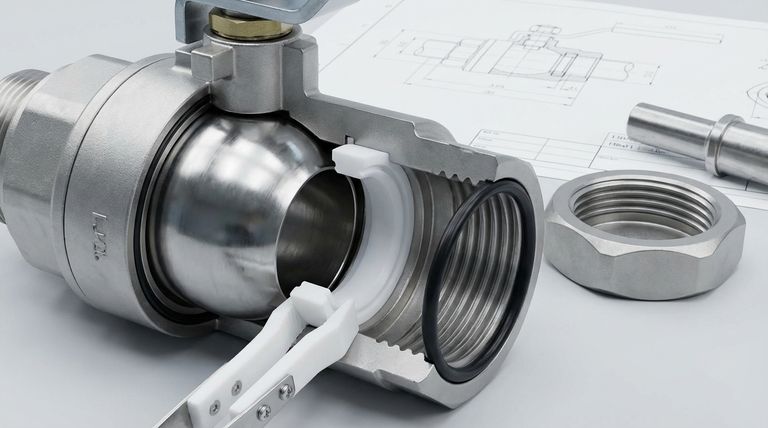
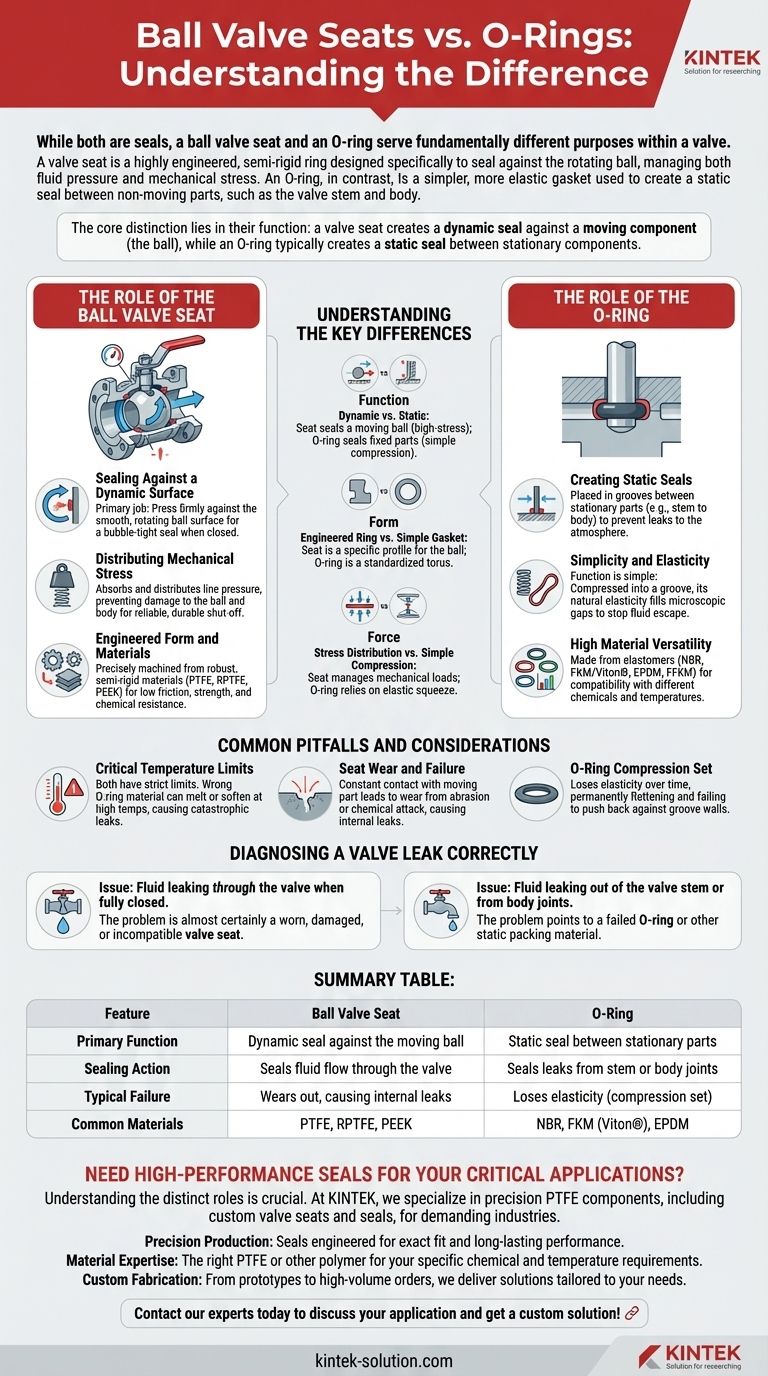
While both are seals, a ball valve seat and an O-ring serve fundamentally different purposes within a valve. A valve seat is a highly engineered, semi-rigid ring designed specifically to seal against the rotating ball, managing both fluid pressure and mechanical stress. An O-ring, in contrast, is a simpler, more elastic gasket used to create a static seal between non-moving parts, such as the valve stem and body.
The core distinction lies in their function: a valve seat creates a dynamic seal against a moving component (the ball), while an O-ring typically creates a static seal between stationary components.

The Role of the Ball Valve Seat
The seat is a critical component responsible for the primary shut-off function of the ball valve. It is not just a simple gasket; it's a structural seal.
Sealing Against a Dynamic Surface
The primary job of the valve seat is to press firmly against the smooth, rotating surface of the ball. It must deform just enough to create a perfect, bubble-tight seal when the valve is in the closed position, stopping the flow of media.
Distributing Mechanical Stress
When the valve is closed, the seat absorbs and distributes the force from the line pressure pushing against the ball. This prevents damage to the ball and valve body, ensuring a reliable and durable shut-off over thousands of cycles.
Engineered Form and Materials
Seats are precisely machined from robust, semi-rigid materials like PTFE (Teflon), RPTFE, or PEEK. These materials offer low friction for smooth valve operation while being strong enough to resist wear and chemical attack.
The Role of the O-Ring
O-rings are one of the most common types of seals in engineering, used for their simplicity and effectiveness in static applications.
Creating Static Seals
In a ball valve, O-rings are not used to seal against the ball itself. Instead, they are placed in grooves between stationary parts, such as sealing the valve stem to prevent leaks to the atmosphere or sealing the two halves of a valve body.
Simplicity and Elasticity
An O-ring's function is straightforward: it is compressed into a groove between two surfaces. Its natural elasticity causes it to push outward, filling the microscopic gap and preventing fluid from escaping.
High Material Versatility
O-rings are made from a wide range of elastomers like NBR, FKM (Viton®), EPDM, and FFKM. This allows them to be selected for specific compatibility with different chemicals and operating temperatures.
Understanding the Key Differences
The distinct roles of seats and O-rings dictate their design, material, and how they fail. Confusing them can lead to incorrect maintenance and troubleshooting.
Function: Dynamic vs. Static
This is the most critical difference. A seat is designed for the high-stress, dynamic environment of sealing a moving ball. An O-ring is designed for the simpler task of sealing two parts that are fixed together.
Form: Engineered Ring vs. Simple Gasket
A valve seat is an engineered component with a specific profile designed to match the ball. An O-ring is a simple, standardized torus (donut shape) designed to be compressed in a groove.
Force: Stress Distribution vs. Simple Compression
The seat must manage significant mechanical loads from the valve's operation. An O-ring works entirely by being squeezed, relying on its elastic properties to maintain a seal.
Common Pitfalls and Considerations
Choosing the right components and understanding their limitations is key to valve longevity.
Critical Temperature Limits
As with any seal, both seats and O-rings have strict temperature limits. An O-ring made of the wrong material can soften or melt at high temperatures, causing a catastrophic leak from the stem or body.
Seat Wear and Failure
Because it is in constant contact with a moving part, the seat is a primary wear item. Over time, abrasion or chemical attack can erode the seat, causing the valve to "pass" or leak fluid even when fully closed.
O-Ring Compression Set
Over time and with exposure to temperature cycles, an O-ring can lose its elasticity and become permanently flattened. This "compression set" means it no longer pushes back against the groove walls, allowing a static leak to develop.
Diagnosing a Valve Leak Correctly
Understanding the difference between these components empowers you to troubleshoot valve issues effectively.
- If your primary issue is fluid leaking through the valve when it is fully closed: The problem is almost certainly a worn, damaged, or incompatible valve seat.
- If your primary issue is fluid leaking out of the valve stem or from body joints: The problem points to a failed O-ring or other static packing material.
Knowing where to look is the first step toward a fast and effective repair.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ball Valve Seat | O-Ring |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Function | Dynamic seal against the moving ball | Static seal between stationary parts |
| Sealing Action | Seals fluid flow through the valve | Seals leaks from stem or body joints |
| Typical Failure | Wears out, causing internal leaks | Loses elasticity (compression set) |
| Common Materials | PTFE, RPTFE, PEEK | NBR, FKM (Viton®), EPDM |
Need High-Performance Seals for Your Critical Applications?
Understanding the distinct roles of valve seats and O-rings is crucial for reliability. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom valve seats and seals, for demanding industries like semiconductor, medical, and laboratory.
We ensure:
- Precision Production: Seals engineered for exact fit and long-lasting performance.
- Material Expertise: The right PTFE or other polymer for your specific chemical and temperature requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we deliver solutions tailored to your needs.
Don't let a seal failure compromise your operations. Contact our experts today to discuss your application and get a custom solution!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE and Nitrile Diaphragm Pump Components for Demanding Applications
People Also Ask
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the main advantages of using PTFE parts in industrial applications? Unlock Unmatched Chemical Resistance and Reliability
- Why is PTFE rod suitable for automotive applications? Boost Vehicle Performance & Durability
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications



















