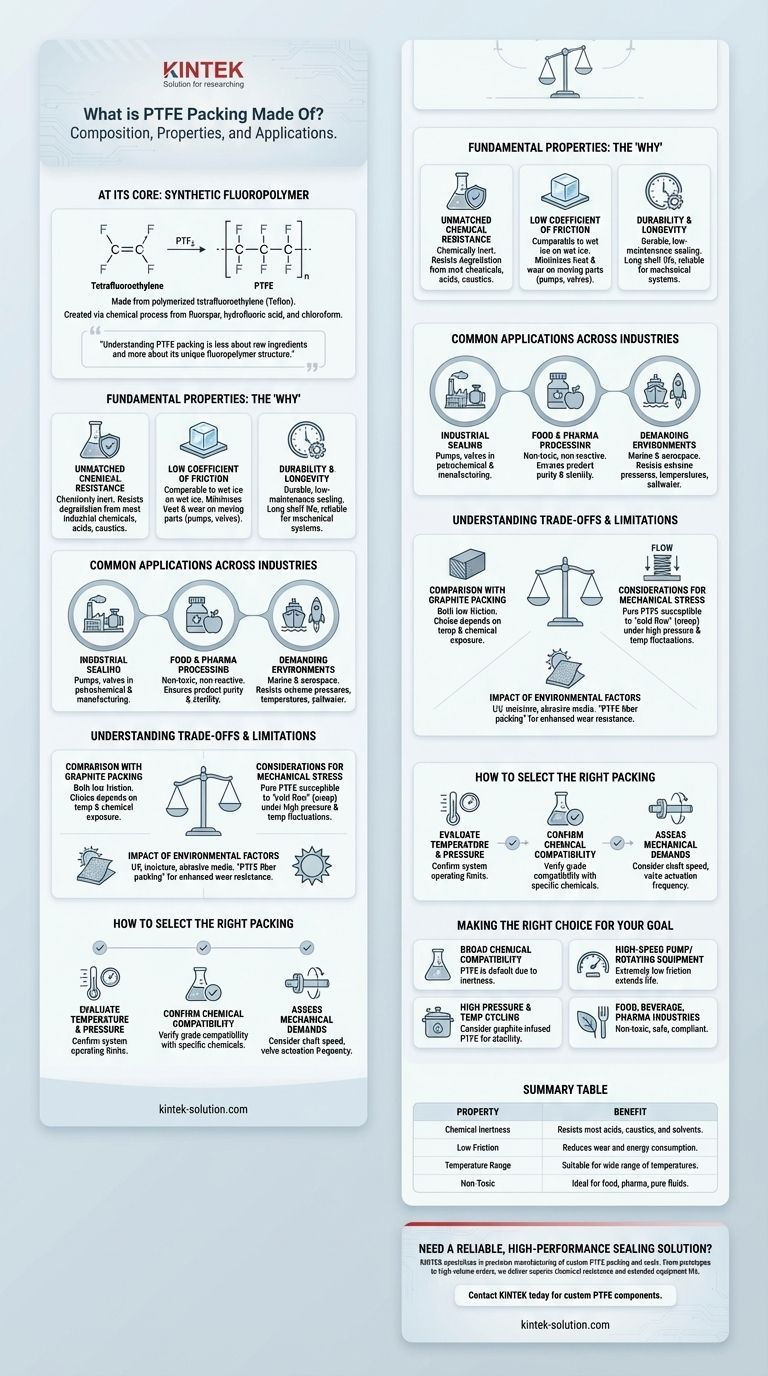
At its core, PTFE packing is made from a synthetic fluoropolymer of tetrafluoroethylene, a material widely known by its brand name, Teflon. This material is created by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene gas, which is synthesized from raw ingredients including fluorspar, hydrofluoric acid, and chloroform in a specialized chemical process.
Understanding what PTFE packing is made of is less about the raw ingredients and more about its resulting properties. Its unique fluoropolymer structure grants it exceptional chemical resistance and a low-friction surface, making it a premier choice for demanding industrial sealing applications.

The Fundamental Properties of PTFE
The molecular structure of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is directly responsible for the high-performance characteristics that make it so valuable as a packing and sealing material.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is famous for being chemically inert. It resists degradation from the vast majority of industrial chemicals, acids, and caustics.
This makes it an ideal choice for equipment in chemical processing plants, such as reactors and mixers, where exposure to corrosive substances is constant.
However, certain highly aggressive substances may require specialized blends, such as PTFE graphite packing, to ensure complete compatibility.
Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, comparable to wet ice on wet ice.
In applications like pumps and valves, this property is critical. It minimizes heat generation from friction, reduces operational energy requirements, and significantly lessens wear on moving parts like shafts and stems.
Durability and Longevity
Braided PTFE packing is a durable, low-maintenance sealing solution. It does not degrade easily and has a long shelf life, making it a reliable and cost-effective choice for many mechanical systems.
Common Applications Across Industries
The unique properties of PTFE make it a versatile solution used in a wide range of critical sectors.
Industrial Sealing
PTFE packing is a workhorse in general industry for sealing pumps, valves, and other mechanical equipment in petrochemical plants and manufacturing facilities.
Food and Pharmaceutical Processing
Because PTFE is non-toxic and non-reactive, it is widely used in the food, beverage, and pharmaceutical industries. It ensures that the sealing material does not contaminate the product, which is essential for maintaining sterile and pure conditions.
Demanding Environments
In marine and aerospace applications, equipment faces extreme pressures, temperatures, and corrosive elements like saltwater. PTFE's resilience makes it a trusted material for sealing in these harsh conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While highly effective, PTFE is not a universal solution. Understanding its operational limits and how it compares to alternatives is key to proper application.
Comparison with Graphite Packing
Graphite is another popular packing material. Both PTFE and graphite packing are often braided, have low friction, and serve as excellent, durable sealants. The choice between them often depends on specific temperature and chemical exposure requirements.
Considerations for Mechanical Stress
Pure PTFE can be susceptible to "cold flow," or creep, under high mechanical pressure, especially when combined with temperature fluctuations. This is a critical factor to evaluate when selecting packing for high-pressure systems.
Impact of Environmental Factors
External conditions like UV light, moisture, and abrasive media must be considered. For applications involving slurries or abrasive materials, specialized versions like PTFE fiber packing are often selected for their enhanced ability to handle wear.
How to Select the Right Packing for Your Application
To ensure optimal performance and safety, you must evaluate several key factors based on your specific operational environment.
Evaluate Temperature and Pressure
Confirm that your system's operating temperatures and pressures fall within the specified limits of the PTFE packing. This is the first and most important step to prevent seal failure.
Confirm Chemical Compatibility
While PTFE is resistant to most chemicals, always verify that the specific grade of packing is compatible with the type and concentration of chemicals it will be exposed to.
Assess Mechanical Demands
Consider the dynamic forces on the packing, such as shaft speed in a pump or the actuation frequency of a valve. These mechanical stresses will influence the longevity and effectiveness of the seal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Ultimately, the right choice depends on your primary objective for the sealing application.
- If your primary focus is broad chemical compatibility: PTFE packing is often the default choice due to its inertness against the majority of industrial chemicals.
- If you are sealing a high-speed pump or rotating equipment: The extremely low friction of PTFE minimizes heat generation and wear, extending equipment life.
- If your application involves high pressure and temperature cycling: You may need to consider specialized variants like graphite-infused PTFE to mitigate cold flow and improve thermal stability.
- If you operate in food, beverage, or pharmaceutical industries: The non-toxic and non-reactive properties of PTFE make it a safe and compliant sealing solution.
By understanding its core composition and operational limits, you can confidently specify the right sealing solution for your system.
Summary Table:
| Property | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists most acids, caustics, and solvents |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear and energy consumption in pumps/valves |
| Temperature Range | Suitable for a wide range of operating temperatures |
| Non-Toxic | Ideal for food, pharmaceutical, and pure fluid applications |
Need a reliable, high-performance sealing solution?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of PTFE components, including custom packing and seals. Whether you're in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sector, we can fabricate the exact solution you need—from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Our expertise ensures you get a seal that delivers superior chemical resistance, reduces maintenance, and extends equipment life.
Contact KINTEB today to discuss your application and get a quote for custom PTFE components.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the limitations of PTFE oil seals, and how are they addressed? Overcome Material Challenges with Engineered Solutions
- What are the main applications of PTFE lined ball valves? Control Corrosive & High-Purity Fluids Safely
- How many variations of PTFE disks are available and what parameters do they differ in? Choose the Right Material for Your Application
- What are the main benefits of using PTFE in cables and wires? Achieve Unmatched Performance in Extreme Environments
- What are some common PTFE-based sealing components and their functions? Discover High-Performance Sealing Solutions
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What are the characteristics of PTFE spherical balls? Key Properties for Demanding Applications
- What are the key features of PTFE bellows? Protect Critical Systems from Chemical & Thermal Stress



















