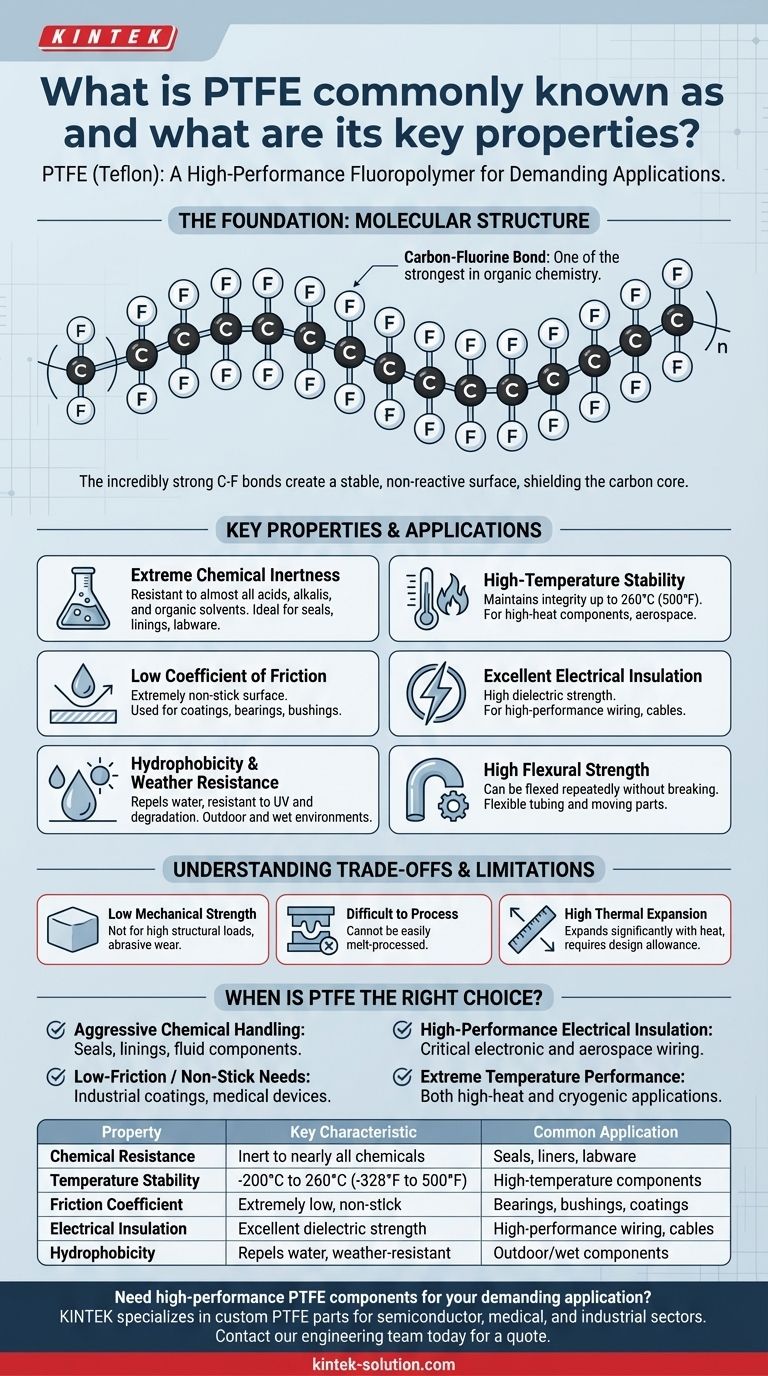
PTFE is the technical name for the material most famously known as Teflon. It is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer, a type of plastic prized for its unique combination of properties, including exceptional chemical inertness, high-temperature stability, and an extremely low coefficient of friction, which makes it incredibly non-stick.
The power of PTFE comes from its molecular structure. The incredibly strong bonds between its carbon and fluorine atoms create a material that is uniquely resistant to heat, chemicals, and friction, making it a "problem-solver" for some of the most demanding engineering challenges.

The Foundation: What Makes PTFE Unique?
PTFE, or polytetrafluoroethylene, is not a naturally occurring material. It is a synthetic polymer created by polymerizing tetrafluoroethylene. Its remarkable characteristics stem directly from its simple but powerful molecular composition.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
At its core, PTFE is a long chain of carbon atoms, but unlike other polymers, each carbon atom is completely shielded by fluorine atoms.
The bond between carbon and fluorine is one of the strongest in organic chemistry. This chemical structure is the source of virtually all of PTFE's famous properties, creating a stable and non-reactive surface.
A Breakdown of PTFE's Key Properties
The unique molecular structure of PTFE gives it a set of high-performance traits that are rarely found together in a single material.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to almost all chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing and laboratory equipment.
High-Temperature Stability
PTFE can withstand a very wide range of temperatures. It maintains its integrity and properties in continuous service at temperatures up to 260°C (500°F) and has a very high melting point of around 327°C (620°F).
Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid material. This is the source of its famous "non-stick" quality, making it invaluable for coatings on cookware as well as for low-friction applications like bearings and bushings.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. It is widely used for insulating high-performance wires and cables, especially in aerospace and computing applications where reliability is critical.
Hydrophobicity and Weather Resistance
The material naturally repels water (it is hydrophobic) and is highly resistant to degradation from UV radiation and weathering. This ensures long-term durability in outdoor or wet environments.
High Flexural Strength
Despite its softness, PTFE can be bent and flexed repeatedly without breaking or losing its structural integrity. This allows it to be used for flexible tubing and components that must endure movement.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While often called the "king of plastics," PTFE is not the solution for every problem. Its unique properties come with practical limitations that are critical to understand.
Relatively Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a soft material. It is not suitable for structural applications that require high tensile strength or resistance to compression and wear from abrasive particles.
Difficult to Process
The same chemical resistance and high melting point that make PTFE so useful also make it difficult to process. It cannot be easily melt-processed or molded using conventional techniques like other plastics.
High Thermal Expansion
PTFE expands and contracts with temperature changes more than many other materials. Engineers must account for this coefficient of thermal expansion in designs where tight tolerances are required.
When is PTFE the Right Choice?
Choosing a material depends entirely on the demands of the application. PTFE excels in specific scenarios where other materials fail.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE's near-total chemical inertness makes it the default choice for seals, linings, and fluid-handling components in corrosive environments.
- If your primary focus is creating a low-friction or non-stick surface: PTFE is unparalleled for applications requiring extreme slipperiness, from industrial coatings to medical devices.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: Its stability at high temperatures and excellent dielectric properties make it ideal for critical electronic and aerospace wiring.
- If your primary focus is performance at extreme temperatures: PTFE maintains its properties in both high-heat and cryogenic applications where most other polymers would degrade or become brittle.
Ultimately, PTFE should be viewed as a specialty material engineered to solve problems in extreme conditions where performance cannot be compromised.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Common Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to nearly all chemicals | Seals, liners, labware |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from cryogenic to 260°C (500°F) | High-temperature components |
| Friction Coefficient | Extremely low, non-stick surface | Bearings, bushings, coatings |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength | High-performance wiring, cables |
| Hydrophobicity | Repels water, weather-resistant | Outdoor and wet environment components |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE parts—including seals, liners, and labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the highest standards for chemical inertness, thermal stability, and reliability.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature resistance of Teflon? Master Its Performance from -200°C to 260°C
- What are the key advantages of PTFE with fillers over pure PTFE? Unlock Superior Mechanical Performance
- What makes PTFE coatings unique in terms of their chemical makeup? The Power of the Carbon-Fluorine Bond
- What are the limitations of silicone gaskets? Key Weaknesses in Strength & Chemical Resistance
- What is the main disadvantage of PTFE? The Challenge of Manufacturing an Elite Material
- What temperature range can Teflon plastic sheets withstand? Unlocking Performance from -200°C to +260°C
- What are the potential causes of color changes in reprocessed PTFE? A Guide to Performance and Purity
- How is Teflon utilized in the electronics industry? Ensuring Signal Integrity and Reliability



















