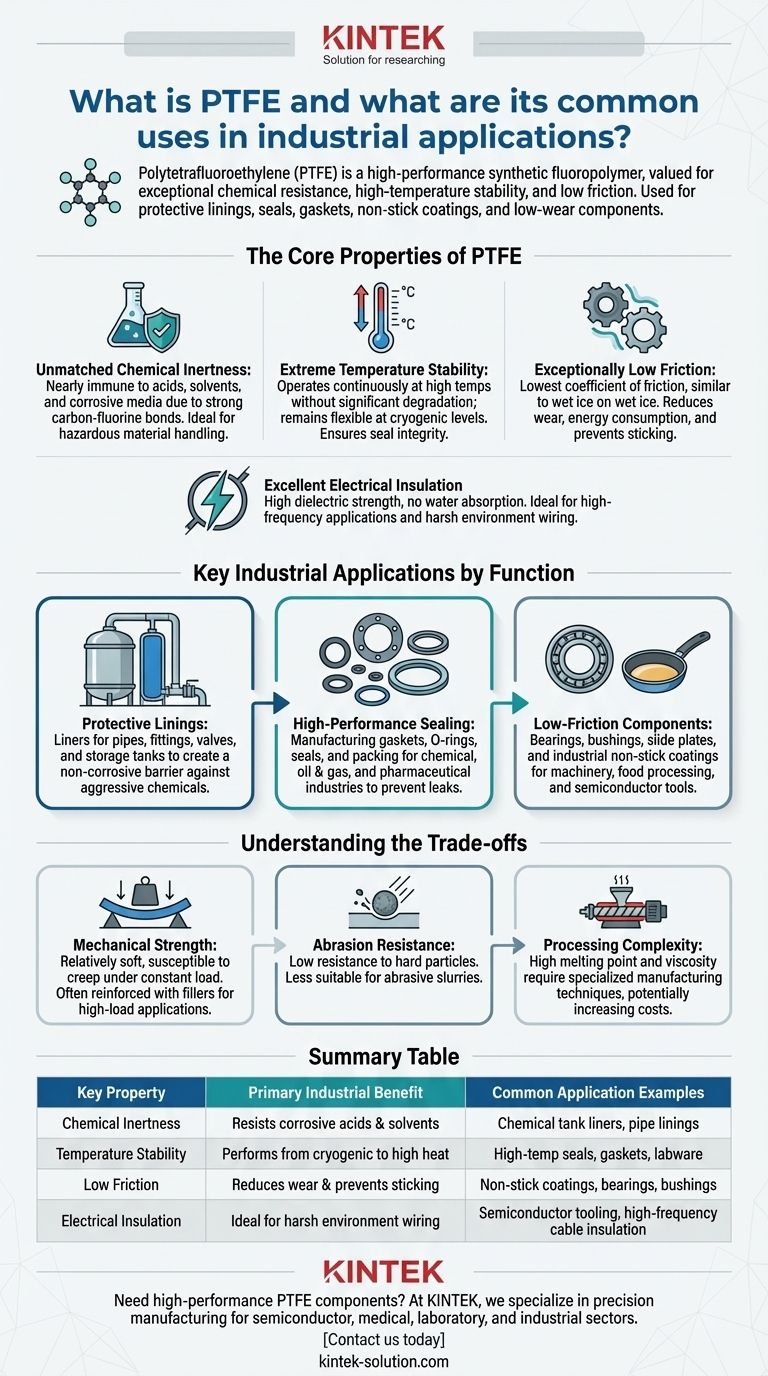
In short, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer valued across nearly every industry for its exceptional chemical resistance, stability at high temperatures, and extremely low friction. It is most commonly used to create protective linings for pipes and tanks, manufacture high-performance seals and gaskets, and serve as non-stick coatings and low-wear components in machinery.
The core reason for PTFE's widespread industrial use is its unique ability to solve multiple problems at once. It reliably withstands environments—highly corrosive chemicals, extreme temperatures, and high-friction contact—where most other materials would quickly fail.

The Core Properties of PTFE
To understand why PTFE is so versatile, we must first examine its fundamental characteristics. These properties are not just distinct advantages; they work in combination to make it a uniquely capable engineering material.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is one of the most nonreactive substances known. Its molecular structure, composed of strong carbon-fluorine bonds, makes it almost entirely immune to attack from aggressive chemicals.
This includes acids, solvents, oxidizing agents, and other corrosive media that would degrade metals and other plastics. This property makes it a default choice for handling and storing hazardous materials.
Extreme Temperature Stability
PTFE maintains its integrity over a very wide temperature range. It can operate continuously at high temperatures without significant degradation and remains flexible even at cryogenic levels.
This thermal stability ensures that components like seals and gaskets do not become brittle or melt when exposed to demanding industrial processes.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, a quality often compared to wet ice on wet ice. This makes its surface exceptionally slippery and "non-stick."
This is crucial for applications involving moving parts, as it drastically reduces wear and energy consumption. It also prevents materials from sticking to surfaces in processing equipment.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a secondary but critical property, PTFE is an outstanding electrical insulator. It has high dielectric strength and does not absorb water, making it ideal for high-frequency applications and insulating wiring in harsh environments.
Key Industrial Applications by Function
PTFE's properties translate directly into specific, high-value industrial applications where performance and reliability are non-negotiable.
Protective Linings
Because of its chemical inertness, PTFE is widely used as a liner for pipes, fittings, valves, and large storage tanks.
This application places a non-corrosive barrier between the aggressive chemical and the structural material (often steel), protecting expensive infrastructure from damage.
High-Performance Sealing
PTFE is a primary material for manufacturing gaskets, O-rings, seals, and packing. Its flexibility and chemical resistance create a durable, leak-proof seal.
These components are essential in the chemical processing, oil and gas, and pharmaceutical industries to prevent leaks of hazardous or high-purity substances.
Low-Friction Components
The material's low-friction nature is leveraged in components designed to reduce wear and improve efficiency.
This includes bearings, bushings, and slide plates in machinery. It's also the basis for industrial non-stick coatings on everything from food processing equipment to semiconductor manufacturing tools.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE is not a universal solution. An objective assessment requires understanding its limitations.
Mechanical Strength
Compared to engineering plastics like nylon or PEEK, pure PTFE is relatively soft. It can be susceptible to "creep," which is slow deformation under a constant load.
For high-load structural applications, PTFE is often reinforced with fillers like glass fiber or carbon to improve its mechanical strength and wear resistance.
Abrasion Resistance
While PTFE has excellent low-friction properties, it has relatively low resistance to abrasion from hard, sharp particles. In environments with abrasive slurries, other materials may be more suitable.
Processing Complexity
PTFE's high melting point and melt viscosity make it more difficult to process than common thermoplastics. It cannot be injection molded or extruded using conventional methods, requiring specialized techniques that can increase manufacturing costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is a decision driven by the specific demands of the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: PTFE's unmatched chemical inertness makes it the default choice for protective linings, seals, and fluid-handling components.
- If your primary focus is reducing friction and wear: Its extremely low coefficient of friction is ideal for creating non-stick surfaces, self-lubricating bearings, and other low-drag components.
- If your primary focus is sealing in high-temperature or cryogenic conditions: PTFE's excellent thermal stability ensures seal integrity and material flexibility where most elastomers would fail.
Ultimately, PTFE's unique combination of properties makes it an essential material for solving some of industry's most demanding engineering challenges.
Summary Table:
| Key Property | Primary Industrial Benefit | Common Application Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists corrosive acids & solvents | Chemical tank liners, pipe linings |
| Temperature Stability | Performs from cryogenic to high heat | High-temp seals, gaskets, labware |
| Low Friction | Reduces wear & prevents sticking | Non-stick coatings, bearings, bushings |
| Electrical Insulation | Ideal for harsh environment wiring | Semiconductor tooling, high-frequency cable insulation |
Need high-performance PTFE components tailored to your exact requirements?
At KINTEK, we specialize in the precision manufacturing of PTFE seals, liners, labware, and custom components for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise ensures your parts meet the demanding standards for chemical resistance, temperature stability, and low friction.
Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how our custom PTFE solutions can enhance your application's reliability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the recommended PTFE formulations for the chemical processing industry and why? Optimize for Durability and Chemical Resistance
- What are the characteristics of PFA Teflon? | Extreme Performance Meets Design Freedom
- What alternatives exist for PTFE in consumer products? Discover Safer Options for Cookware, Clothing & Cosmetics
- What substances can affect the carbon-fluorine bonds of PTFE? The Rare Chemicals That Challenge PTFE
- Are there any chemicals that PTFE is not compatible with? Key Exceptions for Safe Use
- What unique characteristic of PTFE prevents geckos from sticking to it? Its Extremely Low Surface Energy
- What are some key properties of Teflon that make it widely useful? Discover Its Unique Advantages
- What type of polymerization is used to create Teflon? A Guide to Free-Radical Chain-Growth



















