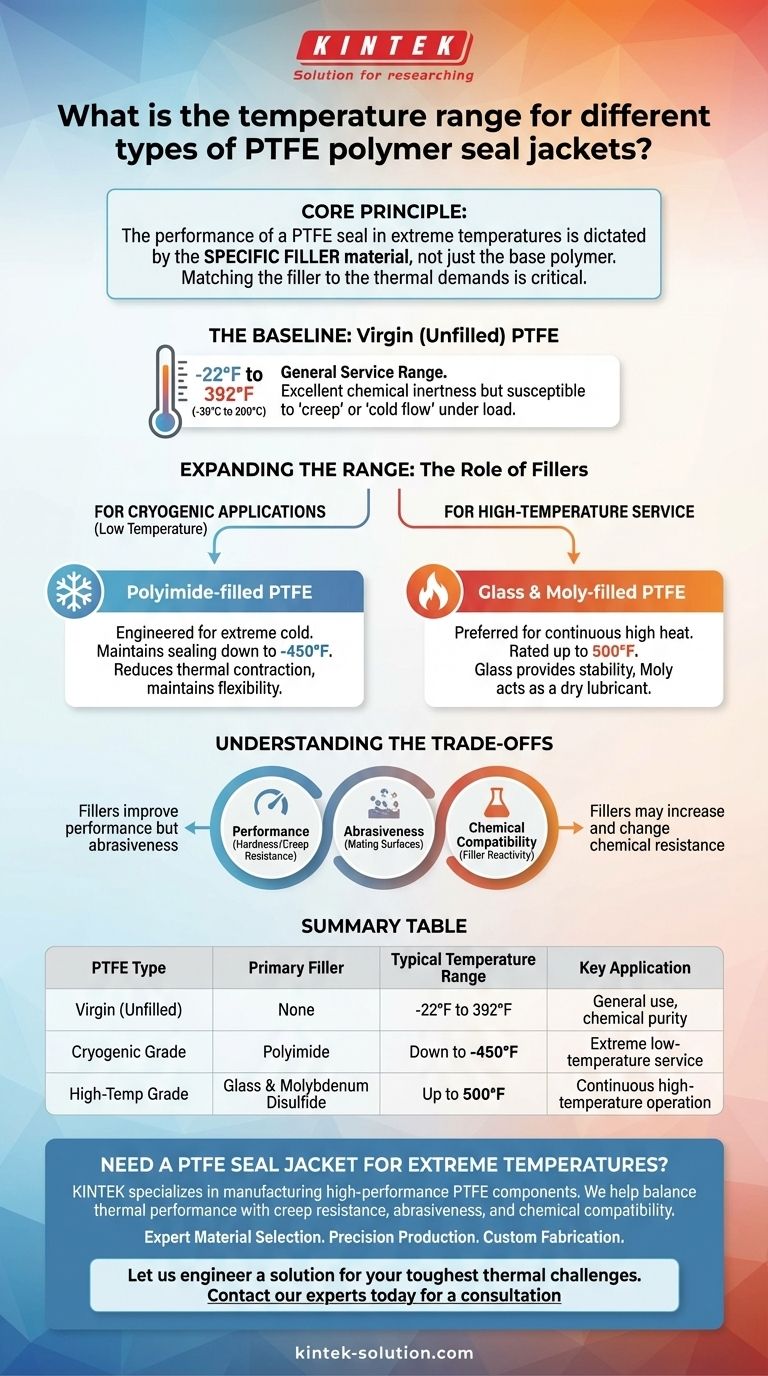
The temperature range of a PTFE seal jacket is not a single value; it is dictated by the specific filler material blended with the base polymer. While standard, unfilled PTFE has a broad range, specialized fillers are required to reach extreme high and low temperatures. For cryogenic applications, polyimide-filled PTFE can function down to -450°F, whereas glass and moly-filled grades are engineered to operate continuously at up to 500°F.
The core principle to understand is that the performance of a PTFE seal in extreme temperatures is not defined by the PTFE itself, but by the specific filler chosen to enhance its properties. Matching the filler to the thermal demands of your application is the critical factor.

The Baseline: Virgin (Unfilled) PTFE
Standard Operating Range
Pure, or virgin, PTFE is a highly capable polymer on its own. It offers a general service temperature range from approximately -22°F to 392°F (-30°C to 200°C).
Inherent Limitations
While its chemical inertness is nearly universal, virgin PTFE is a relatively soft material. Under load, it is susceptible to creep or "cold flow," which can compromise sealing integrity over time. This is a primary reason why fillers are so commonly used.
Expanding the Range: The Role of Fillers
Fillers are not just additives; they are functional components that fundamentally alter the mechanical properties of the base PTFE, including its performance at temperature extremes.
For Cryogenic Applications (Low Temperature)
When an application requires performance in extremely low temperatures, a polyimide-filled PTFE is the standard choice.
This specific blend is engineered to maintain its sealing capability in temperatures as low as -450°F. The polyimide filler helps reduce the significant thermal contraction of PTFE and maintains a degree of flexibility in environments where other materials would become brittle.
For High-Temperature Service
For applications involving sustained high heat, a glass and molybdenum disulfide (moly) filled PTFE is the preferred material.
This formulation is rated for continuous operation at temperatures up to 500°F. The glass fibers provide structural stability and dramatically reduce thermal expansion, while the moly acts as a dry lubricant to maintain low friction at elevated temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting a material for its temperature range is a critical decision, but it introduces trade-offs that must be considered for the entire system.
Performance is Not One-Dimensional
A filler that enhances temperature resistance may alter other key properties. For example, adding fillers increases the material's hardness and compressive strength, which reduces its tendency to creep.
Abrasiveness and Mating Surfaces
Hard fillers, particularly glass, can be more abrasive than virgin PTFE. This must be considered when designing for use with softer shaft or bore materials, as it can accelerate wear on the mating hardware.
Chemical Compatibility
While the PTFE base remains highly inert, the filler material may not be. Glass fillers, for instance, can be attacked by hydrofluoric acid or strong alkalis, compromising the seal in certain chemical environments.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your choice of PTFE seal jacket material must be directly aligned with the specific thermal and mechanical demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is extreme cold (cryogenics): Polyimide-filled PTFE is the optimal choice, engineered to maintain integrity down to -450°F.
- If your primary focus is high heat: A blend of glass and moly-filled PTFE provides the necessary stability for continuous service up to 500°F.
- If your primary focus is general use within a moderate temperature range: Virgin PTFE provides a capable range from -22°F to 392°F and is ideal when chemical purity is paramount.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material depends on a clear understanding of how these engineered compounds balance thermal performance with other critical mechanical properties.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Type | Primary Filler | Typical Temperature Range | Key Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Unfilled) | None | -22°F to 392°F (-30°C to 200°C) | General use, chemical purity |
| Cryogenic Grade | Polyimide | Down to -450°F | Extreme low-temperature (cryogenic) service |
| High-Temp Grade | Glass & Molybdenum Disulfide | Up to 500°F | Continuous high-temperature operation |
Need a PTFE Seal Jacket for Extreme Temperatures?
Choosing the right PTFE compound is critical for your application's success. The wrong material can lead to seal failure, downtime, and costly repairs.
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom seal jackets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand that temperature is just one factor; we help you balance thermal performance with creep resistance, abrasiveness, and chemical compatibility.
We offer:
- Expert Material Selection: Guidance on virgin, polyimide, glass/moly, and other filled PTFE grades.
- Precision Production: Components manufactured to exact specifications for reliable performance.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, tailored to your unique requirements.
Let us engineer a solution for your toughest thermal challenges.
Contact our experts today for a consultation to discuss your specific needs and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- In what forms are Metal-Polymer Bronze Backed PTFE Plain Bearings available? Choose the Right Form for Your Load
- How does the company ensure quality in PTFE wear strips and bands? Achieve Consistent Performance & Dimensional Accuracy
- What cost advantages do expanded PTFE gaskets offer? Lower Your Total Cost of Ownership
- What are the typical properties of 15% glass-filled Teflon balls? Enhanced Durability for Demanding Applications
- What is the heat-set process for PTFE seal elements? Simplify Installation and Ensure a Reliable Seal
- Are Teflon parts capable of withstanding high temperatures? Understanding the 260°C Limit for Performance
- In what applications are PTFE slide bearings superior to conventional supports? Ensuring Predictable Movement for Critical Structures



















