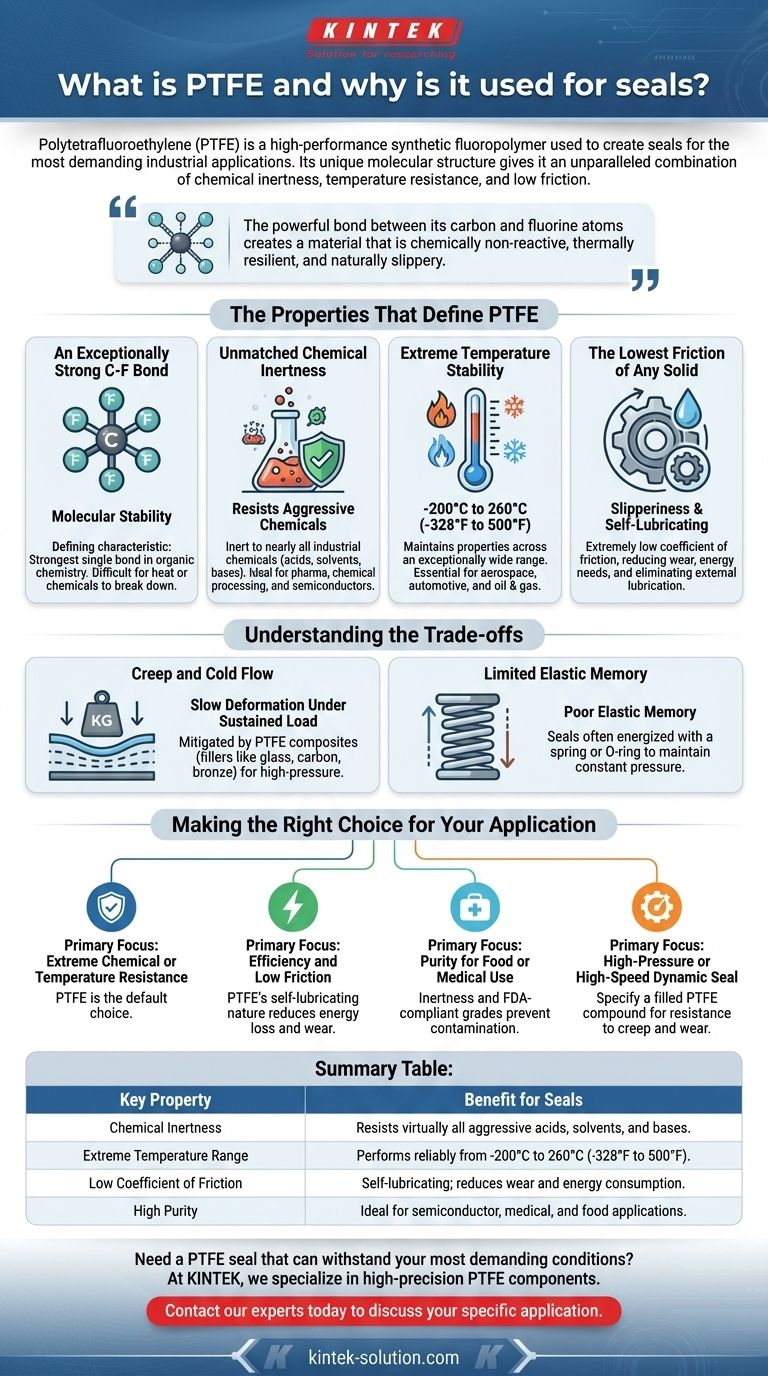
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer used to create seals for the most demanding industrial applications. Its unique molecular structure gives it an unparalleled combination of chemical inertness, temperature resistance, and low friction. This allows PTFE seals to function reliably in extreme environments where conventional materials like rubber or other plastics would quickly degrade and fail.
The core reason engineers specify PTFE for seals is its fundamental stability. The powerful bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms creates a material that is chemically non-reactive, thermally resilient, and naturally slippery, solving sealing challenges that no other polymer can.

The Properties That Define PTFE
To understand why PTFE is a superior sealing material, we must look at its core properties, which originate at the molecular level.
The Foundation: An Exceptionally Strong C-F Bond
The defining characteristic of PTFE is the bond between its carbon and fluorine atoms. This is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry.
This molecular stability is the source of PTFE's most valuable traits, making it incredibly difficult for heat or chemicals to break the material down.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
Because of its stable structure, PTFE is inert to nearly all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, solvents, and bases.
This makes it the material of choice in industries like pharmaceuticals, chemical processing, and semiconductor manufacturing, where seal integrity cannot be compromised by reactive fluids.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE seals maintain their properties across an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, typically from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F).
Where other elastomers become brittle in the cold or melt in the heat, PTFE remains functional, making it essential for aerospace, automotive, and oil & gas applications.
The Lowest Friction of Any Solid
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction—often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This means components can move against the seal with minimal resistance.
This "slipperiness" reduces wear and tear, lowers the energy needed to operate machinery, and often eliminates the need for external lubrication.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE is an exceptional material, it is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is critical for proper application.
Creep and Cold Flow
Unfilled, or "virgin," PTFE can be susceptible to creep—a slow deformation that occurs when the material is under a sustained load or pressure.
This is often mitigated by creating PTFE composites, where fillers like glass, carbon, or bronze are added to enhance strength and resistance to cold flow, especially in high-pressure applications.
Limited Elastic Memory
Unlike rubber elastomers, PTFE has very poor elastic memory. It does not spring back to its original shape effectively after being compressed.
Because of this, PTFE seals are often energized with a spring or an O-ring to ensure they maintain constant pressure against the sealing surface.
Suitability for Application Speed
Standard PTFE seals excel in reciprocating (back-and-forth) and slow rotary applications.
In high-speed dynamic applications, heat can build up due to friction, and abrasive media can cause wear. In these cases, filled PTFE grades are almost always necessary to ensure a long service life.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the right seal material depends entirely on the operational demands of your system.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical or temperature resistance: PTFE is the default choice, providing reliability where nearly all other polymers would fail.
- If your primary focus is efficiency and low friction: PTFE's self-lubricating nature reduces energy loss and component wear, making it ideal for sensitive or non-lubricated systems.
- If your primary focus is purity for food or medical use: The inertness of PTFE and the availability of FDA-compliant grades ensure that it will not contaminate the process media.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure or high-speed dynamic seal: Specify a filled PTFE compound to gain the necessary resistance to creep and wear.
By understanding these core principles, you can leverage the unique strengths of PTFE to engineer a more durable and efficient sealing solution.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Benefit for Seals |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists virtually all aggressive acids, solvents, and bases. |
| Extreme Temperature Range | Performs reliably from -200°C to 260°C (-328°F to 500°F). |
| Low Coefficient of Friction | Self-lubricating; reduces wear and energy consumption. |
| High Purity | Ideal for semiconductor, medical, and food applications. |
Need a PTFE seal that can withstand your most demanding conditions?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require a standard solution or a custom-fabricated part from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures a seal that delivers superior performance, longevity, and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements and get a solution tailored to your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Where are PTFE lined butterfly valves most beneficial? Superior Corrosion Resistance for Harsh Chemicals
- What are the installation advantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves? Simplify Setup & Save on Costs
- What is the temperature tolerance range of PTFE compensators? Ideal for Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Systems
- What happens if standard PTFE is used for both upper and lower members of a slide bearing? Avoid Premature Failure with the Right Design
- What materials are used for PTFE balls? A Guide to Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Composites
- What types of PTFE processing machines are commonly used? From Extrusion to Precision Machining
- How can the susceptibility to creep and cold flow in PTFE washers be addressed? Improve Stability with Filled PTFE or Metal Backing
- How are PTFE rubber seals constructed? Precision Engineering for High-Performance Sealing



















