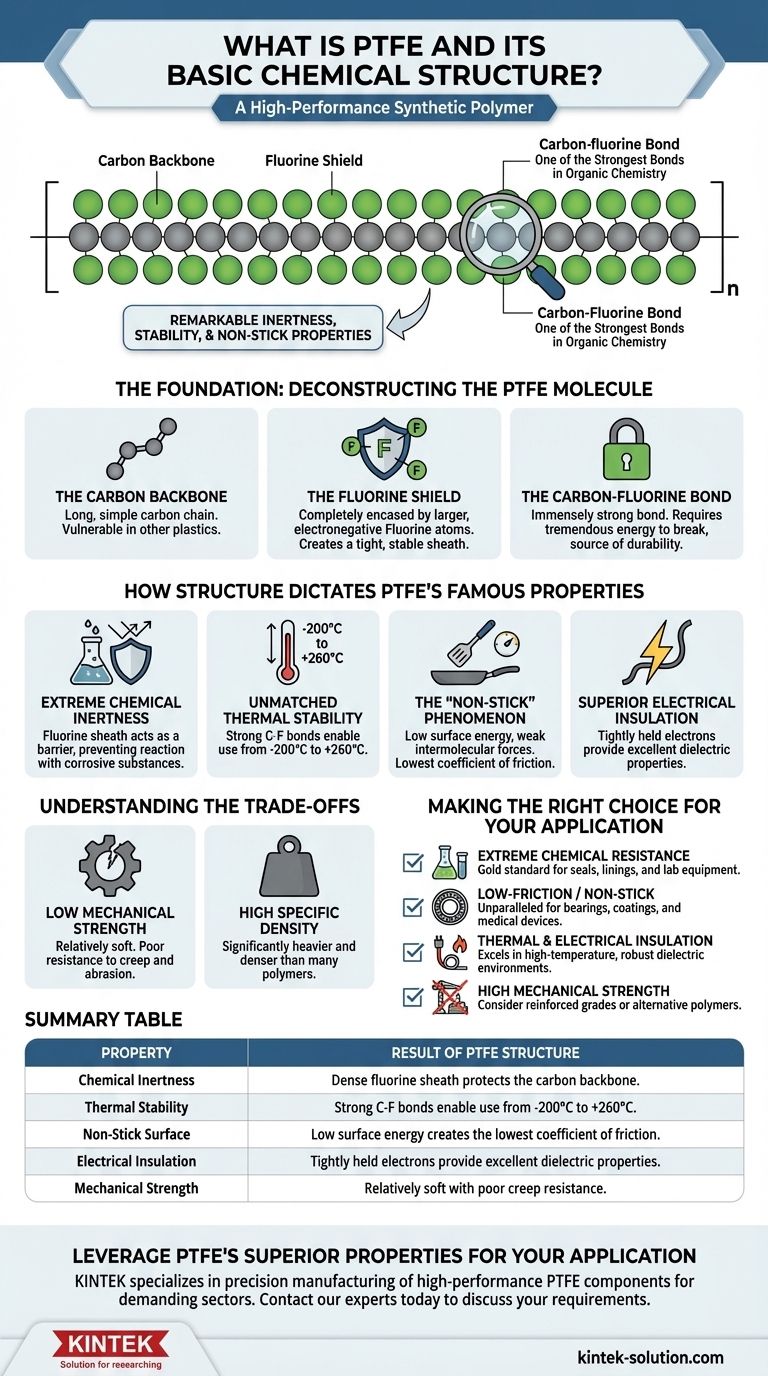
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic polymer. It consists of a long, repeating chain of carbon atoms, where each carbon atom is completely surrounded by two fluorine atoms. This simple but powerful molecular arrangement, chemically noted as (CF2)n, is the source of its legendary properties.
The key to understanding PTFE is recognizing that its remarkable chemical inertness, thermal stability, and non-stick surface are all direct results of the incredibly strong carbon-fluorine bond and the protective "sheath" the fluorine atoms form around the carbon backbone.

The Foundation: Deconstructing the PTFE Molecule
To truly grasp why PTFE behaves the way it does, we must look at its structure on a molecular level. It is a model of simplicity and strength.
The Carbon Backbone
The foundation of the polymer is a long, simple chain of carbon atoms linked together. In many other plastics, this carbon backbone would be vulnerable to chemical attack.
The Fluorine Shield
The defining feature of PTFE is that this carbon backbone is completely encased by fluorine atoms. These atoms are larger and far more electronegative than the hydrogen atoms found in common polymers like polyethylene. This creates a tight, stable, and protective sheath around the carbon chain.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between the carbon and fluorine atoms is one of the strongest single bonds in organic chemistry. It requires a tremendous amount of energy to break, which is the fundamental reason for PTFE's extreme durability and resistance.
How Structure Dictates PTFE's Famous Properties
The unique molecular structure directly translates into the material properties that make PTFE so valuable in demanding applications.
Extreme Chemical Inertness
The dense fluorine sheath acts as a barrier, preventing nearly all chemicals and solvents from reaching and reacting with the vulnerable carbon backbone. This is why PTFE is used to handle highly corrosive substances.
Unmatched Thermal Stability
Because the carbon-fluorine bonds are so strong, they require immense energy to disrupt. This gives PTFE a very high melting point (around 327°C) and an exceptionally wide operating temperature range, from -200°C to +260°C.
The "Non-Stick" Phenomenon
The fluorine atoms create a surface with very low energy and weak intermolecular forces. This means other substances have virtually nothing to adhere to, resulting in an extremely low coefficient of friction—the lowest of any solid material.
Superior Electrical Insulation
The electrons within the carbon-fluorine bonds are held very tightly. This lack of mobile electrons makes PTFE an outstanding electrical insulator with excellent dielectric properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and objectivity requires acknowledging a material's limitations. Despite its incredible stability, PTFE has distinct disadvantages in certain contexts.
Low Mechanical Strength
Compared to other engineering plastics, PTFE is relatively soft. It has poor resistance to creep (the tendency to slowly deform under stress) and is susceptible to wear from abrasion.
High Specific Density
PTFE is significantly heavier and denser than many other common polymers. This can be a critical drawback in applications where minimizing weight is a primary design goal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Understanding PTFE's core nature allows you to deploy it where its unique strengths will have the most impact.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: PTFE is the gold standard for seals, linings, and lab equipment that will be exposed to corrosive substances.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction or non-stick surface: It is the unparalleled choice for applications like bearings, coatings for cookware, or medical devices.
- If your primary focus is thermal and electrical insulation: PTFE excels in high-temperature environments where robust dielectric properties are required, such as in high-performance wiring.
- If your primary focus is high mechanical or structural strength: You must consider reinforced grades of PTFE or look to alternative engineering polymers entirely.
By understanding the direct link between its simple structure and its powerful properties, you can leverage PTFE to solve some of engineering's toughest challenges.
Summary Table:
| Property | Result of PTFE Structure |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Dense fluorine sheath protects the carbon backbone. |
| Thermal Stability | Strong C-F bonds enable use from -200°C to +260°C. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Low surface energy creates the lowest coefficient of friction. |
| Electrical Insulation | Tightly held electrons provide excellent dielectric properties. |
| Mechanical Strength | Relatively soft with poor creep resistance. |
Leverage PTFE's Superior Properties for Your Application
Understanding the science behind PTFE is the first step. KINTEK puts that knowledge to work for you. We specialize in the precision manufacturing of high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the most demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Whether you need a standard component or a custom-fabricated solution from prototype to high-volume production, our expertise ensures you get the exact properties you need.
Ready to solve your toughest engineering challenges with PTFE? Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Volumetric Flasks for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- In which industries is Teflon commonly used? Essential for Chemical, Medical, and Aerospace
- What are mechanical engineering applications of Teflon? Solve Friction, Heat, and Chemical Challenges
- What family of substances does PTFE belong to? Understanding PFAS & Fluoropolymer Safety
- Why is PTFE widely used in the medical device industry? Its Biocompatibility & Low-Friction Drive Safety
- How does PTFE combine properties of different material types? Unlock Unmatched Material Versatility
- What are the main applications of PTFE material? Unlock Superior Performance in Demanding Industries
- What happens during the suspension polymerization process of PTFE? Producing Granular PTFE for Solid Shapes
- What is PTFE commonly used for in construction? Essential Applications for High-Performance Infrastructure



















