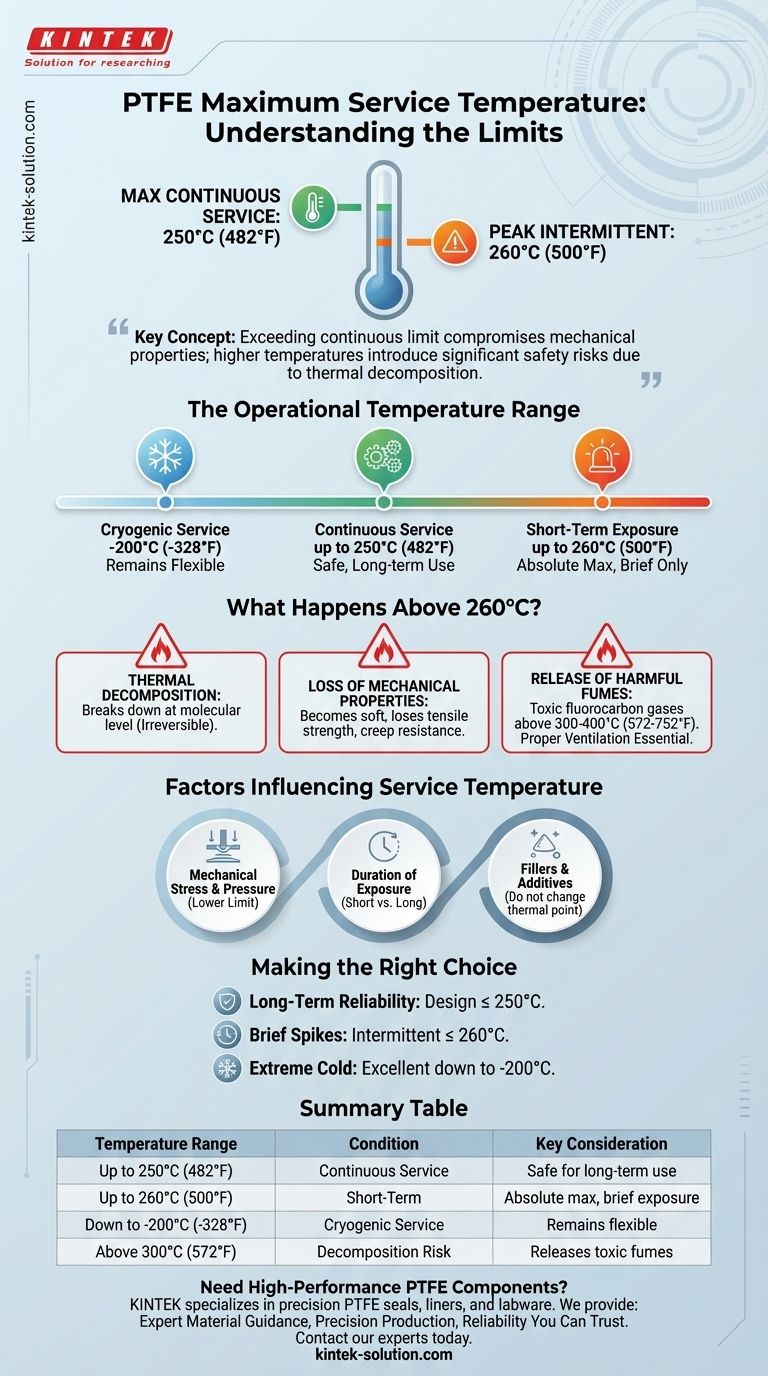
For most applications, the maximum continuous service temperature for Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is 250°C (482°F). While the material can withstand short-term exposure to temperatures as high as 260°C (500°F), operating continuously at this peak temperature is not recommended as it accelerates material degradation.
The key to using PTFE effectively is to understand the difference between its continuous service limit and its peak temperature. Exceeding the continuous limit compromises the material's mechanical properties and, at higher temperatures, introduces significant safety risks due to thermal decomposition.

The Operational Temperature Range of PTFE
Polytetrafluoroethylene is renowned for its exceptionally wide operating temperature range, making it suitable for both high-heat and cryogenic applications. However, its performance is defined by clear upper and lower boundaries.
Maximum Continuous Service Temperature
The safe, long-term operational limit for pure PTFE is 250°C (482°F).
At this temperature, the material retains its excellent chemical inertness and low-friction characteristics without a significant loss of mechanical strength or dimensional stability over time.
Peak Intermittent Temperature
PTFE can tolerate brief, intermittent exposure to temperatures up to 260°C (500°F).
This should be considered an absolute maximum for short durations only. Prolonged exposure at this level will cause the material to soften and degrade more rapidly, increasing the risk of failure in mechanical applications like seals or bearings.
Low-Temperature Performance
PTFE maintains its properties remarkably well in extreme cold.
It remains flexible and functional down to cryogenic temperatures, with a standard low-temperature rating of approximately -200°C (-328°F), making it a preferred choice for applications in aerospace and scientific equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs: What Happens Above 260°C?
Unlike many thermoplastics, PTFE does not have a true melting point. Instead, it undergoes thermal decomposition when overheated, which has critical implications for both performance and safety.
Thermal Decomposition
As temperatures rise significantly above 260°C (500°F), PTFE begins to break down at a molecular level.
This decomposition is not a reversible process like melting. It permanently alters the material's chemical structure.
Loss of Mechanical Properties
As it approaches its decomposition temperature, PTFE becomes significantly softer and loses its tensile strength and resistance to creep (deformation under load).
In a sealing application, for example, an overheated PTFE O-ring will lose its ability to maintain a compressive force, leading to leaks and eventual failure.
The Release of Harmful Fumes
This is the most critical safety consideration. When heated above 300-400°C (572-752°F), the decomposition of PTFE accelerates and releases toxic fluorocarbon gases.
Proper ventilation is essential in any environment where PTFE could be subjected to extreme temperatures, as inhaling these fumes can cause polymer fume fever, a condition with severe flu-like symptoms.
Factors Influencing Service Temperature
The "maximum temperature" is not a single, absolute number but is influenced by the conditions of the specific application.
Mechanical Stress and Pressure
The effective maximum service temperature is lower in high-load applications.
Pressure and mechanical stress increase the rate of creep, especially as the material softens with heat. For a high-pressure seal, the functional temperature limit may be well below 250°C.
Duration of Exposure
The length of time the material spends at an elevated temperature is crucial.
As discussed, PTFE can handle brief spikes to 260°C, but its reliable, long-term performance is defined by the lower continuous service temperature.
Fillers and Additives
Different grades of PTFE contain fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze to enhance specific properties like wear resistance or compressive strength.
While these fillers can improve mechanical performance at high temperatures, they do not change the fundamental thermal decomposition point of the underlying PTFE polymer.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To ensure reliability and safety, you must align your operating conditions with the correct thermal limit of PTFE.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability and safety: Design your application to operate at or below the continuous service temperature of 250°C (482°F), including a suitable safety margin.
- If your application involves brief temperature spikes: You can engineer for intermittent exposure up to 260°C (500°F), but this should not be the normal operating condition.
- If you are operating in extreme cold: PTFE is an excellent choice, retaining its flexibility and sealing capability down to cryogenic temperatures of -200°C (-328°F).
By respecting its thermal limits, you can leverage PTFE's exceptional chemical and temperature resistance for the most demanding applications.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Condition | Key Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Up to 250°C (482°F) | Continuous Service | Safe for long-term use; retains mechanical properties. |
| Up to 260°C (500°F) | Short-Term/Intermittent | Absolute maximum for brief exposure; accelerates degradation. |
| Down to -200°C (-328°F) | Cryogenic Service | Remains flexible and functional. |
| Above 300°C (572°F) | Decomposition Risk | Material breaks down, releasing toxic fumes. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components That Withstand Extreme Temperatures?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the most demanding environments in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between temperature resistance, mechanical integrity, and safety.
We provide:
- Expert Material Guidance: Ensure your PTFE components are specified correctly for your exact temperature and pressure requirements.
- Precision Production: From custom prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver components that meet stringent quality standards.
- Reliability You Can Trust: Avoid costly downtime and safety hazards with components engineered for long-term performance.
Let's discuss your application's thermal challenges. Contact our experts today for a consultation and quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What are the characteristics of PFA Teflon? | Extreme Performance Meets Design Freedom
- What makes PTFE an ideal material for low-friction applications? Achieve Superior Performance with Self-Lubricating Components
- How does Teflon coating benefit cookware? Achieve Effortless Cooking and Easy Cleanup
- What industries commonly use PTFE and why? Unlock the Power of PTFE for Extreme Environments
- What is PTFE and what are its primary applications? Unlock High-Performance Solutions
- What are the key properties of Teflon (PTFE) that make it suitable for industrial applications?
- What are the key properties that make PTFE commercially valuable? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What are the similarities between PTFE and RPTFE? Unlocking the Core Fluoropolymer Identity



















