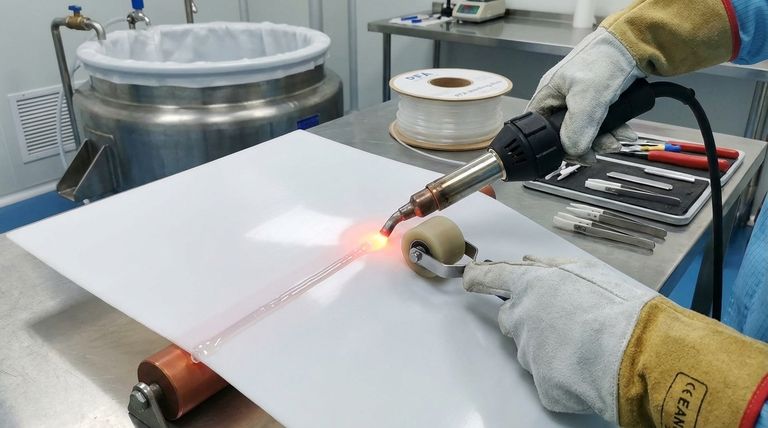
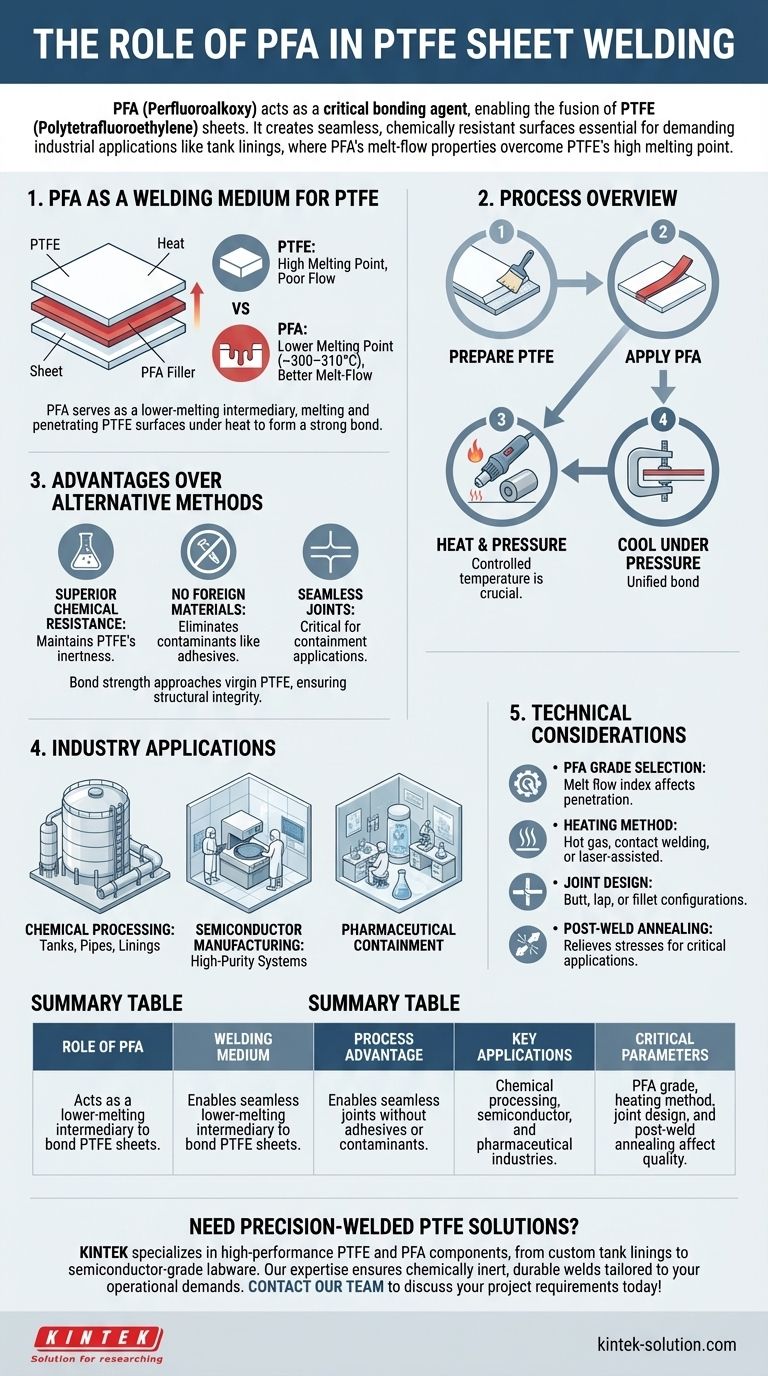
PFA (Perfluoroalkoxy) plays a critical role in welding PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) sheets, particularly in industrial applications like tank linings. While the exact chemical mechanism isn't fully documented, PFA acts as a bonding agent that enables the fusion of PTFE sheets under controlled conditions. This process is essential for creating seamless, chemically resistant surfaces in demanding environments. Specialized companies leverage PFA's unique properties to achieve strong, durable welds that maintain PTFE's non-stick and corrosion-resistant characteristics.

Key Points Explained:
-
PFA as a Welding Medium for PTFE
- PFA serves as an intermediary material that facilitates the welding of PTFE sheets. Unlike PTFE, which has an extremely high melting point and poor flow characteristics, PFA melts at a lower temperature (~300–310°C) and exhibits better melt-flow properties. This allows it to penetrate and bond PTFE surfaces when heated.
-
Process Overview
- The welding process typically involves:
- Preparing PTFE sheet edges (cleaning, beveling)
- Applying PFA as a filler material or interlayer
- Using controlled heat and pressure to fuse the materials
- Cooling under pressure to form a homogeneous bond
- Have you considered how temperature gradients affect weld integrity? Precise control prevents PTFE degradation while ensuring PFA flows adequately.
- The welding process typically involves:
-
Advantages Over Alternative Methods
- Compared to adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening, PFA welding offers:
- Superior chemical resistance (maintains PTFE's inertness)
- No foreign materials (e.g., adhesives) that could contaminate processes
- Seamless joints critical for containment applications like tank linings
- The bond strength approaches that of virgin PTFE, crucial for structural integrity.
- Compared to adhesive bonding or mechanical fastening, PFA welding offers:
-
Industry Applications
- Primarily used in:
- Chemical processing equipment (tanks, pipes)
- Semiconductor manufacturing (high-purity systems)
- Pharmaceutical containment
- These sectors benefit from PTFE's inertness combined with PFA's weldability—technologies that quietly shape modern healthcare and industrial safety.
- Primarily used in:
-
Technical Considerations
- Key parameters influencing weld quality:
- PFA grade selection (melt flow index affects penetration)
- Heating method (hot gas, contact welding, or laser-assisted)
- Joint design (butt, lap, or fillet configurations)
- Post-weld annealing may be required to relieve stresses in critical applications.
- Key parameters influencing weld quality:
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Role of PFA |
|---|---|
| Welding Medium | Acts as a lower-melting intermediary to bond PTFE sheets |
| Process Advantage | Enables seamless joints without adhesives or contaminants |
| Key Applications | Chemical processing, semiconductor, and pharmaceutical industries |
| Critical Parameters | PFA grade, heating method, joint design, and post-weld annealing affect quality |
Need precision-welded PTFE solutions for your industry? KINTEK specializes in high-performance PTFE and PFA components, from custom tank linings to semiconductor-grade labware. Our expertise ensures chemically inert, durable welds tailored to your operational demands. Contact our team to discuss your project requirements today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- Why are ePTFE gaskets considered hygienic? Ensure Product Purity with a Reliable Seal
- What is the chemical composition of PTFE gaskets? Discover the Source of Its Superior Performance
- What are the main benefits of PTFE envelope gaskets? Achieve Superior Chemical Resistance and Sealing Integrity
- What are the characteristics of PTFE spherical balls? Key Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is the difference between Teflon valves and PTFE lined valves? Choose the Right Valve for Your System
- How do spring energized PTFE seals differ from other radial seals? Superior Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are the manufacturing differences between PTFE and elastomer lip seals? A Guide to Performance and Cost
- Which type of PTFE gasket is better for uneven surfaces or fragile flanges? Seal with Confidence Using ePTFE



















