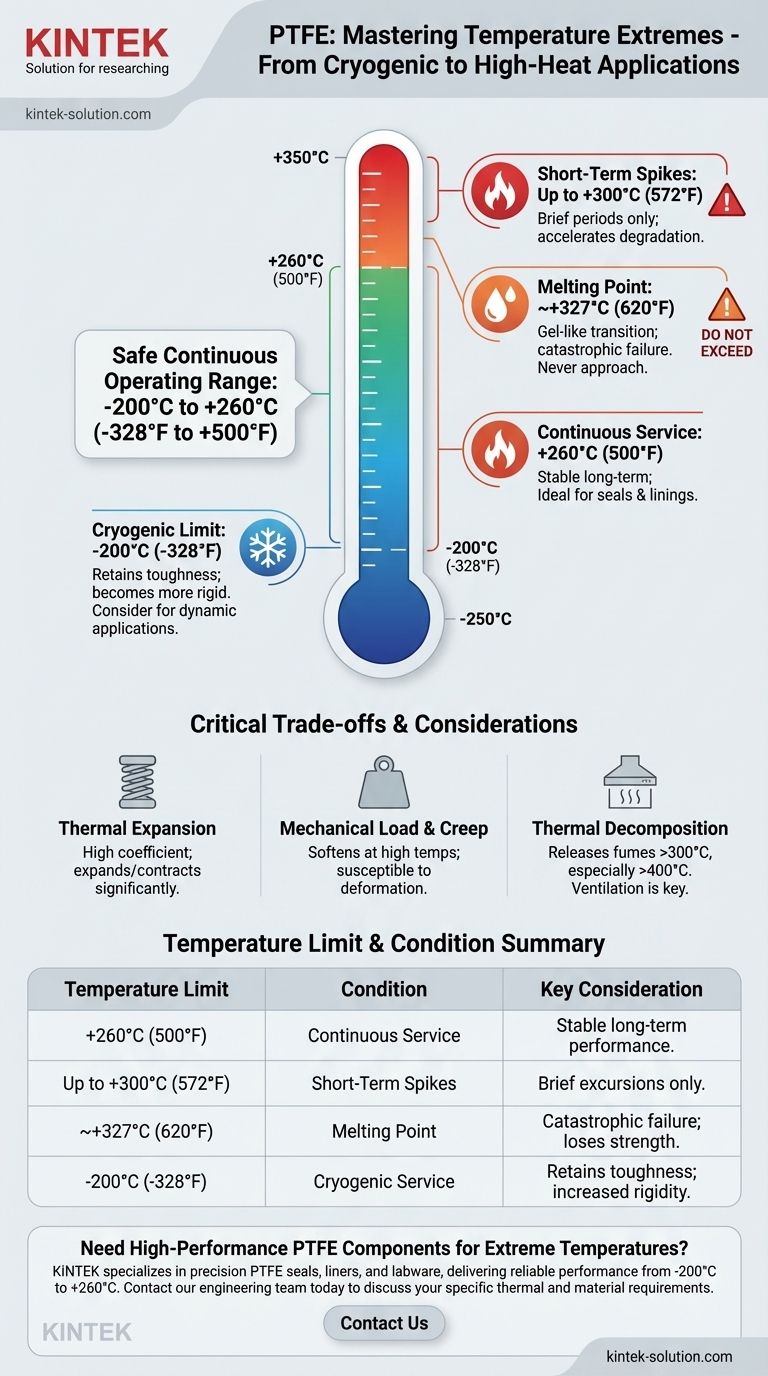
For practical engineering purposes, the safe and continuous operating temperature range for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is from -200°C (-328°F) to +260°C (500°F). This remarkable thermal stability is one of the key reasons PTFE is specified for demanding applications.
The specified temperature range for PTFE represents its limits for continuous, reliable service. While the material can withstand brief excursions beyond these points, its mechanical properties begin to degrade significantly, making the -200°C to +260°C range the definitive guide for most applications.

Understanding the High-Temperature Limit
The upper limit of PTFE's service range is not a single, absolute number but a spectrum defined by duration and mechanical load. Understanding these distinctions is critical for safe and effective design.
The Continuous Service Temperature: 260°C (500°F)
This is the most important number for most applications. PTFE can operate continuously at 260°C without significant degradation to its chemical structure or core properties.
This makes it an excellent choice for high-temperature seals, gaskets, and linings where long-term stability is required.
Short-Term Temperature Spikes: Up to 300°C (572°F)
For brief periods, PTFE can be exposed to temperatures as high as 300°C.
However, prolonged exposure above 260°C will accelerate material degradation, potentially compromising its structural integrity and releasing fumes. This is an excursion limit, not a new operating standard.
The Melting Point: ~327°C (620°F)
PTFE does not have a true melting point in the way most plastics do. Around 327°C, it transitions into a gel-like state, losing all of its structural form and strength.
This temperature represents a catastrophic failure point and should never be approached in an application.
Understanding the Low-Temperature Limit
PTFE's performance in cryogenic conditions is just as impressive as its heat resistance, but its physical properties change in predictable ways.
The Standard Cryogenic Limit: -200°C (-328°F)
Most datasheets specify -200°C as the lower service limit. Down to this temperature, PTFE remains a highly useful and functional material.
Retaining Toughness vs. Losing Flexibility
While PTFE remains strong and tough even at temperatures approaching absolute zero (-268°C / 5°K), it does lose flexibility.
At extremely low temperatures, it becomes more rigid. This is a critical design consideration for dynamic seals or components that need to flex in cryogenic environments.
Critical Trade-offs and Considerations
Temperature is only part of the equation. The performance of PTFE at its thermal limits is also influenced by other environmental factors.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes, a fact that must be accounted for in designs with tight tolerances.
Mechanical Load and Creep
At the upper end of its temperature range, PTFE becomes softer and more susceptible to "creep" or cold flow. A component under high mechanical stress at 250°C will deform more readily than one at room temperature.
Thermal Decomposition Safety
At temperatures above 300°C, and especially above 400°C, PTFE begins to decompose and release potentially toxic fumes. Proper ventilation is essential in any application where overheating is a remote possibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE's thermal properties align with your project's specific demands.
- If your primary focus is continuous high-heat operation: Design around the reliable service ceiling of 260°C (500°F) and account for material softening under load.
- If your primary focus is cryogenic performance: PTFE is an excellent choice down to -200°C (-328°F), but be sure to account for its increased rigidity and reduced flexibility.
- If your application involves brief temperature spikes: You can engineer for short excursions toward 300°C (572°F), but this should not be the normal operating condition.
Ultimately, PTFE's exceptionally wide and stable operating temperature range makes it a uniquely versatile material for solving extreme engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Limit | Condition | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| +260°C (500°F) | Continuous Service | Stable long-term performance; ideal for seals & linings. |
| Up to +300°C (572°F) | Short-Term Spikes | Brief excursions only; accelerates degradation. |
| ~+327°C (620°F) | Melting Point | Catastrophic failure; material loses all strength. |
| -200°C (-328°F) | Cryogenic Service | Retains toughness but becomes more rigid. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components for Extreme Temperatures?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—that deliver reliable performance from cryogenic conditions up to +260°C. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our expertise in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders ensures your application operates safely and efficiently.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your specific thermal and material requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Crucibles for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why are PTFE vials considered environmentally friendly? Reduce Lab Waste with Durable Reusables
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications
- What material is the PTFE bottle made from? Discover the Benefits of 100% Virgin PTFE
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What are the unique properties of PTFE that make it commercially valuable? Unlock Unmatched Performance



















