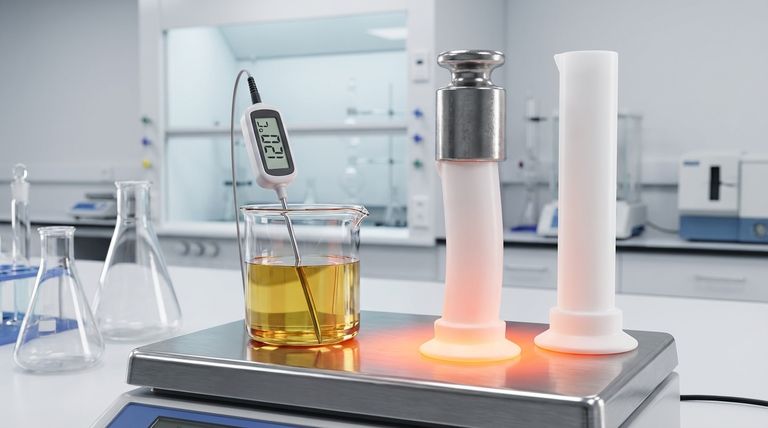
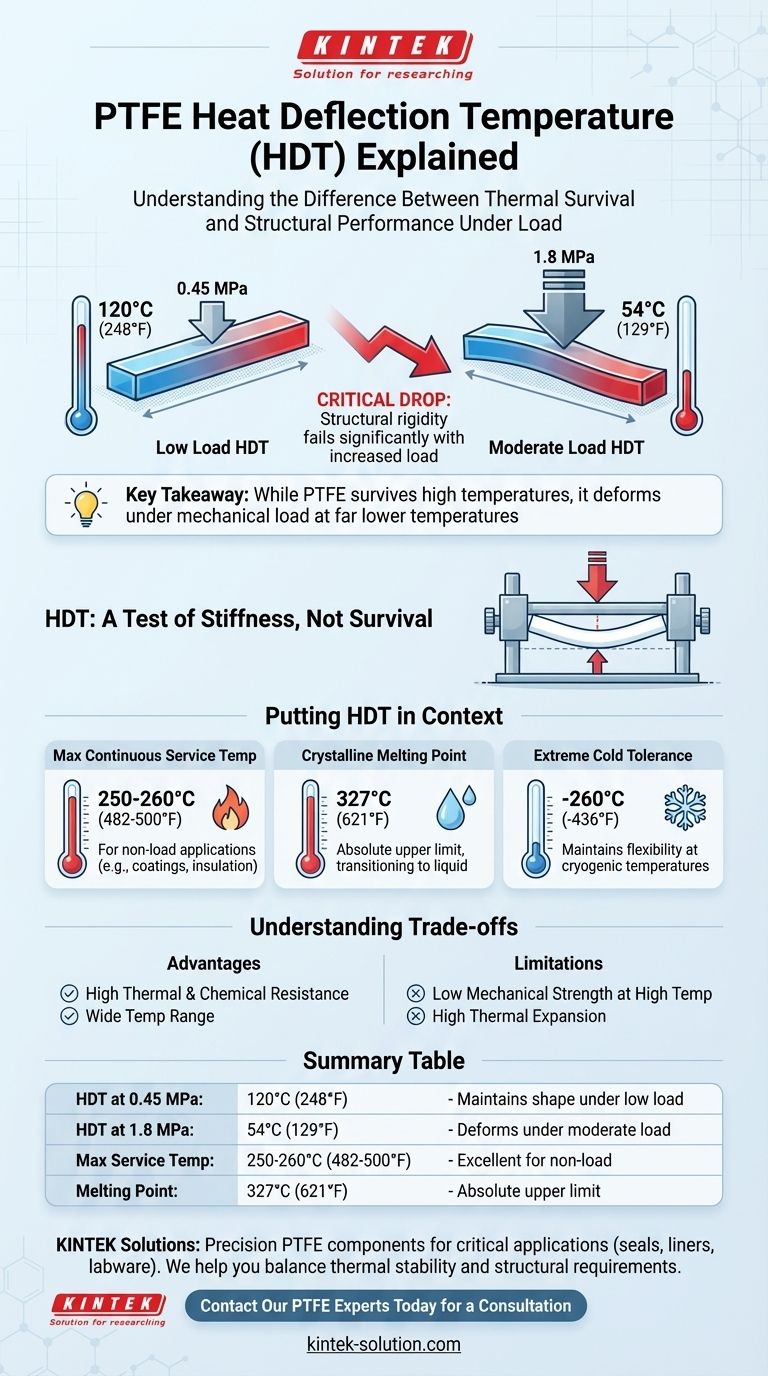
At a standard load, the heat deflection temperature (HDT) of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is 120°C (248°F) under a pressure of 0.45 MPa. However, this value is highly dependent on the applied mechanical stress. When the load is increased to 1.8 MPa, the heat deflection temperature drops significantly to just 54°C (129°F).
The key takeaway is that while PTFE is famous for its high-temperature survival, its structural rigidity is surprisingly low. The Heat Deflection Temperature (HDT) reveals that PTFE will deform under mechanical load at temperatures far below its maximum service limit, a critical distinction for any engineering application.

What "Heat Deflection Temperature" Actually Means
Heat Deflection Temperature is not a measure of a material's melting point or its ultimate survival temperature. It is a specific engineering metric that indicates short-term stiffness as temperature increases.
A Test of Stiffness, Not Survival
The HDT test determines the temperature at which a standard test bar of the material deforms by a specific amount while under a specific load.
It essentially answers the question: "At what temperature does this material begin to lose its structural integrity and get soft?"
The Critical Role of Mechanical Load
For PTFE, the load applied during the test is the most important variable. Its two common HDT ratings tell a clear story about its performance.
At a low load (0.45 MPa), PTFE maintains its shape up to 120°C. Increase that load fourfold to a moderate level (1.8 MPa), and it begins to deform at just 54°C—barely above the temperature of hot tap water.
This demonstrates that PTFE is not a suitable material for components that need to bear significant mechanical loads at elevated temperatures.
Putting HDT in Context: PTFE's Broader Thermal Capabilities
To correctly apply PTFE, you must understand how HDT compares to its other thermal properties. The HDT value alone can be misleading if taken out of context.
Maximum Continuous Service Temperature
This is the property for which PTFE is most famous. It refers to the maximum temperature the material can withstand for extended periods without significant mechanical stress before it begins to degrade.
For PTFE, the maximum service temperature is exceptionally high, typically cited as 250°C to 260°C (482°F to 500°F). This makes it ideal for applications like non-stick coatings, wire insulation, or chemical-resistant linings where it isn't carrying a heavy load.
Crystalline Melting Point
The melting point is the absolute upper limit where the material transitions from a solid to a viscous liquid.
PTFE has a very high melting point of around 327°C (621°F). This provides a significant safety margin above its continuous service temperature.
Extreme Cold Tolerance
Just as impressive as its heat resistance is PTFE's performance at cryogenic temperatures. It maintains useful properties, including flexibility, down to -260°C (-436°F).
Understanding the Trade-offs
PTFE's unique thermal profile presents a clear set of advantages and limitations that are critical for proper material selection.
The Misconception of High-Temperature Strength
The primary trade-off is its low mechanical strength at elevated temperatures.
While PTFE survives up to 260°C, its low HDT proves that it becomes soft and yields to pressure long before that. It has excellent thermal stability but poor "hot hardness" or structural performance.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a relatively high coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts significantly with temperature changes.
For designs with very tight tolerances, this dimensional change must be factored in to prevent parts from binding or failing when they heat up.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Using PTFE effectively requires aligning its specific properties with the demands of your application.
- If your primary focus is structural support under heat: You must be extremely cautious. PTFE will deform under load at relatively modest temperatures (54°C to 120°C), making it unsuitable for most load-bearing roles above room temperature.
- If your primary focus is thermal or chemical resistance without load: PTFE is an excellent choice. Its ability to serve continuously at 260°C makes it a top-tier material for linings, seals, and insulation.
- If your primary focus is performance across a wide temperature range: PTFE is exceptional, but you must design components to accommodate its significant thermal expansion to ensure proper fit and function.
Ultimately, understanding the difference between thermal survival and structural performance under heat is the key to successfully engineering with PTFE.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| HDT at 0.45 MPa | 120°C (248°F) | Maintains shape under low load |
| HDT at 1.8 MPa | 54°C (129°F) | Deforms under moderate load |
| Max Service Temperature | 250-260°C (482-500°F) | Excellent for non-load applications |
| Melting Point | 327°C (621°F) | Absolute upper limit |
Need PTFE Components That Perform Under Pressure?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We understand the critical balance between PTFE's thermal stability and its structural limitations.
We help you:
- Design components that leverage PTFE's chemical and thermal resistance
- Account for thermal expansion and load-bearing requirements
- Fabricate custom solutions from prototypes to high-volume orders
Let's engineer a solution that works for your specific temperature and load conditions.
Contact our PTFE experts today for a consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Three Neck Flasks for Advanced Chemical Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is chemical compatibility important when choosing a PTFE-coated septum? Avoid Sample Contamination and Data Loss
- What are the primary applications of Teflon? Leverage Its Unique Properties for Your Industry
- What are the primary applications of PTFE? Unlocking High-Performance Solutions
- What are the common characteristics of Teflon? Unlocking Extreme Chemical and Thermal Resistance
- What makes the PTFE bottle durable? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Stability for Demanding Applications



















