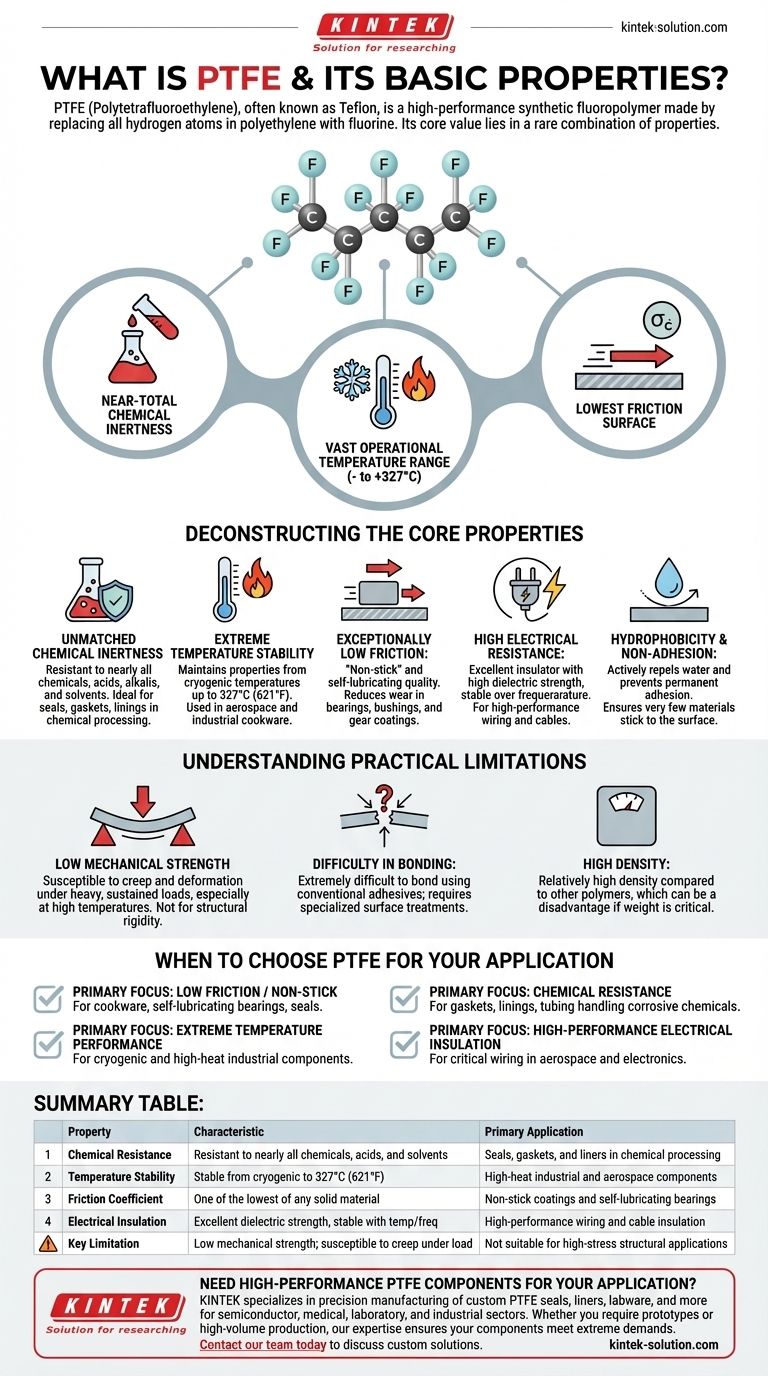
PTFE, or Polytetrafluoroethylene, is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer most famously known by the brand name Teflon. It is engineered by replacing all hydrogen atoms in polyethylene with fluorine, resulting in a material with an extraordinary combination of properties, including extreme chemical resistance, high-temperature stability, and an exceptionally low coefficient of friction.
The core value of PTFE lies not in a single attribute, but in its rare combination of near-total chemical inertness, a vast operational temperature range, and one of the lowest friction surfaces of any known solid. This makes it a "problem-solver" material for extreme environments where others would quickly fail.

Deconstructing the Core Properties of PTFE
To truly understand PTFE's utility, we must examine its individual characteristics. These properties are a direct result of its unique molecular structure, which is dominated by strong carbon-fluorine bonds.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. Its molecular structure is so stable and non-reactive that it is almost entirely insoluble.
This makes it an ideal material for seals, gaskets, and linings in chemical processing and laboratory equipment where exposure to corrosive substances is constant.
Extreme Temperature Stability
The material demonstrates remarkable thermal stability over a wide range. It maintains its properties at very high temperatures, with a melting point around 327°C (621°F), and also retains its flexibility and integrity at cryogenic temperatures.
This dual resistance makes it suitable for applications ranging from aerospace components to industrial cookware coatings.
Exceptionally Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material. This gives it its signature "non-stick" and self-lubricating quality.
This property is critical for applications designed to reduce wear and energy consumption, such as in bearings, bushings, and gear coatings.
High Electrical Resistance
PTFE is an excellent electrical insulator with high dielectric strength. Its resistance to electricity does not degrade with frequency or temperature, making it a superior material for high-performance wiring and cable insulation.
Hydrophobicity and Non-Adhesion
The material is hydrophobic, meaning it actively repels water and water-containing substances. Combined with its low friction, this property ensures that very few materials will permanently adhere to its surface.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While its properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the solution for every engineering problem. Understanding its trade-offs is crucial for proper application.
Low Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft and flexible material. It can be susceptible to creep and deformation when subjected to heavy, sustained loads, especially at higher temperatures. It is not a material chosen for its structural rigidity or tensile strength.
Difficulty in Bonding
The very non-stick properties that make PTFE so valuable also make it extremely difficult to bond to other surfaces using conventional adhesives. Specialized surface treatments, like chemical etching, are often required to achieve a reliable bond.
High Density
Compared to many other polymers, PTFE has a relatively high density. This can be a disadvantage in applications where weight is a critical design factor.
When to Choose PTFE for Your Application
Selecting PTFE is about matching its unique strengths to a specific operational challenge. It is rarely chosen for its mechanical properties but rather for its ability to survive extreme conditions.
- If your primary focus is low friction or a non-stick surface: PTFE is an ideal choice for coatings on cookware, self-lubricating bearings, and seals that must operate without external lubricants.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: It is the go-to material for gaskets, linings, and tubing that will handle highly corrosive or pure chemicals.
- If your primary focus is performance in extreme temperatures: PTFE is highly effective for components used in both cryogenic applications and high-heat industrial processes.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electrical insulation: It is a top-tier choice for insulating critical wiring in aerospace, computing, and telecommunications.
Ultimately, PTFE should be considered a specialty material chosen for its outstanding ability to resist chemical attack, heat, and surface adhesion.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and solvents | Seals, gaskets, and liners in chemical processing |
| Temperature Stability | Stable from cryogenic to 327°C (621°F) | High-heat industrial and aerospace components |
| Friction Coefficient | One of the lowest of any solid material | Non-stick coatings and self-lubricating bearings |
| Electrical Insulation | Excellent dielectric strength, stable with temperature/frequency | High-performance wiring and cable insulation |
| Key Limitation | Low mechanical strength; susceptible to creep under load | Not suitable for high-stress structural applications |
Need high-performance PTFE components for your application?
KINTEK specializes in the precision manufacturing of custom PTFE seals, liners, labware, and more for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume production, our expertise ensures your components meet the extreme demands of chemical resistance, temperature stability, and low friction.
Contact our team today to discuss how our custom PTFE solutions can solve your most challenging engineering problems.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- PTFE Chemical Solvent Sampling Spoon
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to renewable energy systems? Enhancing Durability and Efficiency
- Which industries commonly use PTFE due to its special properties? Solve Critical Engineering Challenges
- How does PTFE perform when exposed to different types of water? Unmatched Chemical Resistance in Any Aqueous Environment
- How do the non-stick properties of PTFE benefit its applications? Boost Efficiency, Hygiene & Performance
- How is Teflon used in industrial applications? Solve Extreme Heat, Chemical & Friction Challenges
- Why is PTFE suitable for solar panel manufacturing? Unmatched Durability for 25+ Year Lifespan
- What is PTFE's most familiar household application? Discover the Versatile Material Behind Non-Stick Cookware
- What is the electrical insulation capability of PTFE? Unmatched Reliability for Demanding Applications



















