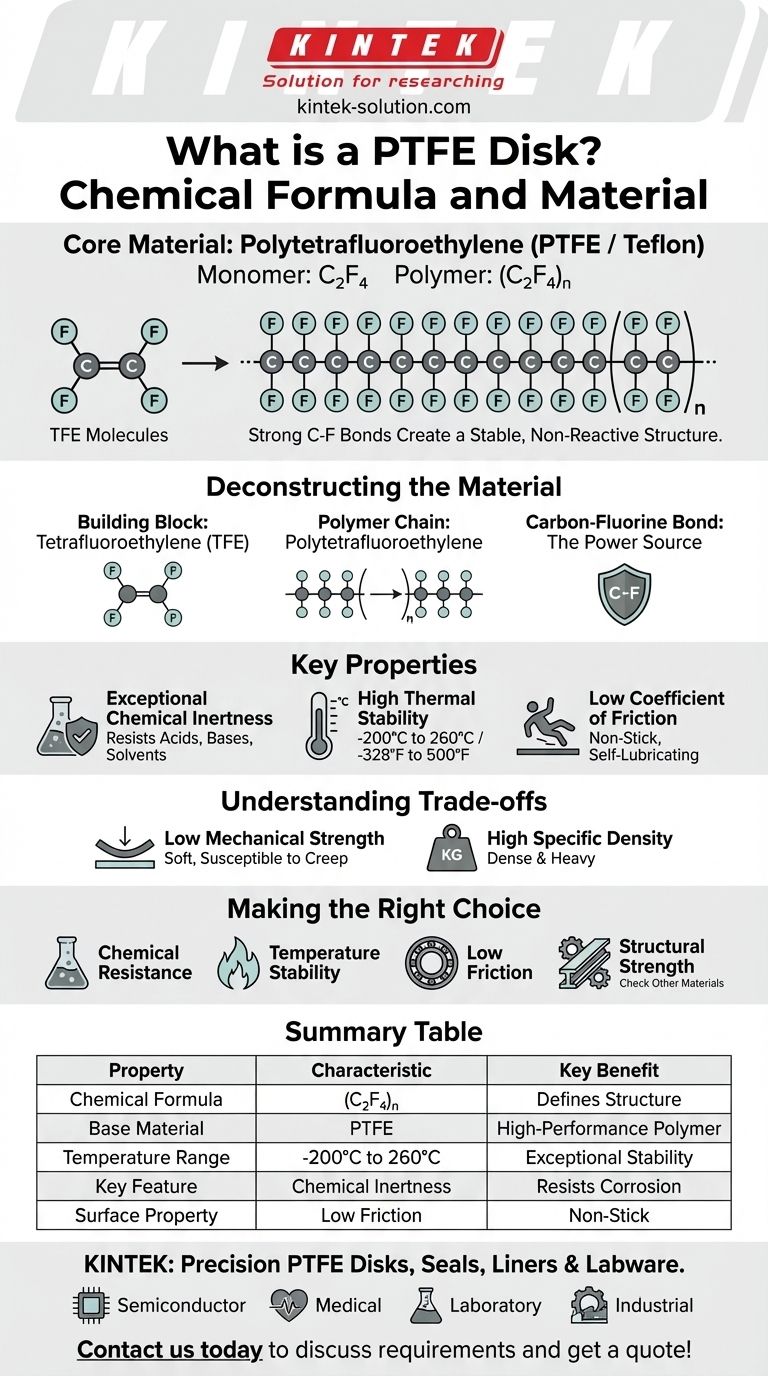
At its core, a PTFE Disk is made of a high-performance synthetic polymer called Polytetrafluoroethylene. Its common trade name is Teflon. The empirical chemical formula for the repeating monomer unit that forms this polymer is C₂F₄, which links together in long chains represented as (C₂F₄)n.
PTFE's remarkable properties, including extreme chemical resistance and a non-stick surface, are a direct result of the incredibly strong bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms, which create a stable and non-reactive molecular structure.

Deconstructing the Material: From Molecule to Polymer
To truly understand a PTFE disk, we must look at how it's built from the molecular level up. The name itself, Poly-tetra-fluoro-ethylene, tells the whole story.
The Building Block: Tetrafluoroethylene (TFE)
The foundation of PTFE is a simple gas molecule called tetrafluoroethylene (TFE). This molecule consists of two carbon atoms double-bonded to each other, with four fluorine atoms attached.
The Polymer Chain: Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE)
The "Poly" prefix simply means "many." During manufacturing, countless TFE molecules are linked together in a process called polymerization to form extremely long, stable chains. This creates the solid material we know as PTFE.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond: The Source of Its Power
The secret to PTFE's unique characteristics lies in the carbon-fluorine (C-F) bond. This is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
The fluorine atoms are large and form a tight, protective, and non-reactive "sheath" around the carbon backbone of the polymer chain. This molecular armor is what gives the material its definitive properties.
Key Properties and Why They Matter
The unique molecular structure of PTFE translates directly into valuable real-world performance characteristics that make it suitable for demanding applications.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
Because the fluorine sheath protects the vulnerable carbon backbone so effectively, very few chemicals can attack or react with PTFE. It is resistant to almost all acids, bases, and solvents.
High Thermal Stability
The immense strength of the C-F bonds requires a great deal of energy to break. This allows PTFE to remain stable across an exceptionally wide temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Low Coefficient of Friction
The fluorine sheath is not only protective but also very "low energy." It doesn't attract other molecules, which is why almost nothing sticks to it. This results in an extremely low coefficient of friction, making it one of the most slippery materials known.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While PTFE excels in chemical and thermal stability, it is essential to understand its mechanical limitations.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. Compared to other engineering plastics, it has low tensile strength and is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can deform over time under a constant load.
High Specific Density
PTFE is also quite dense and heavy compared to many other polymers. This can be a consideration in applications where weight is a critical factor.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right material depends entirely on the demands of your application. Here is how to decide if a PTFE disk is the correct choice.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is an almost unparalleled choice for seals, gaskets, or containers handling corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is temperature stability: Its performance in both high-heat and cryogenic environments makes it ideal for extreme applications.
- If your primary focus is low friction: Its non-stick, self-lubricating surface is perfect for creating low-wear bearings, slide plates, or non-stick linings.
- If your primary focus is structural strength: You may need to consider a different material or a composite version (like a glass-filled PTFE) to meet mechanical requirements.
Ultimately, understanding the molecular structure of PTFE is the key to leveraging its powerful and unique properties for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Characteristic | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Formula | (C₂F₄)n | Defines the polymer structure |
| Base Material | Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) | High-performance synthetic polymer |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to 260°C | Exceptional thermal stability |
| Key Feature | Extreme chemical inertness | Resists acids, bases, and solvents |
| Surface Property | Very low coefficient of friction | Non-stick, self-lubricating surface |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE disks, seals, liners, and labware for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial applications. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get components that deliver superior chemical resistance, thermal stability, and non-stick performance.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the general conclusions about PTFE and PEEK for ball valve seats? PTFE vs. PEEK for Valve Performance
- What are the benefits of different spring types used in PTFE seals? Optimize Sealing Performance & Lifespan
- How does PTFE's soft nature affect surface finish quality during machining? Mastering the Slice, Not Tear, Process
- What are the main disadvantages of machining Teflon/PTFE? Navigating Material Instability for Precision Parts
- What are the benefits of PTFE spring-energized seals? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resilience for Harsh Environments
- Why are PTFE washers advantageous in mechanical assemblies? Enhance Performance & Durability
- What support is available for selecting the right PTFE valve design and size? Get Expert Guidance for Your Application
- Why are PTFE expansion bellows considered versatile in technology? Mastering Chemical, Thermal, and Mechanical Challenges



















