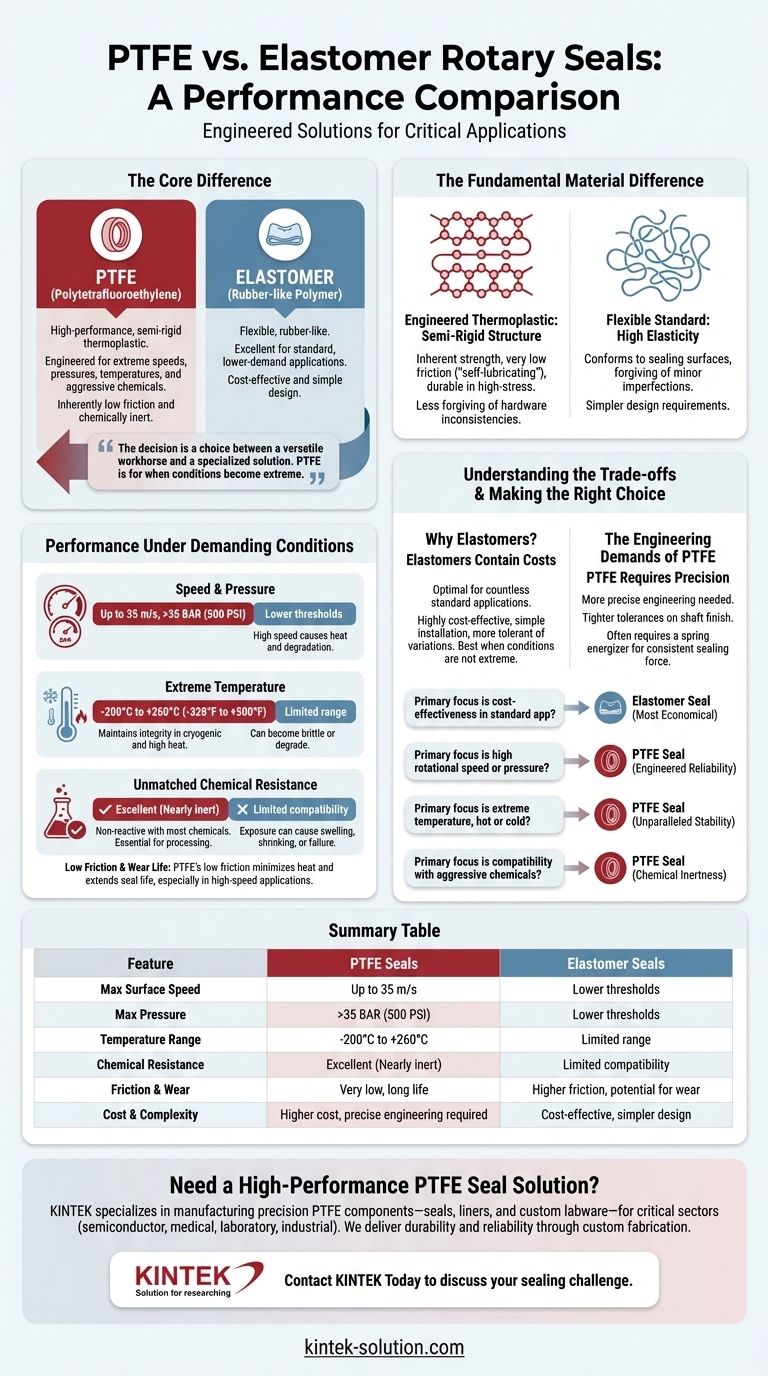
At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance, semi-rigid thermoplastic engineered for rotary sealing applications that operate beyond the limits of traditional elastomers. While elastomer seals are flexible and suitable for many standard uses, PTFE provides superior durability and reliability in high-stress environments involving extreme speeds, pressures, temperatures, and aggressive chemicals. Its inherently low friction and chemical inertness make it the material of choice for the industry's most demanding challenges.
The decision between PTFE and an elastomer seal is a choice between a versatile workhorse and a specialized solution. Elastomers are excellent for general-purpose applications, but when conditions become extreme, PTFE's unique material properties are not just an advantage—they are a necessity.
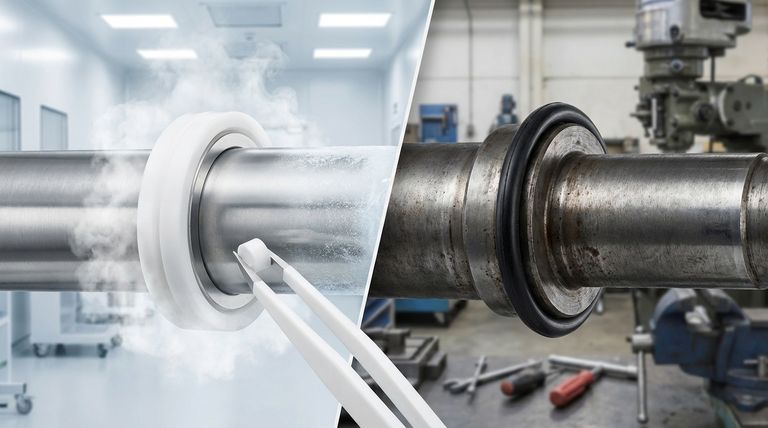

The Fundamental Material Difference
The performance gap between these two seal types originates from their basic polymer structure. Understanding this distinction is key to selecting the right material for your design.
Elastomers: The Flexible Standard
Elastomers are rubber-like polymers known for their high elasticity. This flexibility allows them to conform easily to sealing surfaces, making them forgiving of minor shaft imperfections.
They are the go-to choice for a vast range of standard, lower-demand applications due to their cost-effectiveness and simple design requirements.
PTFE: The Engineered Thermoplastic
PTFE is a semi-rigid fluoropolymer. Its structure provides inherent strength and a very low coefficient of friction, giving it a "self-lubricating" characteristic.
This rigidity is the source of its durability in high-stress scenarios, but it also means PTFE seals are less forgiving of hardware inconsistencies than their elastomeric counterparts.
Performance Under Demanding Conditions
The true value of PTFE becomes clear when analyzing its performance metrics in environments where elastomers would quickly fail.
Operating Speed and Pressure
PTFE seals are specifically designed for high-dynamic applications. They can reliably operate at surface velocities up to 35 m/s and handle pressures exceeding 35 BAR (500 PSI).
Elastomer seals typically operate at much lower speed and pressure thresholds. High speeds can cause them to generate significant frictional heat, leading to material degradation and premature failure.
Extreme Temperature Tolerance
PTFE exhibits remarkable thermal stability across an exceptionally wide temperature range, often from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F).
This allows it to maintain its sealing integrity without becoming brittle in cryogenic applications or degrading in high-heat environments, a common failure point for many elastomers.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
PTFE is nearly inert, meaning it is non-reactive with almost all industrial chemicals and lubricants. This makes it an essential choice for applications in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, and oil and gas.
Elastomers, by contrast, have limited chemical compatibility. Exposure to the wrong media can cause them to swell, shrink, or dissolve, resulting in catastrophic seal failure.
Low Friction and Wear Life
The low-friction nature of PTFE minimizes heat generation at the contact point, reducing wear and extending the seal's service life, especially in high-speed applications.
While both seal types use a metal casing, PTFE seals are often designed with a wider lip-to-shaft footprint but with lighter unit loading to optimize for a low wear rate over a long operational life.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing PTFE is not a universal upgrade; it's an engineering decision based on specific needs and accompanied by unique design considerations.
Why Elastomers Remain the Default
For countless standard applications, elastomer seals are the optimal choice. They are highly cost-effective, simpler to install, and more tolerant of minor variations in shaft runout or surface finish.
Their inherent flexibility provides excellent sealing force with minimal complexity, making them a reliable and economical solution when extreme conditions are not a factor.
The Engineering Demands of PTFE
The semi-rigid nature of PTFE requires more precise engineering. It demands tighter tolerances on shaft surface finish and concentricity to ensure a proper seal.
Furthermore, because PTFE lacks the natural "memory" or elasticity of rubber, PTFE seals often incorporate a spring energizer to provide a consistent sealing force throughout the life of the seal. This adds a layer of complexity to the design.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the correct material, you must align the seal's capabilities directly with the operational demands of your equipment.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness in a standard application: An elastomer seal is almost always the correct and most economical choice.
- If your primary focus is high rotational speed or high operating pressure: PTFE is engineered specifically for these dynamic conditions and will provide the necessary reliability.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperatures, hot or cold: PTFE's unparalleled thermal stability makes it the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is compatibility with aggressive chemicals: PTFE's chemical inertness eliminates the risk of material degradation and ensures system integrity.
Ultimately, choosing the right seal is not about finding a superior material, but about precisely matching the material's capabilities to your application's demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PTFE Seals | Elastomer Seals |
|---|---|---|
| Max Surface Speed | Up to 35 m/s | Lower thresholds |
| Max Pressure | >35 BAR (500 PSI) | Lower thresholds |
| Temperature Range | -200°C to +260°C | Limited range |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent (Nearly inert) | Limited compatibility |
| Friction & Wear | Very low, long life | Higher friction, potential for wear |
| Cost & Complexity | Higher cost, precise engineering required | Cost-effective, simpler design |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal Solution?
When your application involves extreme speeds, aggressive chemicals, or wide temperature swings, standard elastomers may not be enough. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We deliver the durability and reliability your critical equipment demands through custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific sealing challenge and discover how our PTFE expertise can enhance your system's performance and longevity.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the main ingredients used to make PTFE? The Chemistry Behind a High-Performance Polymer
- What temperature range can PTFE seals typically operate in? From Cryogenic -200°C to High-Temp 260°C
- What is the chemical formula and material of PTFE Disk? Unlock the Power of C₂F₄ Polymer
- What are some common components made from PTFE? Seals, Bearings & More for Demanding Applications
- What are some common applications of Teflon square bars? Solve Extreme Engineering Challenges
- What are some examples of ePTFE applications in aerospace and automotive industries? Critical Components for Extreme Environments
- How does the company ensure quality in PTFE wear strips and bands? Achieve Consistent Performance & Dimensional Accuracy
- Why are Teflon bushings preferred in the aerospace industry? Achieve Lighter, More Reliable Aircraft Systems



















