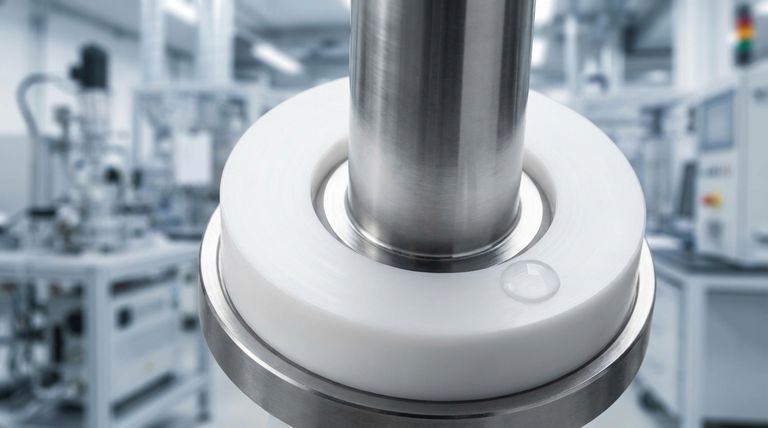
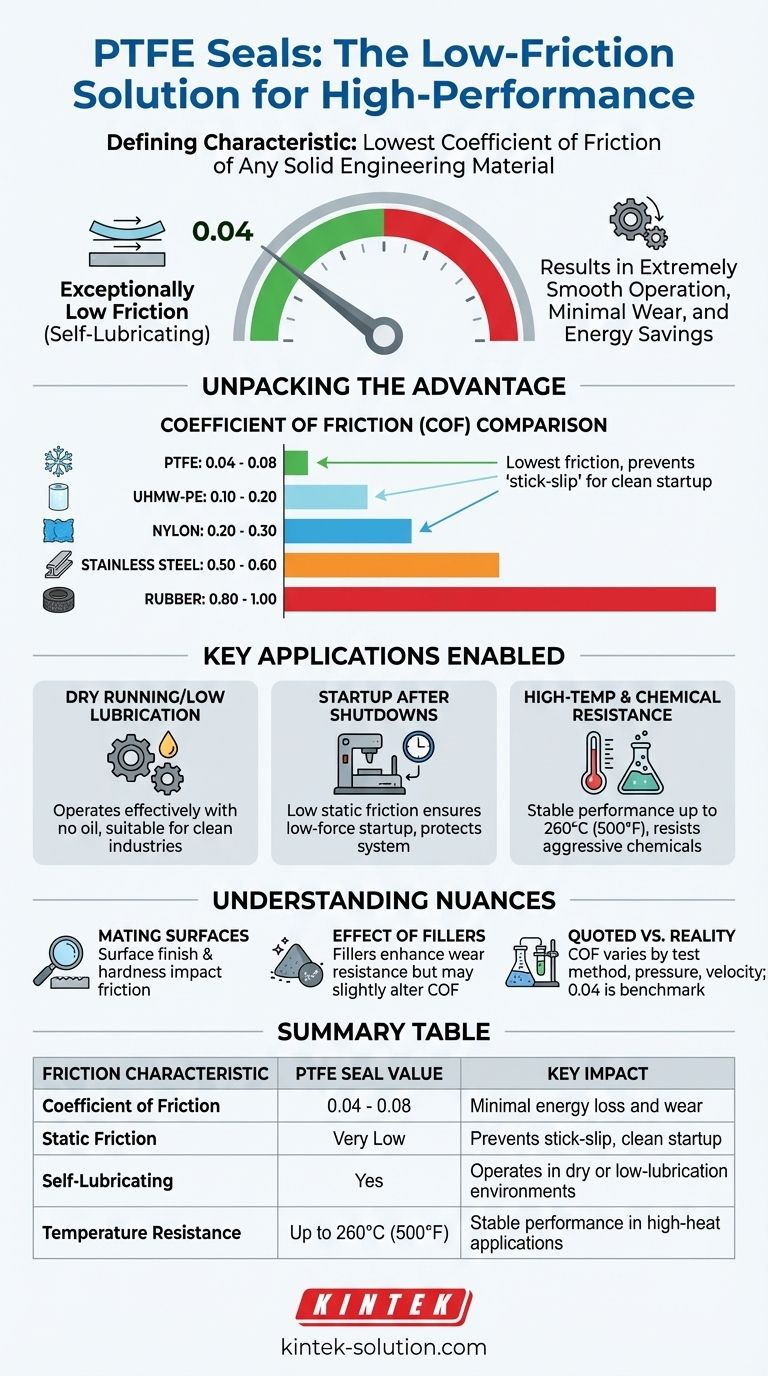
The defining friction characteristic of PTFE seals is that they possess the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid engineering material. This unique, self-lubricating property results in exceptionally smooth operation with minimal wear. With a typical coefficient of friction around 0.04, PTFE seals reduce energy loss and are suitable for applications with little to no oil, even after prolonged shutdowns.
PTFE's exceptionally low friction is not just a minor benefit; it is a core functional advantage. This property fundamentally changes how systems can be designed, enabling reliable operation in high-temperature, chemically aggressive, and dry-running environments where traditional seals would quickly fail.

Unpacking the Low-Friction Advantage
The performance of any seal is directly tied to its frictional properties. For PTFE, these properties are so superior that they create a class of their own.
An Exceptionally Low Coefficient of Friction (COF)
The coefficient of friction is a measure of how much force is required to move two surfaces against each other. PTFE's COF is typically cited as 0.04, a value nearly as low as ice on ice.
This applies to both static friction (the force to initiate movement) and kinetic friction (the force to maintain movement). This is critical for preventing "stick-slip" behavior, where a seal sticks to a shaft upon startup, causing a damaging jolt.
How PTFE Compares to Other Materials
To understand how significant PTFE's low friction is, it's best to compare it directly with other common engineering materials.
- PTFE: 0.04 – 0.08
- UHMW-PE: 0.10 – 0.20
- Nylon: 0.20 – 0.30
- Stainless Steel: 0.50 – 0.60
- Rubber: 0.80 – 1.00
Even when compared to lubricated steel, which has a kinetic COF of around 0.05, PTFE often performs better, especially in scenarios where lubrication is inconsistent.
The Impact on System Performance
This dramatic reduction in friction has direct, measurable benefits for mechanical systems. It leads to significantly less wear on both the seal and the shaft it runs against.
This translates directly to a longer service life for the components and lower maintenance costs over the lifetime of the equipment.
Key Applications Enabled by Low Friction
The unique characteristics of PTFE seals make them the preferred, and sometimes only, solution for several challenging industrial applications.
Dry Running and Low-Lubrication Scenarios
Because PTFE is inherently self-lubricating, seals made from it can operate effectively with no oil or minimal lubrication. This is essential in industries like food processing or in specific mechanical designs where lubricants are undesirable.
Startup After Prolonged Shutdowns
In equipment that sits idle for long periods, other seals can adhere to the shaft. Upon restart, this can cause high initial torque and potential seal damage.
PTFE's low static friction ensures a clean, low-force startup every time, protecting the integrity of the system.
High-Temperature and Chemical Resistance
A key advantage of PTFE is that its low-friction properties remain stable across a wide temperature range (up to 260°C or 500°F) and when exposed to aggressive chemicals, oils, and solvents.
Understanding the Practical Nuances
While PTFE's properties are exceptional, a few factors can influence its real-world performance. It's important to understand these for proper application.
The Role of Mating Surfaces
The friction coefficient of PTFE is not solely a property of the material itself but of the system. The surface finish and hardness of the mating shaft play a critical role in achieving the lowest possible friction and wear rates.
The Effect of Fillers
To enhance properties like wear resistance or reduce creep, PTFE is often blended with fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze. These fillers can slightly alter the coefficient of friction, representing a design trade-off for improved mechanical strength.
Quoted Values vs. Application Reality
The published COF for PTFE can range from 0.02 to 0.2. This variation depends heavily on the specific test method, pressure, velocity, and surface preparation. The commonly cited value of 0.04 is a reliable benchmark for well-designed dynamic applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use a PTFE seal often comes down to specific operational demands where friction is a primary concern.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy loss and wear: PTFE is the benchmark choice, significantly outperforming elastomers like rubber or other plastics like nylon.
- If your application involves dry running or intermittent lubrication: The self-lubricating properties of PTFE make it one of the only truly viable options for long-term reliability.
- If you need reliable startup after long periods of inactivity: PTFE's low static friction prevents the stick-slip phenomena that can damage other types of seals and shafts.
Ultimately, the unique low-friction nature of PTFE seals allows for more robust, efficient, and reliable mechanical designs.
Summary Table:
| Friction Characteristic | PTFE Seal Value | Key Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction (COF) | 0.04 - 0.08 | Minimal energy loss and wear |
| Static Friction | Very Low | Prevents stick-slip, clean startup |
| Self-Lubricating | Yes | Operates in dry or low-lubrication environments |
| Temperature Resistance | Up to 260°C (500°F) | Stable performance in high-heat applications |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Friction Properties for Your Application
PTFE's uniquely low coefficient of friction is a game-changer for reliability and efficiency in demanding environments. Whether your industry is semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial, KINTEK's precision PTFE components—including custom seals, liners, and labware—are engineered to deliver unmatched performance.
We specialize in custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your seals are optimized for low friction, chemical resistance, and long service life.
Ready to solve your toughest sealing challenges? Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific needs and discover how our PTFE expertise can benefit your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE Teflon washers suitable for electrical applications? Superior Insulation for Harsh Environments
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What temperature range can PTFE seals and rings operate within? Withstand -200°C to +260°C Extremes
- What is the overall function of PTFE bushes in mechanical systems? Achieve Low-Friction, Maintenance-Free Operation
- What makes PTFE suitable for custom industrial parts? Discover the Ideal Material for Harsh Environments
- Are the specifications of PTFE bushings customizable? Get a Tailored Solution for Your Application
- What makes PTFE envelope gaskets resistant to contamination? The Key to Process Purity and Chemical Inertness
- What are the differences between virgin PTFE and mechanical PTFE? Select the Right Grade for Your Application



















