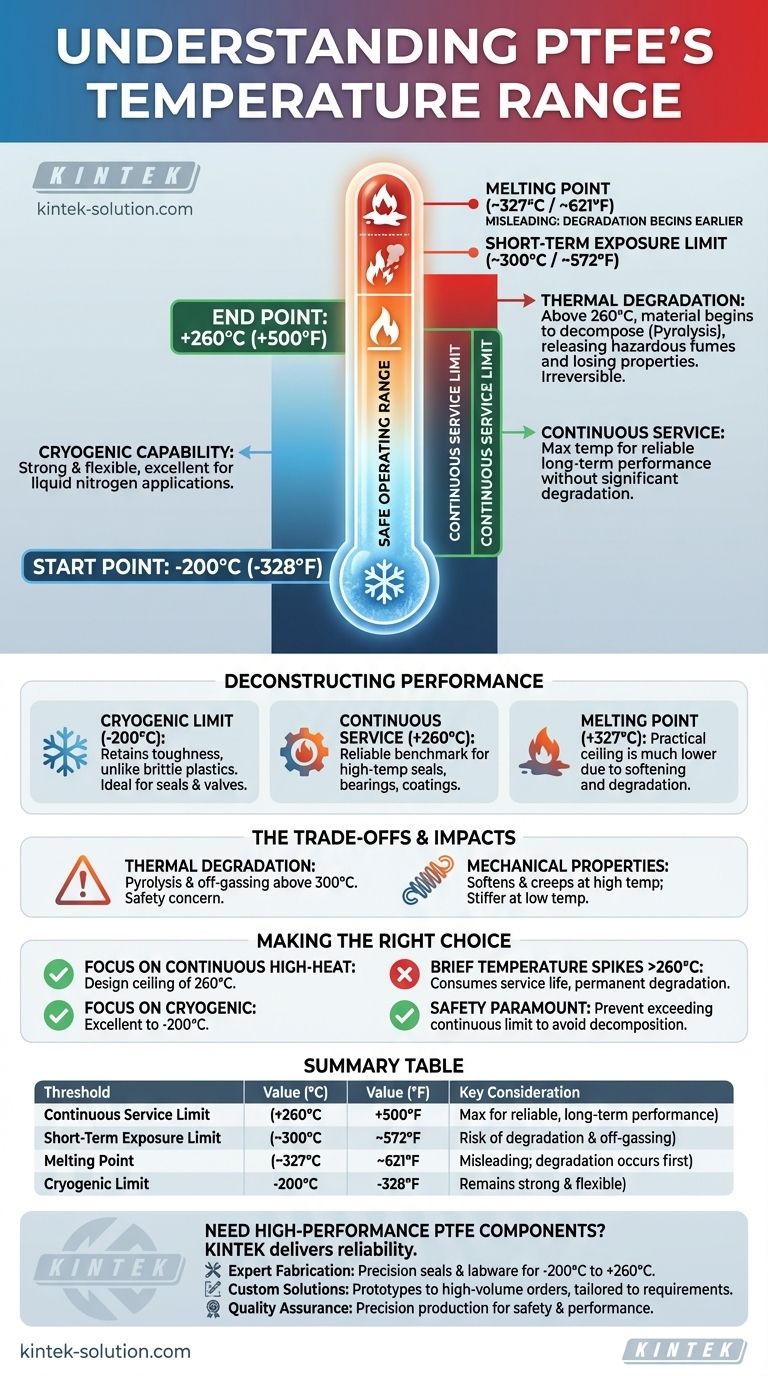
In short, the widely accepted service temperature range for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). While its theoretical melting point is much higher at approximately 327°C (621°F), the material begins to lose critical mechanical properties and degrade long before it melts. This distinction is vital for any engineering or industrial application.
The core takeaway is that PTFE's value lies in its exceptionally wide operating range, not just its high melting point. For reliable, long-term performance, you must design for its continuous service temperature of 260°C, as exceeding this limit leads to irreversible degradation and potential off-gassing.

Deconstructing PTFE's Thermal Performance
To use PTFE effectively, you must understand the difference between its continuous service limit, short-term exposure limit, and its actual melting point. These are not interchangeable terms.
The Upper Limit: Continuous Service
The most important figure for any engineer or designer is 260°C (500°F). This is the maximum temperature at which PTFE can operate continuously without significant degradation of its mechanical and chemical properties.
Most data sheets and safety factors are based on this continuous service temperature. It provides a reliable benchmark for applications like high-temperature seals, bearings, and non-stick coatings.
The Lower Limit: Cryogenic Capability
PTFE performs exceptionally well at low temperatures. It remains strong, flexible, and functional down to approximately -200°C (-328°F).
Unlike many plastics that become extremely brittle and fracture at such temperatures, PTFE retains a useful degree of toughness, making it a primary material for cryogenic seals, valves, and components used with liquid nitrogen or other supercooled fluids. Some specialized grades can even function at lower temperatures near -270°C (-454°F).
Melting Point vs. Service Temperature: A Critical Distinction
PTFE has a high melting point of around 327°C (621°F). However, this figure is often misleading for practical purposes.
The material begins to soften and lose its structural integrity well below this point. More importantly, as it approaches and exceeds its 260°C continuous limit, it will begin to thermally degrade and release fumes, a process that accelerates with higher temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
PTFE is not a universally perfect solution. Its thermal properties come with important considerations that impact safety and performance.
The Impact of Thermal Degradation
When heated above its continuous service temperature, and especially above 300°C (572°F), PTFE begins to decompose.
This process, known as pyrolysis, causes the material to lose mass and releases fluorocarbon gases. These fumes can be hazardous, making ventilation a critical safety concern in any application where temperature limits might be accidentally exceeded. This degradation is irreversible.
Mechanical Properties at Temperature Extremes
While PTFE functions across a wide temperature range, its mechanical properties are not constant.
At the upper end of its service range, PTFE becomes softer and more susceptible to creep (deformation under a constant load). At cryogenic temperatures, it becomes stiffer and harder, which can affect its sealing performance if not accounted for in the design.
Why You See Different Numbers
You may find slightly different temperature ratings from various manufacturers. This variation often stems from the specific grade of PTFE, the presence of fillers (like glass or carbon), or the testing standards used. For example, a PTFE coating may have a different rating than a solid, molded part. Always consult the data sheet for the specific product you are using.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal profile fits your project's requirements.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat operations: Design with a firm ceiling of 260°C (500°F) to ensure long-term reliability and material stability.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE is an excellent choice for applications down to -200°C (-328°F), where it will maintain its structural integrity better than most plastics.
- If you anticipate brief temperature spikes above 260°C: Understand that this will consume the material's service life and may cause permanent degradation. These excursions must be very short.
- If safety is paramount in your application: Be acutely aware of thermal decomposition and ensure robust controls are in place to prevent the material from ever exceeding its recommended continuous temperature.
Understanding these distinct thermal thresholds is the key to leveraging PTFE's remarkable properties safely and effectively.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Threshold | Value (°C) | Value (°F) | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Continuous Service Limit | +260°C | +500°F | Maximum for reliable, long-term performance |
| Short-Term Exposure Limit | ~300°C | ~572°F | Risk of thermal degradation and off-gassing |
| Melting Point | ~327°C | ~621°F | Misleading for practical use; degradation occurs first |
| Cryogenic Limit | -200°C | -328°F | Remains strong and flexible at extreme lows |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Thermal Environments?
PTFE's exceptional temperature range makes it ideal for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. However, success depends on precision manufacturing and the right material grade.
KINTEK delivers the reliability you need:
- Expert Fabrication: We manufacture precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware that perform consistently within the critical -200°C to +260°C range.
- Custom Solutions: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we tailor components to your exact thermal and mechanical requirements.
- Quality Assurance: Our focus on precision production ensures your components meet the highest standards for safety and performance.
Ensure your application's success. Contact our experts today to discuss your custom PTFE needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What modifications can be made to PTFE for enhanced performance? Boost Wear Resistance & Strength with Fillers
- What are filled PTFE resins and how are they produced? A Guide to Enhanced Performance Materials
- Where can PTFE materials be sourced? A Guide to Teflon™, Generic PTFE, and Fabricators
- What is the flexural strength of PTFE? Discover Its Unique Flexibility & Performance
- What are the properties of bronze-filled PTFE? A High-Performance Composite for Demanding Applications
- How was PTFE discovered and what is its history? From Accidental Discovery to a Modern Marvel
- What are the benefits of stainless steel-filled PTFE? Enhance Strength and Temperature Resistance
- How does PTFE's molecular neutrality affect its properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical and Electrical Performance



















