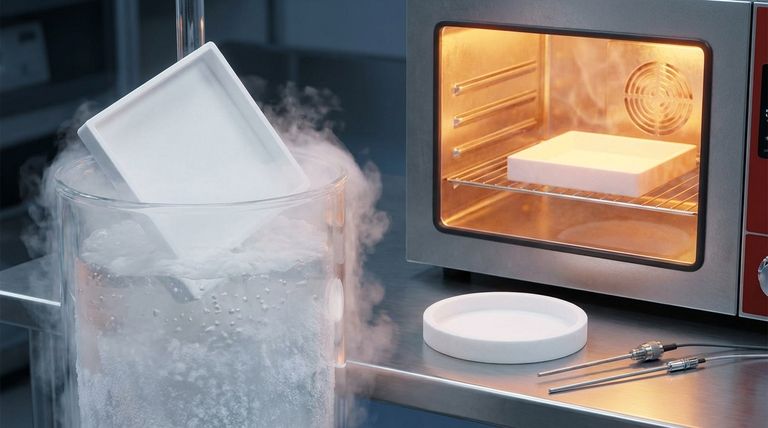
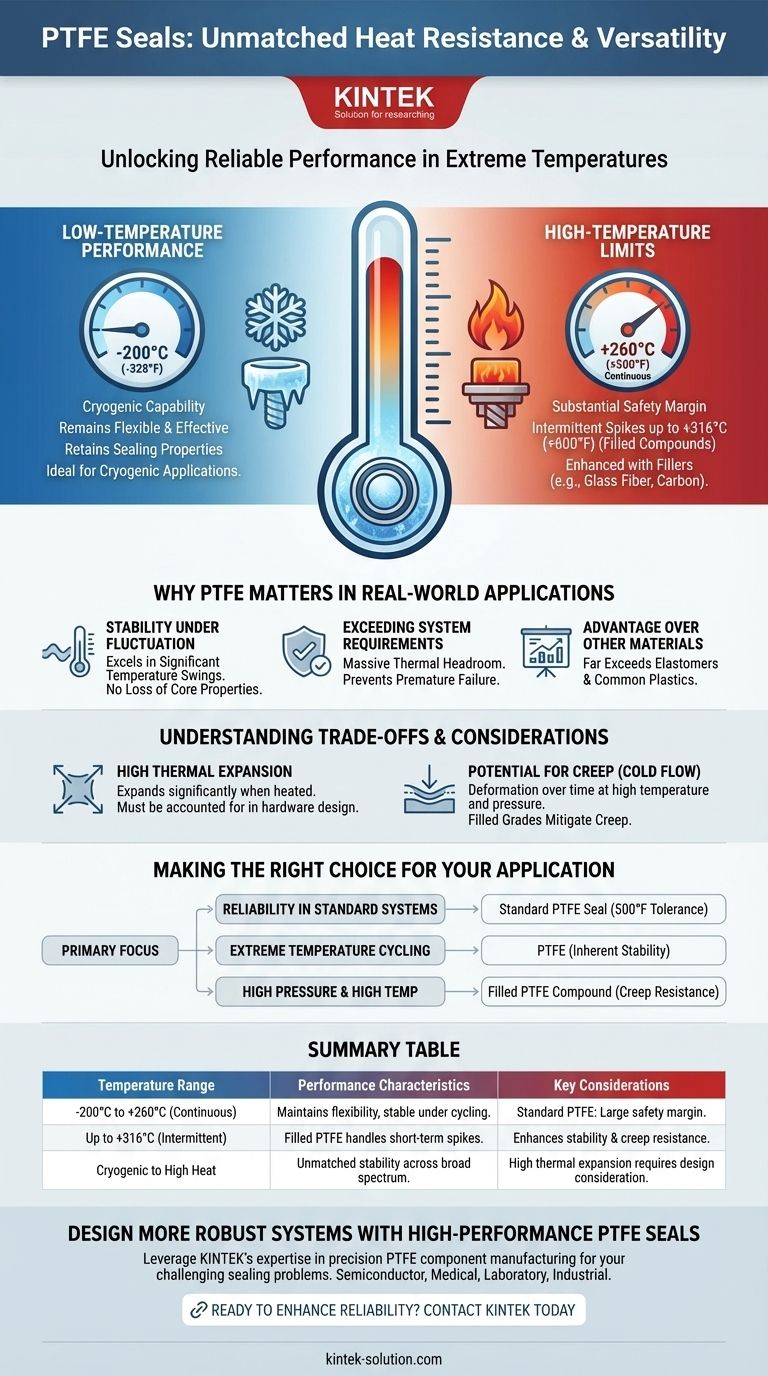
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) offers exceptional thermal resistance, making it one of the most versatile sealing materials available. Standard PTFE seals can operate continuously in temperatures ranging from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to a high of 260°C (500°F). This remarkable stability across such a broad spectrum ensures reliable performance where most elastomers and other plastics would fail.
The true value of PTFE is not just its high heat tolerance, but its ability to maintain its mechanical and chemical properties across an incredibly wide temperature range. This makes it a definitive choice for applications involving thermal cycling or extreme operating conditions.

The Exceptional Thermal Range of PTFE
To properly evaluate PTFE for your application, it's important to understand the specifics of its performance at both high and low temperatures.
Upper Temperature Limits
Most standard PTFE seals are rated for continuous service up to 260°C (500°F). This provides a substantial safety margin for the vast majority of industrial and hydraulic applications.
Some specialized, filled PTFE compounds can even endure intermittent temperature spikes up to 316°C (600°F), offering short-term protection during system upsets or unusual conditions.
Unmatched Low-Temperature Performance
PTFE is equally impressive at the other end of the spectrum, remaining flexible and effective down to -200°C (-328°F).
Unlike many materials that become brittle and fracture at low temperatures, PTFE retains its sealing properties, making it a reliable choice for cryogenic applications.
How Fillers Influence Thermal Performance
The term "PTFE" often refers to a family of materials. Adding fillers like glass fiber, carbon, or graphite to the virgin PTFE resin can enhance specific properties.
While these fillers primarily improve wear resistance and reduce creep, they can also bolster the material's stability and strength at the upper end of its temperature range.
Why This Matters in Real-World Applications
A material's datasheet temperature range is only useful when applied to a specific engineering problem. The thermal stability of PTFE provides several key advantages.
Stability Under Fluctuation
PTFE seals excel in environments with significant temperature swings. The material does not lose its core mechanical properties when cycled between hot and cold, ensuring a consistent and reliable seal.
Exceeding System Requirements
Consider a typical hydraulic system where fluid temperatures are kept below 60°C (140°F) for optimal performance. Using a PTFE seal rated for 260°C (500°F) isn't overkill; it's a critical design choice for reliability.
This massive thermal headroom provides a safety margin against temperature spikes from localized friction or system faults, preventing premature seal failure.
A Clear Advantage Over Other Materials
The operational range of PTFE far exceeds that of most common elastomers and plastics. Materials like Polypropylene and ABS cannot approach its high-temperature tolerance, while many rubbers will degrade long before reaching 260°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs at High Temperatures
While PTFE's performance is impressive, no material is without its limitations. Acknowledging these factors is key to successful seal design.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means the seal will expand significantly as it heats up, a factor that must be accounted for in the hardware design to prevent excessive pressure or binding.
Potential for Creep (Cold Flow)
At elevated temperatures and under load, PTFE can be susceptible to "creep," or cold flow, where the material slowly deforms over time. Using filled PTFE grades is the most effective way to mitigate this effect in demanding applications.
The Combined Effect of Pressure
The maximum operating temperature is always related to system pressure. High pressure combined with high temperature creates the most demanding environment for any seal. For these applications, a specialized filled PTFE compound is almost always required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires matching its properties to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is reliability in standard systems: A standard PTFE seal is an excellent choice, as its 500°F tolerance provides a massive safety margin for most industrial or hydraulic equipment.
- If your primary focus is performance under extreme temperature cycling: PTFE is the ideal material due to its inherent stability from cryogenic lows to high heat, which prevents material degradation over time.
- If your primary focus is handling high pressure at high temperatures: Select a filled PTFE compound (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) to improve creep resistance and ensure mechanical stability under combined stresses.
Ultimately, understanding PTFE's thermal capabilities empowers you to design more robust and reliable systems.
Summary Table:
| Temperature Range | Performance Characteristics | Key Considerations |
|---|---|---|
| -200°C to 260°C (Continuous) | Maintains flexibility and sealing properties; stable under thermal cycling. | Standard PTFE provides a large safety margin for most applications. |
| Up to 316°C (Intermittent) | Filled PTFE compounds can handle short-term spikes. | Enhances stability and creep resistance under extreme conditions. |
| Cryogenic to High Heat | Unmatched stability across a broad spectrum where other materials fail. | High thermal expansion must be accounted for in hardware design. |
Design More Robust Systems with High-Performance PTFE Seals
Leverage KINTEK's expertise in precision PTFE component manufacturing to solve your most challenging sealing problems. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, our custom-fabricated PTFE seals, liners, and labware are engineered for reliability in extreme conditions.
We specialize in creating solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your systems benefit from the unmatched thermal stability of PTFE.
Ready to enhance your application's reliability? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific requirements and receive a custom solution quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- When and by whom was PTFE discovered? A Tale of Accidental Innovation
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- What is the hardness range of PTFE on the Shore D scale? Leveraging Its Softness for Superior Performance
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- How does PTFE compare to other low-friction plastics like UHMW-PE and Nylon? A Guide to Material Selection



















