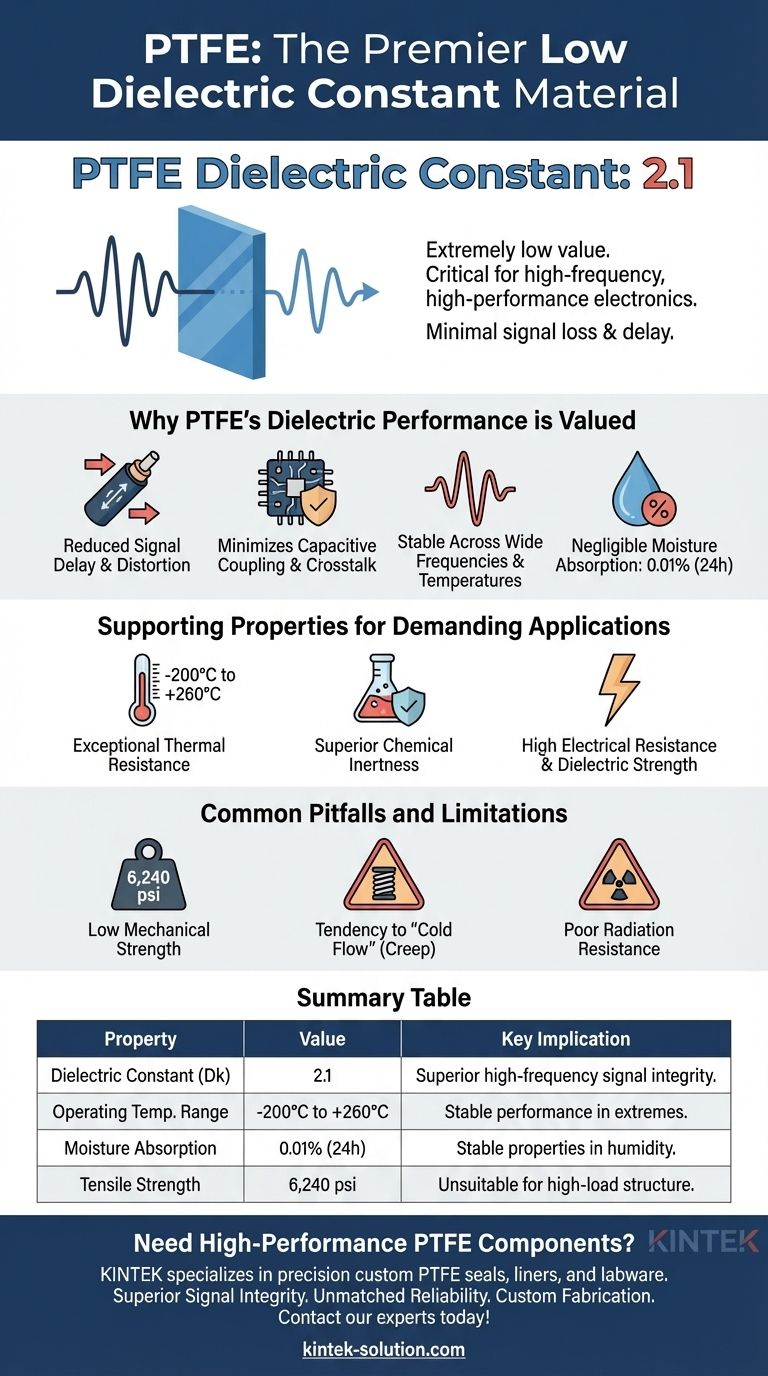
In short, the dielectric constant of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is 2.1. This extremely low value is one of its most defining electrical properties, making it a premier material for high-frequency and high-performance electronic applications where signal integrity and minimal energy loss are critical.
The true value of PTFE is not just its low dielectric constant, but its remarkable ability to maintain this excellent electrical performance across an exceptionally wide range of temperatures, frequencies, and harsh chemical environments.

Why PTFE's Dielectric Performance is So Valued
A material's dielectric constant measures its ability to store electrical energy in an electric field. For insulation and high-frequency circuit applications, a lower number is almost always better.
The Impact of a Low Dielectric Constant
A low dielectric constant of 2.1 allows signals to travel through the material with less delay and distortion. This is essential for high-frequency applications like coaxial cables, microwave circuits, and high-speed data connectors.
It also minimizes the capacitive coupling between conductors, reducing crosstalk and interference in dense electronic circuits. This ensures a cleaner, more reliable signal.
Unmatched Stability Across Frequencies
Critically, PTFE's dielectric constant remains stable from very low frequencies well into the microwave and millimeter-wave bands. This consistency makes it a predictable and reliable insulator for a vast array of radio frequency (RF) systems.
Negligible Moisture Absorption
PTFE absorbs virtually no water, with a specified absorption rate of just 0.01% over 24 hours. This is a crucial supporting property, as moisture absorption can drastically increase a material's dielectric constant and degrade its insulating capabilities.
Supporting Properties for Demanding Electrical Applications
PTFE's elite electrical performance is made practical by its extraordinary physical and chemical resilience.
Exceptional Thermal Resistance
PTFE operates reliably over an enormous temperature range, from -200°C to +260°C. This means its excellent dielectric properties do not degrade in extreme thermal conditions, a failure point for many lesser plastics.
Superior Chemical Inertness
The material is resistant to almost all chemicals, solvents, and corrosive agents. This allows it to be used as an insulator in environments where other materials would quickly fail, protecting the electrical integrity of the system.
High Electrical Resistance
Beyond its low dielectric constant, PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with very high dielectric strength. This allows it to prevent electrical arcing and withstand high voltages without breaking down.
Common Pitfalls and Limitations
While its electrical performance is superb, PTFE is not the solution for every engineering problem. Its mechanical properties present notable trade-offs.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material with low tensile strength (6,240 psi) compared to engineering plastics. It is not suitable for applications requiring high structural rigidity or load-bearing capability.
Tendency to "Cold Flow"
The material can deform or "creep" over time when subjected to a constant compressive load, especially at elevated temperatures. This can be a problem in applications that require tight, long-term dimensional stability under pressure.
Poor Radiation Resistance
PTFE is known to degrade when exposed to high-energy radiation, like gamma rays or electron beams. The polymer chains break down, causing the material to become brittle and lose its mechanical properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use these guidelines to determine if PTFE is the optimal choice for your project.
- If your primary focus is high-frequency signal integrity: PTFE is a top-tier choice due to its exceptionally low and stable dielectric constant.
- If your component will operate in extreme temperatures or harsh chemical environments: PTFE's unparalleled resistance makes it one of the most reliable insulators available.
- If your application requires high mechanical strength or structural rigidity: You should consider a different material or look into filled/reinforced grades of PTFE.
- If the component will be exposed to significant radiation: Avoid using standard PTFE, as its properties will degrade rapidly.
Ultimately, selecting PTFE is a decision to prioritize elite electrical insulation and environmental stability above all else.
Summary Table:
| Property | Value | Key Implication |
|---|---|---|
| Dielectric Constant (Dk) | 2.1 | Superior high-frequency signal integrity with minimal loss and delay. |
| Operating Temperature Range | -200°C to +260°C | Stable electrical performance in extreme thermal environments. |
| Moisture Absorption | 0.01% (24h) | Dielectric properties remain stable in humid conditions. |
| Tensile Strength | 6,240 psi | Low mechanical strength; unsuitable for high-load structural parts. |
Need High-Performance PTFE Components?
Leverage PTFE's exceptional dielectric properties for your most demanding applications. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE components—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver:
- Superior Signal Integrity: Components that maintain the low dielectric constant (2.1) critical for high-frequency and high-speed electronics.
- Unmatched Reliability: Parts that perform consistently across extreme temperatures and harsh chemical environments.
- Custom Fabrication: From initial prototypes to high-volume production runs, tailored to your exact specifications.
Enhance your product's performance and reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your PTFE component needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What makes PTFE an ideal material for corrosion-resistant applications? Unmatched Chemical Inertness for Harsh Environments
- Why is PTFE resistant to corrosion? Discover the Secret to Unmatched Chemical Inertness
- Why is PTFE considered an ideal substitute for other plastics in high-temperature applications? Superior Thermal Stability & Performance
- What makes Teflon suitable for electret manufacturing? Achieve Unmatched Charge Stability for Your Devices
- How is graphite packing made? Discover the Braiding Process for Superior Seals
- Why is PTFE compliance with USDA and FDA standards important? Ensure Safety in Food, Pharma & Medical
- What temperature range can Teflon withstand? From Cryogenic -328°F to High Heat 500°F
- Why is PTFE a good choice for UV resistance? Its molecular structure provides inherent, lasting protection.



















