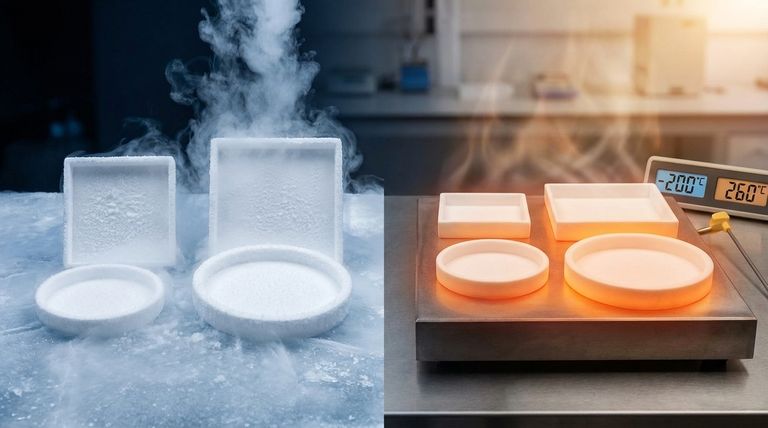
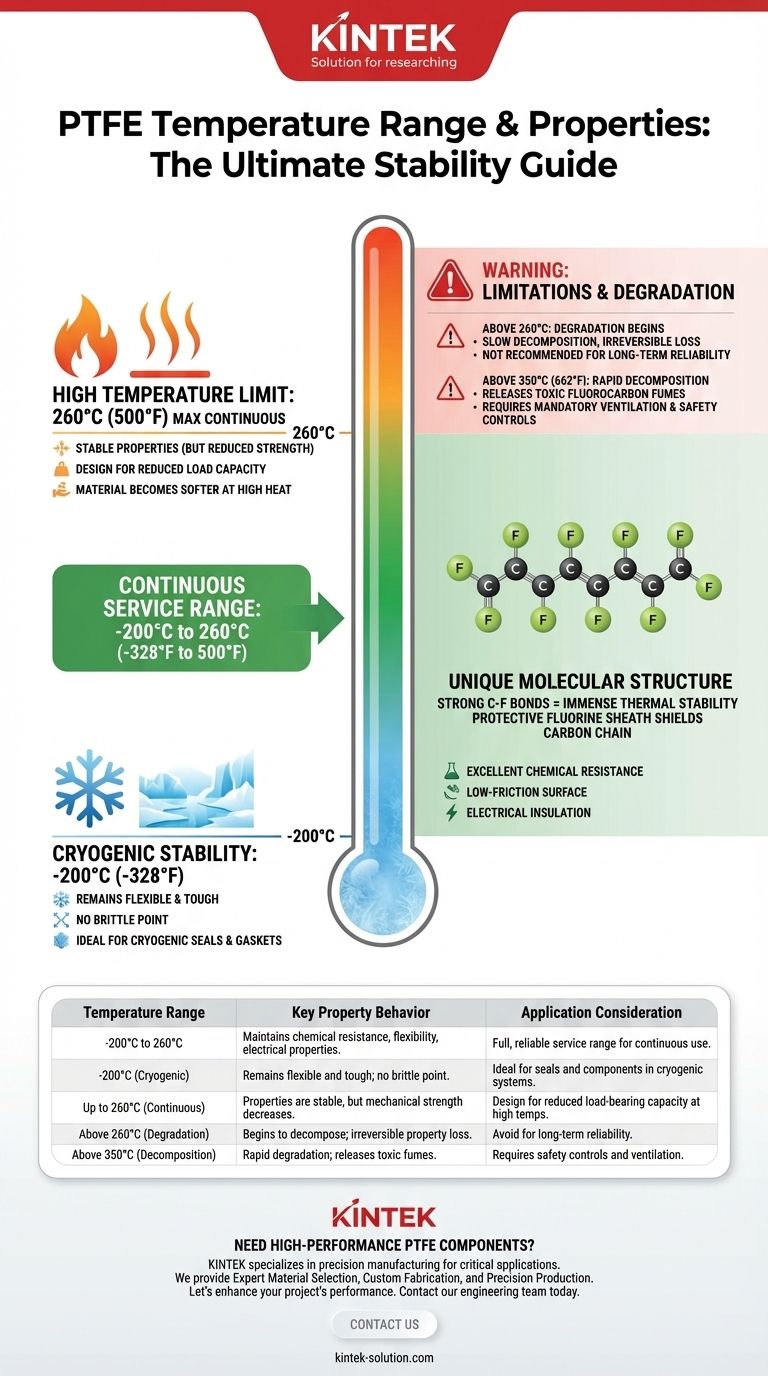
The effective service temperature range for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is remarkably wide. It reliably maintains its essential properties from cryogenic conditions as low as -200°C (-328°F) up to a continuous high temperature of 260°C (500°F). This stability across such a vast thermal spectrum is one of the key characteristics that defines its use in demanding applications.
The core reason for PTFE's exceptional temperature range lies in its unique molecular structure. The strength of the carbon-fluorine bond provides immense thermal stability, allowing the material to perform predictably where most other polymers would fail.

Why PTFE Has Such a Wide Temperature Range
Understanding the source of this thermal stability is key to using the material correctly. It isn't arbitrary; it's a direct result of its fundamental chemistry.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry. This immense bond energy requires a significant amount of thermal energy to break.
As a result, the PTFE molecule is inherently stable and resistant to thermal degradation, allowing it to function at both very low and very high temperatures.
The Protective Fluorine Sheath
The fluorine atoms are larger than the carbon atoms they are bonded to, creating a tight, uniform "sheath" around the carbon backbone.
This sheath effectively shields the more vulnerable carbon chain from chemical and thermal attacks, further contributing to its overall stability and inertness.
Performance at the Temperature Extremes
While the range is wide, the material's behavior differs at the low and high ends of its spectrum.
At Cryogenic Temperatures (-200°C)
Unlike many plastics that become extremely brittle and fracture at low temperatures, PTFE retains a surprising amount of flexibility and toughness.
This lack of a distinct brittle point makes it a reliable choice for seals, gaskets, and components used in cryogenic systems and laboratory equipment.
At High Temperatures (Up to 260°C)
260°C (500°F) is the widely accepted maximum continuous service temperature. At this point, PTFE maintains its excellent chemical resistance, low-friction surface, and electrical insulating properties.
It's crucial to understand that this is the limit for long-term, reliable operation without significant decomposition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is without its limits. Being aware of PTFE's thermal boundaries is critical for safe and effective engineering design.
The 260°C Service Limit is Not Absolute
While 260°C is the recommended continuous limit, mechanical properties like tensile strength, wear resistance, and resistance to creep (deformation under load) are reduced at higher temperatures.
As PTFE heats up, it becomes softer. This must be accounted for in any load-bearing application.
Degradation Begins Above 260°C
Pushing PTFE beyond its continuous service temperature will initiate a slow decomposition process. The material will begin to lose mass and its properties will degrade irreversibly.
For very short durations, it may withstand slightly higher temperatures, but this is not recommended for any critical application.
Toxic Fumes at High Decomposition Temperatures
At significantly higher temperatures, typically above 350°C (662°F), PTFE decomposes more rapidly. This process can release toxic fluorocarbon fumes.
Proper ventilation and engineering controls are mandatory in any application where PTFE could potentially be exposed to such extreme temperatures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal properties align with your specific operational needs.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE is an exceptional candidate, as it avoids the brittleness that plagues many other polymers at low temperatures.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat operation (up to 260°C): PTFE is a suitable choice, but you must design for the reduction in its mechanical strength and stiffness.
- If your application involves brief temperature spikes above 260°C: You are operating outside the recommended range, and this requires careful testing and acceptance of accelerated material degradation.
- If your design must prevent failure in over-temperature events: Ensure your system has safeguards to prevent PTFE from ever reaching decomposition temperatures above 350°C.
Ultimately, leveraging PTFE successfully depends on respecting its thermal limits and designing your system accordingly.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Key Property Behavior | Application Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C | Maintains chemical resistance, flexibility, and electrical properties. | Full, reliable service range for continuous use. |
| -200°C (Cryogenic) | Remains flexible and tough; no brittle point. | Ideal for seals and components in cryogenic systems. |
| Up to 260°C (Continuous) | Properties are stable, but mechanical strength decreases. | Design for reduced load-bearing capacity at high temps. |
| Above 260°C (Degradation) | Begins to decompose; irreversible property loss. | Avoid for long-term reliability. |
| Above 350°C (Decomposition) | Rapid degradation; releases toxic fumes. | Requires safety controls and ventilation. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Demanding Environments?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components that excel within this critical temperature range. We serve the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors, delivering the material stability and reliability your applications demand.
We provide:
- Expert Material Selection: Ensuring your components perform reliably from cryogenic conditions up to 260°C.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume production, tailored to your exact specifications.
- Precision Production: Quality components that meet the stringent requirements of specialized industries.
Let's discuss how our PTFE solutions can enhance your project's performance and safety. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the key properties of PTFE? Discover the Material for Extreme Environments
- Who discovered PTFE and how? The Accidental Invention of Teflon by Dr. Roy Plunkett
- How does Teflon coating benefit cookware? Achieve Effortless Cooking and Easy Cleanup
- What is PTFE and what are its primary applications? Unlock High-Performance Solutions
- What is the chemical name for Teflon? Unpacking PTFE's Versatile Properties
- What happens when PTFE is incinerated? The Hidden PFAS Pollution Risk
- What are the main ingredients used in the production of PTFE? Unlocking its High-Performance Properties
- What are some emerging applications of PTFE? Discover Its Critical Role in Aerospace, Medical, and Semiconductor Tech



















