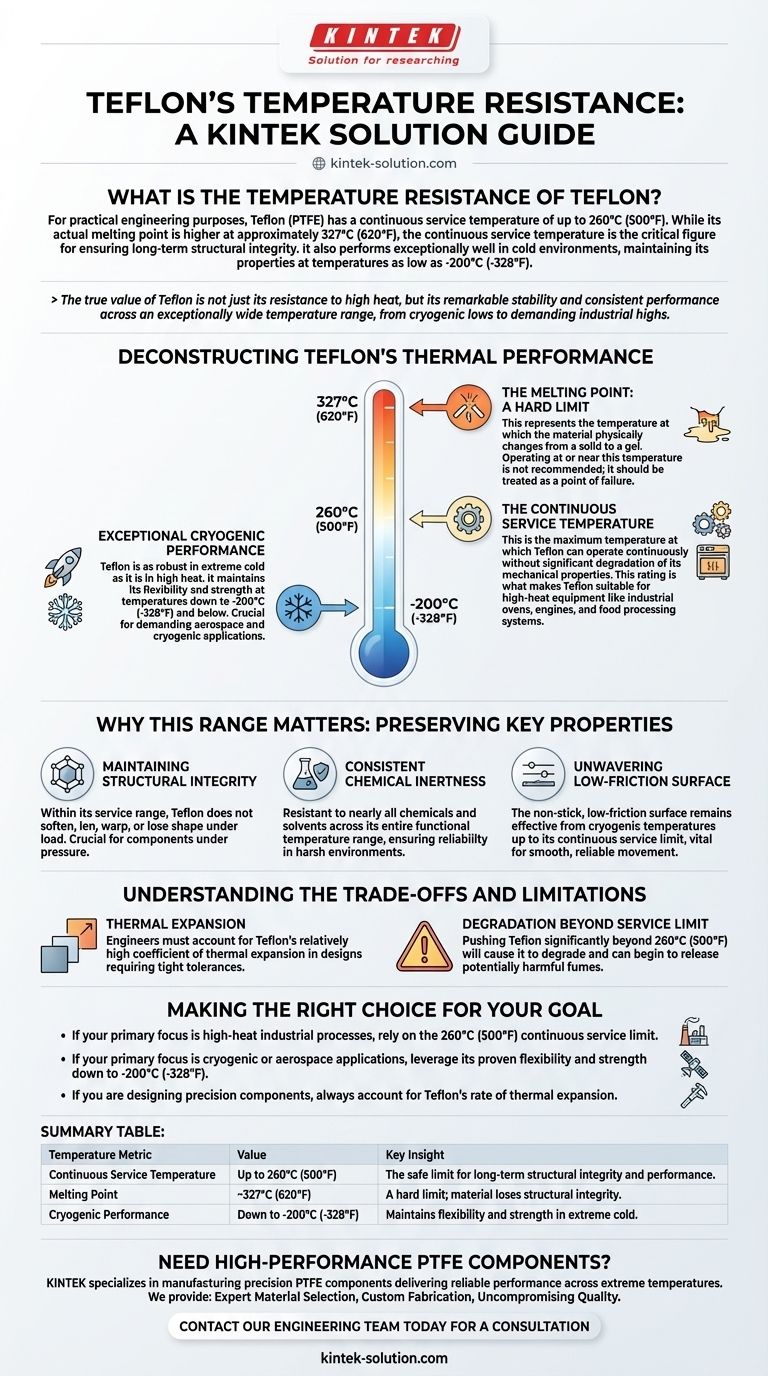
For practical engineering purposes, Teflon (PTFE) has a continuous service temperature of up to 260°C (500°F). While its actual melting point is higher at approximately 327°C (620°F), the continuous service temperature is the critical figure for ensuring long-term structural integrity. It also performs exceptionally well in cold environments, maintaining its properties at temperatures as low as -200°C (-328°F).
The true value of Teflon is not just its resistance to high heat, but its remarkable stability and consistent performance across an exceptionally wide temperature range, from cryogenic lows to demanding industrial highs.

Deconstructing Teflon's Thermal Performance
To properly leverage Teflon in any application, it's essential to understand the distinction between its different temperature ratings. These figures define the boundaries of its reliability and safety.
The Continuous Service Temperature
The most important number for any design or application is 260°C (500°F). This is the maximum temperature at which Teflon can operate continuously without significant degradation of its mechanical properties.
This rating is what makes Teflon suitable for high-heat equipment like industrial ovens, engines, and food processing systems.
The Melting Point: A Hard Limit
Teflon's melting point of 327°C (620°F) represents the temperature at which the material physically changes from a solid to a gel.
Operating at or near this temperature is not recommended, as the material will lose all structural integrity. It should be treated as a point of failure, not a performance benchmark.
Exceptional Cryogenic Performance
Teflon is as robust in extreme cold as it is in high heat. It maintains its flexibility and strength at temperatures down to -200°C (-328°F) and below.
This unique characteristic makes it a critical material for demanding aerospace and cryogenic applications where other polymers would become brittle and fail.
Why This Range Matters: Preserving Key Properties
Teflon's value comes from a unique combination of properties. Its wide operating temperature range ensures these characteristics remain stable and reliable whether the environment is hot or cold.
Maintaining Structural Integrity
Within its service range, Teflon does not soften, warp, or lose its shape under load. This physical stability is crucial for components like seals, rings, and bushes that must perform under pressure.
Consistent Chemical Inertness
Teflon is famous for its resistance to nearly all chemicals and solvents. This inertness is maintained across its entire functional temperature range, ensuring reliability in harsh environments.
Unwavering Low-Friction Surface
The non-stick, low-friction surface that Teflon is known for remains effective from cryogenic temperatures up to its continuous service limit. This consistency is vital for applications requiring smooth, reliable movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While extremely capable, Teflon is not without engineering considerations that must be respected for successful implementation.
Thermal Expansion
Like all materials, Teflon expands when heated and contracts when cooled. Its coefficient of thermal expansion is relatively high compared to metals.
Engineers must account for this dimensional change in designs requiring tight tolerances to prevent parts from failing or seizing.
Degradation Beyond the Service Limit
Pushing Teflon significantly beyond its 260°C (500°F) service temperature will cause it to degrade. As it approaches its melting point, it can begin to release potentially harmful fumes.
Adhering to the recommended continuous service temperature is therefore a critical safety and performance consideration.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge effectively, match Teflon's thermal properties to the primary demand of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-heat industrial processes: Rely on the 260°C (500°F) continuous service limit for safe, long-term performance in components like bearings or seals.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic or aerospace applications: Leverage its proven flexibility and strength at temperatures down to -200°C (-328°F).
- If you are designing precision components: Always account for Teflon's rate of thermal expansion to ensure your design maintains tolerances across its full operating temperature range.
By respecting these thermal boundaries, you can confidently leverage Teflon's unique properties to achieve exceptional durability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Metric | Value | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Temperature | Up to 260°C (500°F) | The safe limit for long-term structural integrity and performance. |
| Melting Point | ~327°C (620°F) | A hard limit; material loses structural integrity. |
| Cryogenic Performance | Down to -200°C (-328°F) | Maintains flexibility and strength in extreme cold. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that deliver reliable performance across extreme temperatures, from cryogenic applications to high-heat industrial processes.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Ensuring your components meet the exact thermal demands of your application.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your specifications.
- Uncompromising Quality: Precision production for critical industries like semiconductor, medical, and aerospace.
Let us help you leverage Teflon's full potential. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE? Unlock Superior Performance in Harsh Environments
- Why is PTFE a good choice for UV resistance? Its molecular structure provides inherent, lasting protection.
- What are the dielectric properties of PTFE? The Ultimate Insulator for Demanding Applications
- Why is it dangerous to overheat Teflon cookware? Avoid Toxic Fumes & Protect Your Family
- What are some applications of PTFE due to its properties? Discover Its Versatility in Demanding Industries
- Why is PTFE considered an excellent electrical insulator? Discover Its Elite Electrical Properties
- What does PTFE stand for and what is its chemical composition? Unlock the Secrets of a High-Performance Polymer
- What is the main disadvantage of PTFE? The Challenge of Manufacturing an Elite Material



















