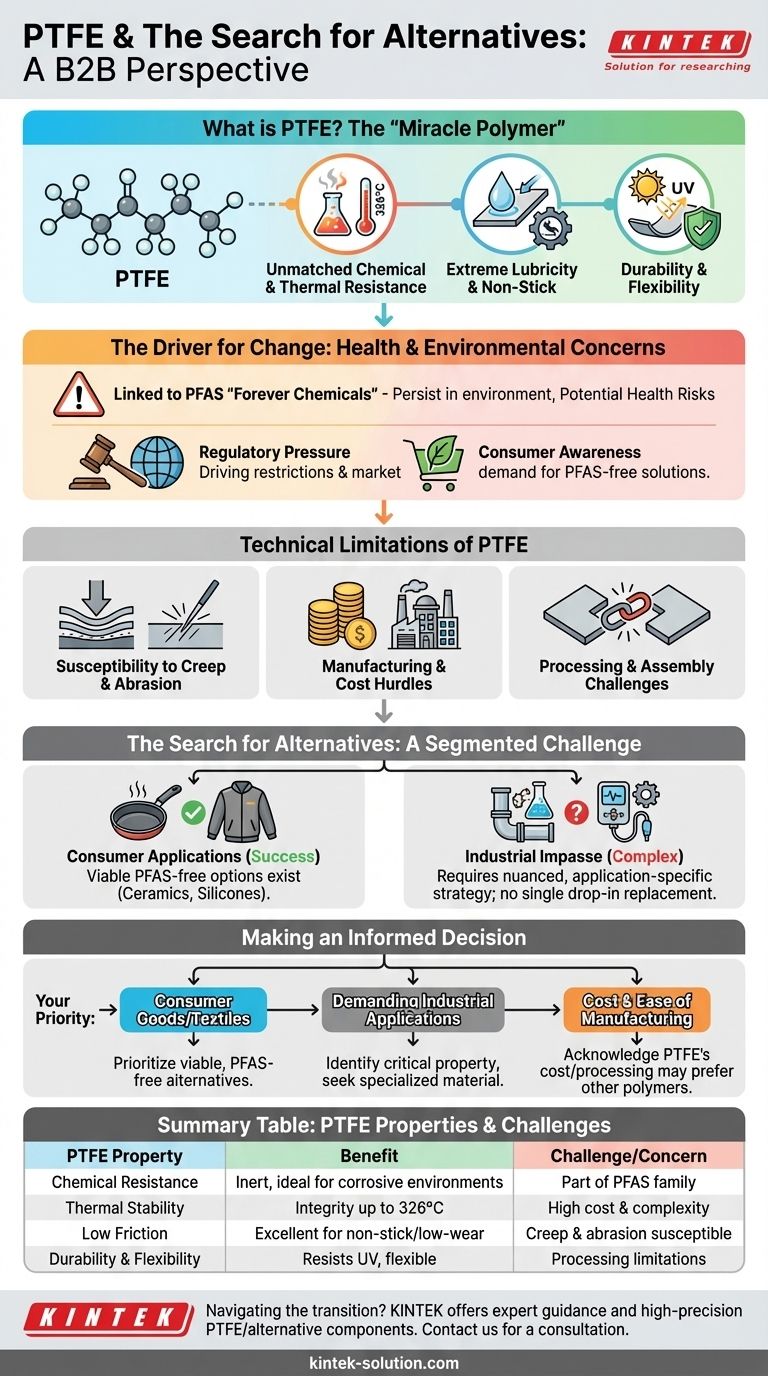
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic polymer prized for a unique combination of properties. It is famously non-stick, highly resistant to chemicals and extreme temperatures, and an excellent electrical insulator. However, growing concerns over its environmental persistence and potential health impacts are driving a significant industry-wide search for viable alternatives.
The central challenge with PTFE is resolving a conflict: its exceptional and often irreplaceable performance in demanding applications versus its identity as a "forever chemical" with documented health and environmental risks. The path forward is not a single replacement, but a nuanced, application-specific strategy.

Deconstructing PTFE: The "Miracle Polymer"
To understand the search for alternatives, we must first appreciate why PTFE became so essential. Its value stems from a rare combination of physical and chemical characteristics that are difficult to replicate in a single material.
### Unmatched Chemical and Thermal Resistance
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it does not react with most chemicals. This makes it invaluable for lining pipes, valves, and containers in corrosive industrial environments.
It also maintains its integrity at high temperatures, with a melting point around 326°C, allowing its use in applications from high-performance wiring to non-stick cookware.
### Extreme Lubricity and Non-Stick Properties
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, giving it a uniquely slippery feel. This property, known as lubricity, is essential for creating self-lubricating gears, bearings, and other low-friction components.
Its surface is also "non-wetting," meaning liquids and other substances bead up and fail to stick to it. This is the principle behind its most famous application: non-stick coatings on cookware.
### Durability and Flexibility
Beyond its other traits, PTFE is resistant to degradation from UV radiation, making it suitable for long-term outdoor use. It also remains flexible across a wide temperature range, a key property for seals, gaskets, and membranes in outdoor apparel.
The Driver for Change: Health and Environmental Concerns
The primary motivation for replacing PTFE is its classification within a broader group of chemicals that have come under intense scrutiny.
### The Link to PFAS "Forever Chemicals"
PTFE belongs to the per- and polyfluoroalkyl substances (PFAS) family. These are often called "forever chemicals" because they do not break down naturally and can persist in the environment for centuries.
Studies have linked certain PFAS chemicals to adverse health effects, leading to widespread concern about their accumulation in water, soil, and living organisms, including humans.
### Regulatory and Consumer Pressure
This scientific understanding has triggered a wave of regulatory action in many regions, restricting or banning the use of certain PFAS. Simultaneously, consumer awareness has grown, creating market pressure on brands—especially in cookware and apparel—to move toward PFAS-free alternatives.
Understanding the Trade-offs: The Technical Limitations of PTFE
While its performance is remarkable, PTFE is not a perfect material. Acknowledging its inherent drawbacks is crucial for a balanced assessment and for identifying where alternatives might already hold an advantage.
### Susceptibility to Creep and Abrasion
Despite its durability, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is susceptible to "creep," meaning it can slowly deform when held under a constant load. It also has poor abrasion resistance and can be damaged by scratching.
### Manufacturing and Cost Hurdles
PTFE is significantly more expensive than common polymers like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its manufacturing processes are also more complex, making mass production challenging and costly.
### Processing and Assembly Challenges
Unlike many other plastics, PTFE cannot be easily cemented or welded. This limits how it can be joined or integrated into larger assemblies, often requiring mechanical fastening or complex molding techniques.
The Search for Alternatives: A Segmented Challenge
Finding a single, drop-in replacement for PTFE has proven impossible. The difficulty of the task varies dramatically depending on the application.
### Success in Consumer Applications
For products like non-stick cookware, outdoor jackets, and cosmetics, the market has successfully introduced effective alternatives. Ceramic-based coatings, silicone, and specialized wax-based polymers now offer performance that meets the needs of most consumers without relying on PTFE.
### The Industrial Impasse
The challenge is far greater in high-stakes industrial and professional settings. For applications like chemical processing pipes, high-performance seals, or medical device coatings, the unique combination of PTFE's properties is often critical for safety and function.
In these cases, the search is not for one alternative, but for a portfolio of different materials that can replace PTFE in specific circumstances. This requires a deep analysis of which property—be it chemical resistance, temperature stability, or lubricity—is the most critical for a given component.
Making an Informed Decision
As you evaluate materials for your project, your priority will determine your path.
- If your primary focus is consumer goods or textiles: Viable, high-performance, PFAS-free alternatives are readily available and should be prioritized to meet regulatory and market demands.
- If your primary focus is demanding industrial applications: A direct drop-in replacement is unlikely; focus on identifying the single most critical PTFE property for your use case and seek a specialized material that excels in that area.
- If your primary focus is cost and ease of manufacturing: Acknowledge that PTFE's high cost and processing challenges may make other polymers a better fit, even if they do not match its peak chemical or thermal performance.
Understanding this balance between unparalleled performance and significant drawbacks is the key to navigating the post-PTFE material landscape.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Property | Benefit | Challenge/Concern |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Inert to most chemicals, ideal for corrosive environments | Part of PFAS 'forever chemical' family |
| Thermal Stability | Maintains integrity up to 326°C | High manufacturing cost and complexity |
| Low Friction (Lubricity) | Excellent for non-stick surfaces and low-wear parts | Susceptible to creep and abrasion |
| Durability & Flexibility | Resists UV degradation, flexible across temperatures | Processing and assembly limitations |
Navigating the transition from PTFE requires a partner who understands both performance and compliance. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We also offer expert guidance on material selection and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to meet your specific application needs while addressing evolving regulatory demands. Let's discuss your project requirements and explore the optimal material solution for you. Contact our team today for a consultation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
People Also Ask
- What factors can cause variations in the actual properties of PTFE? Don't Rely on Generic Data Sheets
- What is PTFE and what is it commonly known as? The Ultimate Guide to Teflon & Its Uses
- What are the disadvantages or safety concerns with Teflon? A Guide to Safe and Effective Use
- What are the key chemical resistance properties of PTFE? Discover Its Near-Universal Inertness
- What are the main properties that make PTFE versatile across industries? Discover Its 5 Key Advantages
- How does PTFE perform against common acids and bases? Discover Unmatched Chemical Resistance
- What are the advantages of PTFE's impact resistance? Ensure Unmatched Durability in Harsh Environments
- What are the applications of PTFE aqueous dispersions? Coating, Impregnation, and More



















