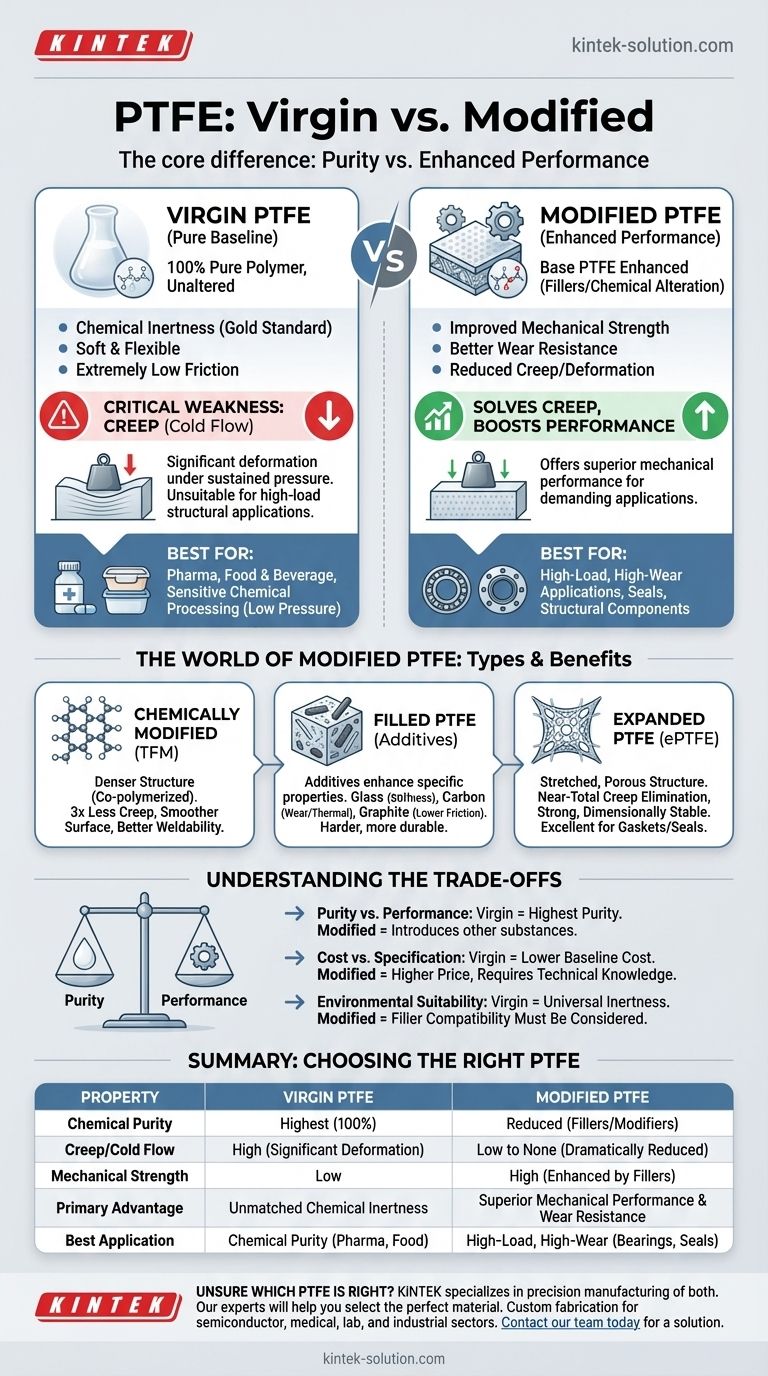
At its core, the difference is simple: virgin PTFE is the pure, chemically unaltered polymer, prized for its exceptional chemical inertness. Modified PTFE is a broad category of materials where the base PTFE is enhanced—either by adding fillers or by slightly altering its chemical structure during production—to improve specific properties like mechanical strength, wear resistance, and resistance to deformation.
While virgin PTFE is the gold standard for chemical purity, its primary drawback is "creep," or the tendency to deform under sustained pressure. Modified PTFE variants were developed specifically to solve this problem, offering superior mechanical performance for demanding applications.

Understanding Virgin PTFE: The Pure Baseline
Defining Characteristics
Virgin Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is 100% pure polymer. It is known for its signature white color, soft and flexible texture, and extremely low coefficient of friction.
It contains no additives or fillers, making it the most chemically pure version of the material available.
Core Strengths
The primary advantage of virgin PTFE is its unmatched chemical resistance across a very wide temperature range. It is almost completely inert, making it the material of choice for applications in the pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and sensitive chemical processing industries.
The Critical Weakness: Creep
The most significant limitation of virgin PTFE is its tendency to creep, also known as cold flow. When subjected to a sustained load, especially at elevated temperatures, the material will slowly deform and move away from the pressure point.
This makes it unsuitable for many structural or high-pressure sealing applications, as components can lose their shape and fail over time.
The World of Modified PTFE: Enhancing the Original
Modified PTFE is not a single material but a family of materials designed to overcome the weaknesses of virgin PTFE. The modifications fall into two main categories: chemical alteration and the addition of fillers.
Chemically Modified PTFE (TFM)
This version is created by co-polymerizing PTFE with a very small amount (typically less than 1%) of a modifier, such as perfluoropropylvinylether. This subtle chemical change results in a denser molecular structure.
This denser structure yields significant benefits, including a threefold reduction in creep, smoother machined surfaces, improved weldability, and higher dielectric strength for better electrical insulation.
Filled PTFE
In this approach, additives or "fillers" are physically blended with the PTFE resin before it is processed. These fillers directly enhance specific mechanical properties.
Common fillers include glass fibers to increase stiffness and compressive strength, carbon to improve wear resistance and thermal conductivity, and graphite to lower the coefficient of friction. Filled grades are much harder and more durable than virgin PTFE.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
This unique material is still 100% pure PTFE but has been physically processed by stretching it in multiple directions. This process creates a porous, fibrous structure that is incredibly strong and dimensionally stable.
The key benefit of ePTFE is the near-total elimination of creep while maintaining the chemical purity of virgin PTFE. This makes it an exceptional material for gaskets and seals, particularly in demanding chemical plant flanges.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between virgin and modified PTFE requires a clear understanding of the compromises involved. The "best" material is entirely dependent on the application.
Purity vs. Performance
The central trade-off is chemical purity versus mechanical performance. Virgin PTFE offers the highest purity. Any modification, whether a chemical co-polymer or a physical filler, introduces another substance into the material.
For ultra-high purity applications, such as in semiconductor manufacturing, this may be unacceptable. However, for a mechanical component like a bearing, the enhanced wear resistance of a filled PTFE is far more important.
Cost and Specification
Virgin PTFE is often seen as the baseline material and can be less expensive. Modified grades are specialized products that command a higher price.
Furthermore, specifying the correct modified PTFE requires a deeper level of technical knowledge. Choosing the right filler or chemical modification is critical to achieving the desired performance enhancement.
Environmental Suitability
While all PTFE variants have excellent chemical resistance, the fillers in filled PTFE may not share the same level of near-universal inertness as the base polymer. The compatibility of the filler material must also be considered for the specific chemical environment.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be driven entirely by the specific demands of your project. Each type of PTFE is a tool engineered for a different job.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and inertness: Choose virgin PTFE, especially for low-pressure, low-load applications in the food, beverage, or pharmaceutical sectors.
- If you need to prevent deformation under load while maintaining high purity: Choose a chemically modified PTFE (like TFM) for its dramatically reduced creep and smoother, less porous surface.
- If your application involves high wear, friction, or mechanical load: Choose a filled PTFE with a filler (like glass or carbon) specifically suited to increase hardness and durability for parts like bearings or wear rings.
- If you require a reliable, leak-free seal in a high-pressure flange: Choose expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its ability to conform and seal perfectly without creeping over time.
By understanding these fundamental differences, you can select the precise material engineered to solve your specific challenge.
Summary Table:
| Property | Virgin PTFE | Modified PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Purity | Highest (100% pure) | Reduced (contains fillers/modifiers) |
| Creep/Cold Flow | High (significant deformation) | Low to None (dramatically reduced) |
| Mechanical Strength | Low | High (enhanced by fillers) |
| Primary Advantage | Unmatched chemical inertness | Superior mechanical performance & wear resistance |
| Best For | Chemical purity applications (pharma, food) | High-load, high-wear applications (bearings, seals) |
Unsure which PTFE is right for your project?
KINTEK specializes in precision manufacturing of both virgin and modified PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware. Whether you require the ultimate chemical purity of virgin PTFE or the enhanced mechanical properties of a modified grade, our experts will help you select the perfect material.
We provide custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let's engineer a solution for you. Contact our team today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the chemical composition of Teflon? The Science Behind Its Non-Stick Properties
- What was the key finding about Teflon's friction mechanism? Unlocking the Secret of Its Self-Lubricating Slipperiness
- Why is PTFE suitable for electrical applications? Discover Its Superior Insulating Properties
- How is Teflon classified in terms of plastic types? A Guide to Thermoplastic Fluoropolymers
- How does Teflon improve the cooking process? Achieve Effortless, Non-Stick Cooking
- Why is PTFE considered an excellent electrical insulator? Discover Its Elite Electrical Properties
- How does PTFE react to hydrogen peroxide? Discover Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What are the friction and surface properties of PTFE? Discover the Science Behind Its Low Friction & Non-Stick Performance



















