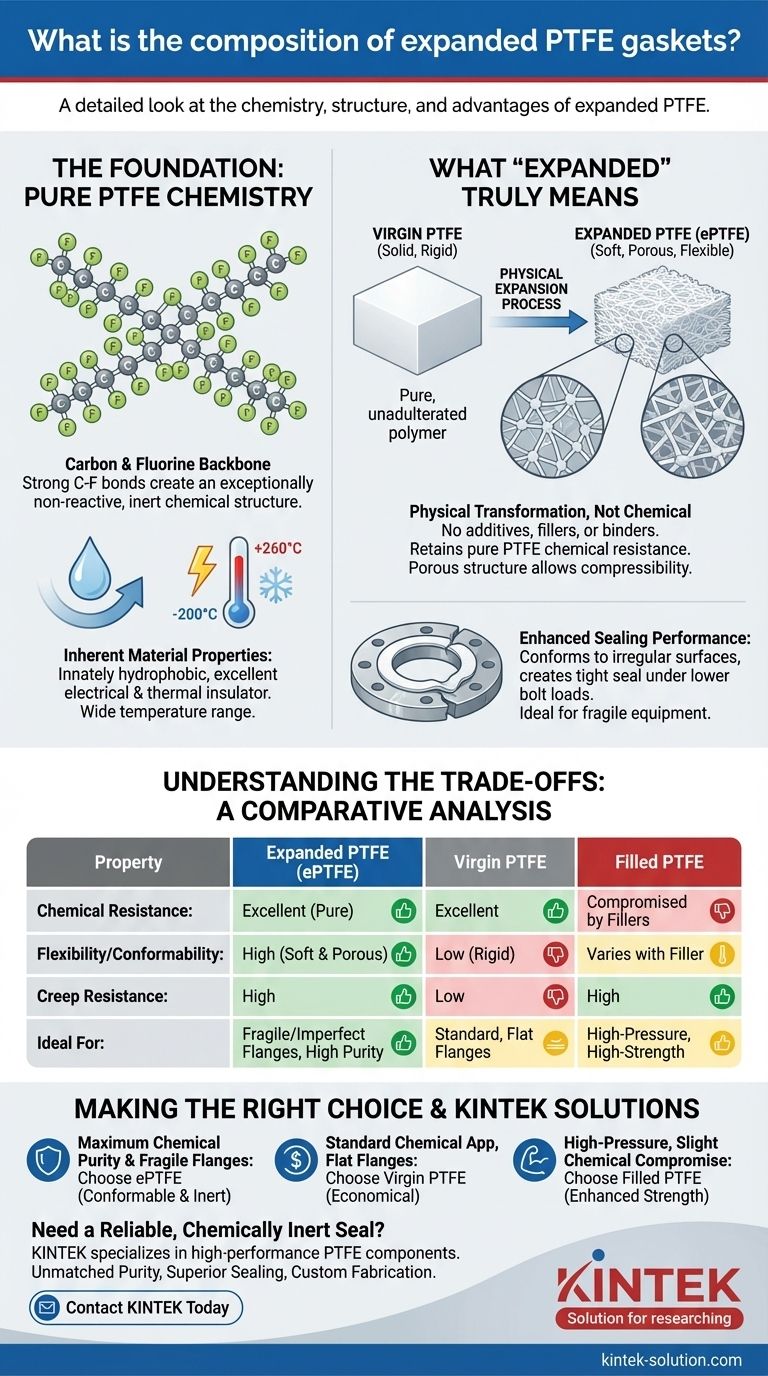
Expanded PTFE gaskets are composed of a pure synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene. This material consists entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms, creating a simple yet incredibly robust chemical structure. This composition is the foundation for its exceptional performance characteristics in demanding industrial environments.
The critical takeaway is not just the chemical makeup, but the physical structure. Expanded PTFE is pure, virgin PTFE that has been physically processed to create a soft, porous, and highly conformable material without using any additives, retaining its unparalleled chemical resistance.

The Foundation: Pure PTFE Chemistry
The unique properties of expanded PTFE (ePTFE) begin with its fundamental chemical composition. This simple structure is responsible for its high-performance characteristics.
A Carbon and Fluorine Backbone
Expanded PTFE consists solely of carbon and fluorine. The carbon atoms form a long chain, which is completely saturated by strong bonds with fluorine atoms.
The Source of Chemical Inertness
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This makes the material exceptionally non-reactive. It is unaffected by nearly all corrosive liquids, vapors, and gases.
Inherent Material Properties
This pure composition makes expanded PTFE innately hydrophobic, meaning it repels water. It is also an excellent electrical and thermal insulator, capable of performing from cryogenic temperatures up to +260°C (+500°F).
What "Expanded" Truly Means
The term "expanded" refers to a specialized manufacturing process that transforms the material's physical structure, giving it significant advantages over standard PTFE.
From Solid to Porous
The process takes pure, virgin PTFE and stretches it. This creates a porous, fibrous structure that is incredibly soft, flexible, and compressible, unlike the rigid nature of standard PTFE.
Maintaining Chemical Purity
Crucially, this expansion is a physical transformation, not a chemical one. No additives, fillers, or binders are introduced. The resulting gasket material retains the exact same chemical resistance as pure virgin PTFE.
Enhanced Sealing Performance
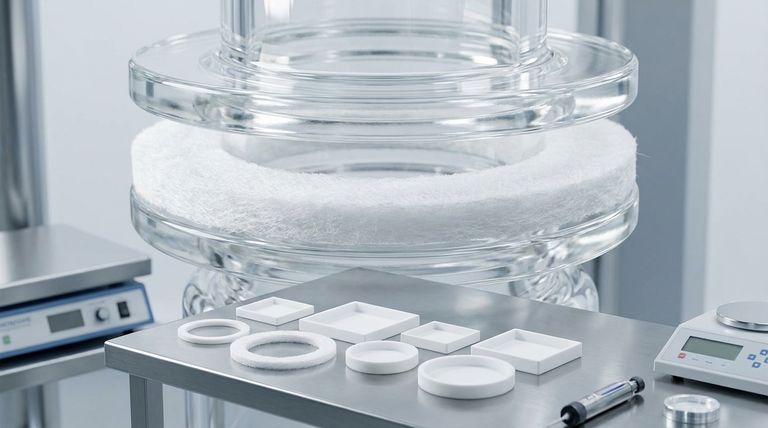
This soft, porous structure allows the gasket to conform easily to irregular or damaged flange surfaces. It creates a tight seal under lower bolt loads, which is ideal for fragile equipment made of glass, plastic, or ceramic.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While expanded PTFE offers superior performance in many areas, it's essential to understand its context relative to other PTFE gasket types.
Comparison to Virgin PTFE
Virgin PTFE is the raw, unadulterated polymer. It is cost-effective and has excellent chemical and electrical properties, but it is much more rigid and prone to creep (cold flow) under pressure. Expanded PTFE is far more flexible and creep-resistant.
Comparison to Filled PTFE
Filled PTFE gaskets include additives like glass, silica, or carbon to improve mechanical properties like strength or creep resistance. However, these fillers compromise the gasket's chemical purity and can limit its use in certain applications. Expanded PTFE offers creep resistance while maintaining absolute chemical inertness.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket material depends entirely on the demands of your specific sealing environment.
- If your primary focus is maximum chemical purity and sealing on imperfect or fragile flanges: Expanded PTFE is the ideal choice due to its conformability and chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is a low-cost seal for a standard chemical application with perfectly flat, rigid flanges: Virgin PTFE may be a sufficient and economical option.
- If your primary focus is enhanced mechanical strength for a high-pressure system where slight chemical compromises are acceptable: A filled PTFE gasket with a specific additive may be required.
Ultimately, choosing expanded PTFE is a decision for superior sealing reliability and chemical purity, especially in demanding or imperfect conditions.
Summary Table:
| Property | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE) | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Pure) | Excellent | Compromised by Fillers |
| Flexibility/Conformability | High (Soft & Porous) | Low (Rigid) | Varies with Filler |
| Creep Resistance | High | Low | High |
| Ideal For | Fragile/Imperfect Flanges, High Purity | Standard, Flat Flanges | High-Pressure, High-Strength |
Need a Reliable, Chemically Inert Seal?
For semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications where failure is not an option, the right gasket material is critical. KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components, including expanded PTFE gaskets.
We offer:
- Unmatched Chemical Purity: Our ePTFE gaskets are made from 100% virgin PTFE, ensuring maximum resistance to corrosive chemicals.
- Superior Sealing Performance: The expanded structure provides excellent conformability for leak-tight seals on uneven or fragile surfaces.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, we tailor solutions to your exact specifications.
Enhance the reliability of your equipment. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your sealing challenges and get a quote for custom PTFE components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What role do Teflon rods play in the electrical and electronics industry? Ensure Superior Insulation and Reliability
- What are the key considerations when designing a PTFE PCB? Master High-Frequency Performance
- What are the key characteristics of PTFE PCB material? Superior Performance for Harsh Environments
- What is PTFE commonly known as and why is it used for gaskets? | Superior Sealing Solutions
- Why is PTFE an excellent material for coating machine parts? Achieve Superior Performance & Durability
- What are the common applications of PTFE oil seals? Master Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What are the key features and benefits of PTFE envelope gaskets? Achieve Superior Sealing in Corrosive Environments
- Why are PTFE sheets used in the medical industry? For Biocompatibility, Inertness & Low Friction



















