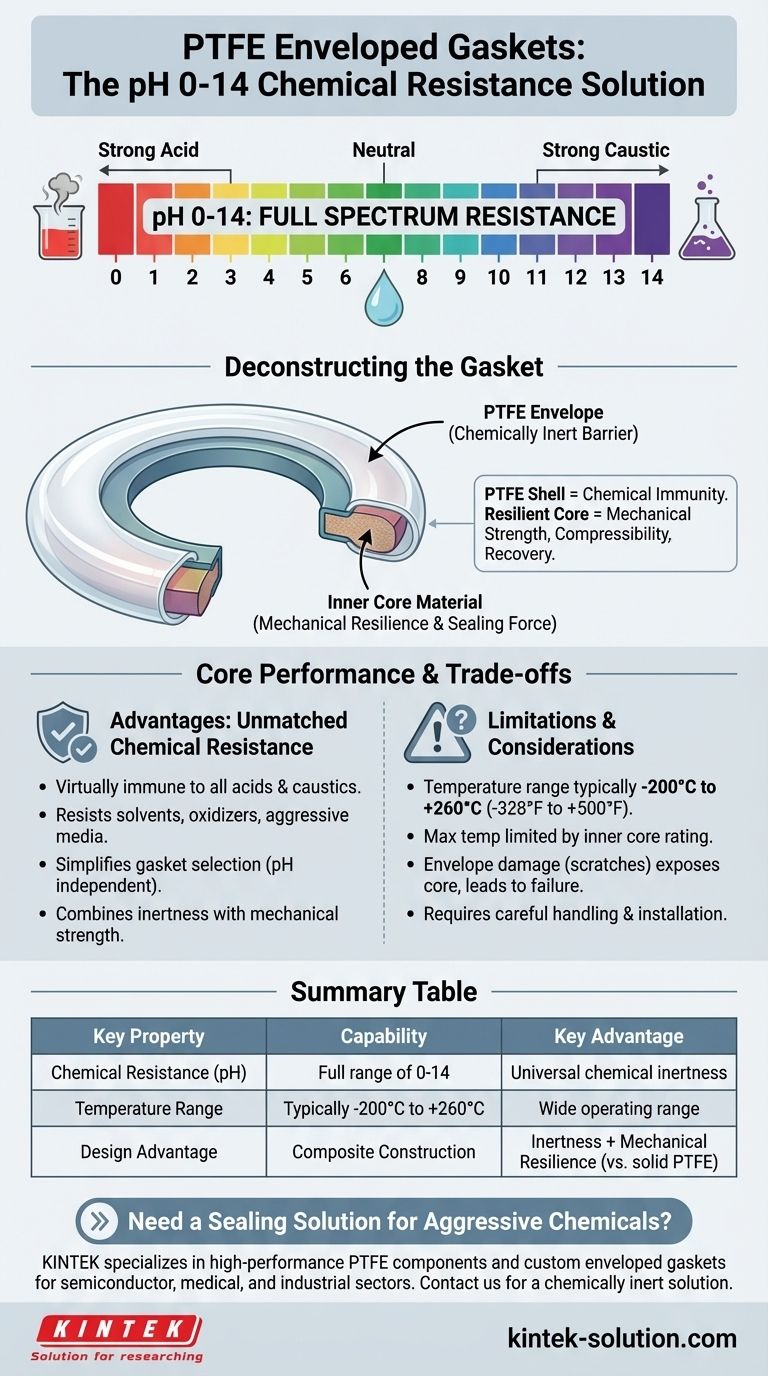
In short, a PTFE enveloped gasket can handle the entire pH spectrum. It is chemically resistant to all acid and caustic media within a full pH range of 0-14, making it one of the most chemically inert sealing solutions available for industrial applications.
The key takeaway is that while PTFE provides near-universal chemical resistance, the "enveloped" design is a crucial engineering solution. It combines the inertness of a PTFE shell with the mechanical strength and resilience of an inner core material, overcoming the physical limitations of using pure PTFE alone.

Deconstructing the PTFE Enveloped Gasket
To understand the performance of these gaskets, you must first understand their construction. They are not made of solid PTFE but are a composite of two distinct parts.
The PTFE Envelope
The outer layer, or "envelope," is made from Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This is the component that comes into direct contact with the process fluid. Its primary job is to act as a chemically impenetrable barrier, protecting the inner core.
The Inner Core Material
Inside the PTFE envelope is a different gasket material. This core provides the mechanical properties—like compressibility and recovery—that pure PTFE lacks. The core gives the gasket the resilience needed to create and maintain a tight seal under the pressure of flange bolts.
The Core Performance Factor: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The reason PTFE is chosen for demanding applications is its extreme chemical inertness. This quality is what defines its operational range.
Full pH Spectrum (0-14)
PTFE is virtually immune to chemical attack from the most aggressive acids to the strongest caustics. This allows it to be specified without concern for the pH of the media, simplifying gasket selection in complex chemical processes.
Inert to Aggressive Media
Beyond acids and bases, PTFE resists a vast range of solvents, oxidizers, and other reactive chemicals. This makes it a default choice in industries like chemical processing and pharmaceuticals where fluid compatibility is a primary safety and operational concern.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While chemically superior, a PTFE enveloped gasket is not a universal solution. Its effectiveness is bound by physical and mechanical constraints you must consider.
Temperature's Critical Role
PTFE maintains its integrity across a wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). However, the gasket's true maximum temperature may be limited by the inner core material, which often has a lower thermal rating than the PTFE itself. Always verify the temperature rating for the entire gasket assembly.
Mechanical Limitations and Creep
Pure PTFE is a relatively soft material that can "creep" or cold-flow when subjected to high pressure and temperature over time. This can lead to a loss of bolt torque and potential leaks. The enveloped design mitigates this by using a more mechanically stable core to maintain sealing pressure.
The Integrity of the Envelope
The primary vulnerability of this gasket type is physical damage to the PTFE envelope. A scratch, cut, or improper installation can create a leak path, exposing the chemically vulnerable inner core. This would lead to rapid gasket failure. Careful handling and installation are therefore non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if a PTFE enveloped gasket fits your specific operational goals.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical resistance: A PTFE enveloped gasket is a top-tier choice, providing a reliable seal against virtually any fluid within the pH 0-14 range.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature sealing: Verify that both the PTFE envelope and the inner core material are rated for your operating temperature, typically up to a maximum of 260°C (500°F).
- If your primary focus is managing high-pressure or vibration: The enveloped design provides superior mechanical resilience and resistance to creep compared to a solid PTFE gasket, making it better suited for these conditions.
By understanding both the chemical inertness of the PTFE and the mechanical function of the core, you can confidently specify the right gasket for your most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | PTFE Enveloped Gasket Capability |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance (pH) | Full range of 0-14 |
| Temperature Range | Typically -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F) |
| Key Advantage | Combines PTFE's inertness with a resilient core's mechanical strength |
Need a sealing solution for aggressive chemicals?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components, including custom enveloped gaskets, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our precision production ensures reliable sealing against the harshest acids and caustics across the entire pH spectrum.
We offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to meet your exact specifications. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and get a quote for a chemically inert sealing solution.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- In which industries are PTFE sheets commonly used? Key Applications for Non-Stick & Heat-Resistant Materials
- What are the main properties of PTFE gaskets? Unlock Superior Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What requirements must energized-seal jacket materials meet for medical devices? A Guide to Sterilizability, Biocompatibility & Strength
- What is the difference between carbon and graphite as fillers in PTFE? Optimize Strength vs. Lubricity
- What challenges do elastomeric seals face in oil and gas operations? Ensuring Reliability Under Extreme Conditions
- What additional materials are used in PTFE laminate materials and why? Enhance Performance for Demanding Applications
- How do PTFE gaskets handle friction in flange connections? Achieve Low-Stress Sealing for Delicate Flanges
- What makes PTFE gaskets suitable for the food industry? Ensure Purity and Compliance



















