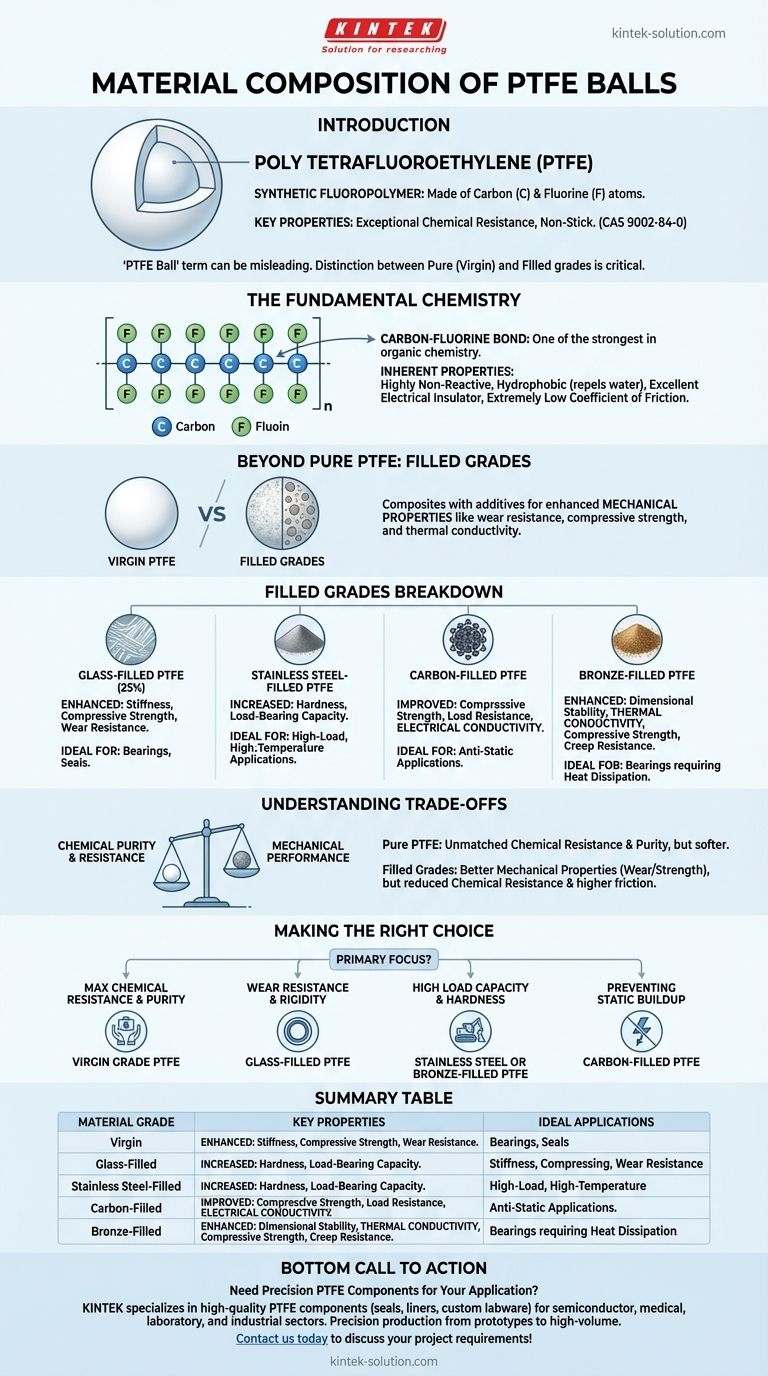
At their core, PTFE balls are composed of polytetrafluoroethylene, a synthetic fluoropolymer made entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. This material, identified by the CAS Number 9002-84-0, is known for its exceptional chemical resistance and non-stick properties.
The term "PTFE ball" can be misleading. While the base material is always the same carbon-fluorine polymer, many high-performance variants exist where fillers like glass, carbon, or stainless steel are added to enhance specific mechanical properties. Understanding the difference between pure "virgin" PTFE and these "filled" grades is critical for any technical application.

The Fundamental Chemistry of PTFE
The unique properties of PTFE stem directly from its simple but powerful molecular structure. This structure dictates its performance in nearly every application.
A Polymer of Carbon and Fluorine
PTFE consists of a long, linear chain of carbon atoms. Each carbon atom in this chain is bonded to two fluorine atoms.
This repeating (-CF2-CF2-)n structure forms a very stable and high-molecular-weight polymer.
The Strength of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest known in organic chemistry. This exceptionally strong bond is the primary reason for PTFE's signature characteristics.
It makes the material highly non-reactive, as it is energetically difficult for other chemicals to break these bonds.
Inherent Material Properties
This molecular arrangement gives pure PTFE several key properties. It is hydrophobic, meaning it repels water and does not absorb it.
It is also an excellent electrical insulator and possesses an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most "slippery" solid materials known.
Beyond Pure PTFE: Understanding Filled Grades
For many industrial applications, the mechanical properties of pure PTFE are insufficient. To overcome this, fillers are blended into the PTFE matrix to create a composite material with enhanced characteristics.
What Are Filled Grades?
Filled grades are composite materials where a percentage of the PTFE is replaced by another substance. This is done to improve properties like wear resistance, compressive strength, and thermal conductivity.
25% Glass-Filled PTFE
Adding glass fibers significantly increases the stiffness and compressive strength of the material. It also greatly improves wear resistance, making it suitable for bearings and seals.
Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE
Adding stainless steel powder (often 316-grade) dramatically increases the hardness and load-bearing capacity of the balls. This grade is used in high-load, high-temperature applications.
Carbon-Filled PTFE
Carbon provides excellent compressive strength and load resistance. Critically, it also improves electrical conductivity, making it a choice for anti-static applications.
Bronze-Filled PTFE
Bronze fillers enhance dimensional stability and improve thermal conductivity, allowing heat to dissipate more effectively from bearing surfaces. This also increases compressive strength and resistance to creep.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between pure PTFE and a filled grade involves a direct trade-off between chemical purity and mechanical performance. This decision is fundamental to successful material selection.
Pure (Virgin) PTFE: The Benchmark
The primary advantage of virgin PTFE is its unmatched chemical resistance and purity. It is the best choice for medical, pharmaceutical, or semiconductor applications where contamination is a concern.
However, it is relatively soft and prone to "creep," or deforming slowly under a sustained load. Its wear resistance is also lower than filled grades.
Filled Grades: Performance at a Price
Adding fillers enhances mechanical properties like strength and wear resistance. This makes the material far more durable for demanding industrial use.
The downside is a reduction in overall chemical resistance, as the filler material itself may not be as inert as the PTFE. The coefficient of friction is also slightly higher compared to virgin PTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final material selection must be guided by the primary demands of its intended environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical resistance and purity: Choose Virgin Grade PTFE, especially for food-grade, medical, or high-purity chemical handling.
- If your primary focus is wear resistance and rigidity under load: A glass-filled PTFE is the standard choice for components like seals, gaskets, and bearings.
- If your primary focus is high load capacity and hardness: A stainless steel or bronze-filled PTFE is necessary for high-pressure or heavy-load mechanical systems.
- If your primary focus is preventing static buildup: A carbon-filled PTFE provides the required electrical conductivity that other grades lack.
Ultimately, selecting the correct material composition is the key to ensuring operational reliability and performance.
Summary Table:
| Material Grade | Key Properties | Ideal Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Virgin (Pure) PTFE | Maximum chemical resistance, non-stick, low friction | Medical, pharmaceutical, semiconductor, food-grade |
| Glass-Filled PTFE | Enhanced wear resistance, rigidity, compressive strength | Seals, gaskets, bearings |
| Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE | High load capacity, hardness, temperature resistance | High-pressure, heavy-load mechanical systems |
| Carbon-Filled PTFE | Electrical conductivity, compressive strength | Anti-static applications |
| Bronze-Filled PTFE | Improved thermal conductivity, dimensional stability | Bearings requiring heat dissipation |
Need Precision PTFE Components for Your Application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-quality PTFE components—from seals and liners to custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require the purity of virgin PTFE or the enhanced performance of filled grades, we provide precision production and custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Let us help you select the perfect material composition for reliability and performance. Contact us today to discuss your project requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What temperature range can PTFE-lined valves operate within? Key Limits for Safe & Reliable Performance
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- Are PTFE flange gaskets customizable? Tailor Your Sealing Solution for Peak Performance
- What should be considered when bonding PTFE sheets? A Guide to Achieving a Reliable, Permanent Bond
- In which aerospace applications are PTFE spring-energized seals used? Ensuring Reliability in Extreme Environments
- Why are PTFE-free bushings considered environmentally friendly? Reduce PFAS Risk & Enhance Sustainability
- What are spring-energized PTFE seals and how do they work? Achieve Leak-Proof Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What recent advancements have been made in PTFE expansion joint technology? Enhance Durability & Precision



















