At its core, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is a high-performance synthetic fluoropolymer, a type of plastic composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms. This unique chemical structure gives it a remarkable combination of properties, including extreme chemical resistance, a very high melting point, and an exceptionally low-friction surface. While the material itself is singular, it is applied in different systems, most commonly as either a single-layer (one-coat) or dual-layer (two-coat) protective coating.
Understanding PTFE is less about different "types" of the material and more about recognizing its core properties and how they are leveraged in its various physical forms—such as coatings, gaskets, and sheets—to solve specific industrial challenges.

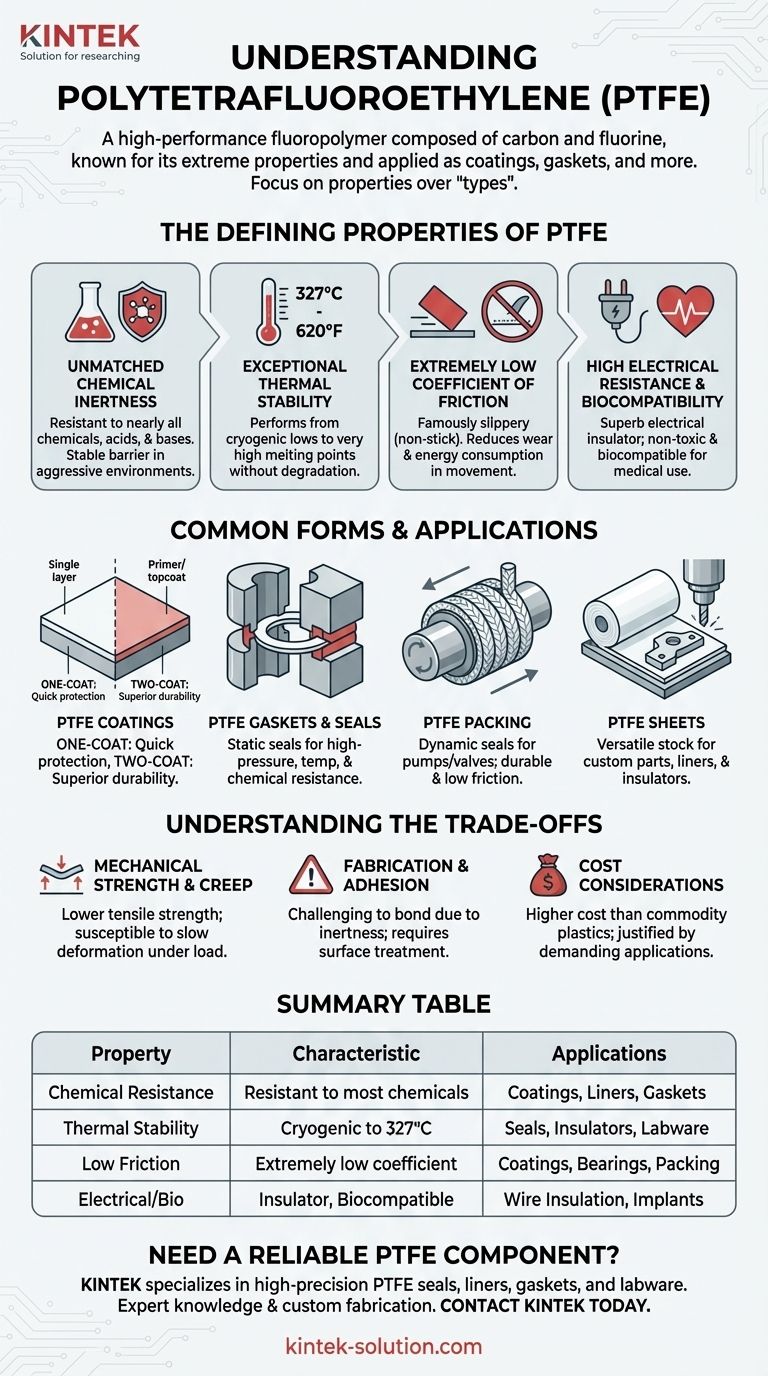
The Defining Properties of PTFE
The value of PTFE comes from a set of extreme characteristics that make it suitable for environments where other materials would fail. These properties are a direct result of its strong carbon-fluorine molecular bonds.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases. This makes it an ideal material for handling corrosive substances.
Because it does not react with other elements, it provides a stable and protective barrier in chemically aggressive industrial processes.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
The material maintains its integrity across a vast temperature range, from cryogenic lows up to a high melting point of approximately 327°C (620°F).
This allows PTFE components to perform reliably in both extreme cold and high-heat applications without degrading.
Extremely Low Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest friction coefficients of any known solid, giving it a famously "slippery" or non-stick surface.
This property is critical for applications requiring smooth movement, such as coatings on cookware or bearings in machinery, as it reduces wear and energy consumption.
High Electrical Resistance
As a superb electrical insulator, PTFE does not conduct electricity. This makes it an essential material for insulating wires, cables, and other electronic components.
Biocompatibility
PTFE is non-toxic and biocompatible, meaning the human body does not reject it. This has made it a trusted material for use in various medical implants and devices.
Common Forms and Applications of PTFE
The term "types" of PTFE often refers to its different physical forms and application methods. Each form is tailored to a specific function.
PTFE Coatings
This is where the one-coat versus two-coat distinction is relevant. A one-coat system is a single layer applied for quick, cost-effective surface protection.
A two-coat system involves a primer for adhesion and a topcoat for performance. This dual-layer approach provides superior durability and longevity, making it ideal for high-demand applications.
PTFE Gaskets and Seals
A gasket is a static seal used to prevent leaks between two stationary parts. PTFE's ability to resist high pressure, extreme temperatures, and chemical attack makes it a premier material for durable, leak-proof gaskets in automotive and industrial machinery.
PTFE Packing
Packing is a form of dynamic seal used in equipment with moving parts, like pumps and valves. PTFE packing is braided into a rope-like form and used to prevent fluid leaks around rotating shafts or valve stems, valued for its low friction and resilience.
PTFE Sheets
Sheets of PTFE serve as a versatile stock material. They can be machined into custom parts, used as corrosion-proof liners for chemical tanks, or employed as high-performance electrical insulators.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While PTFE's properties are exceptional, it is crucial to understand its limitations to select it appropriately.
Mechanical Strength and Creep
Compared to metals, PTFE has lower tensile strength and is susceptible to "creep"—a tendency to deform slowly under sustained mechanical stress. Its use in high-load structural applications must be carefully engineered.
Fabrication and Adhesion
Due to its chemical inertness and low-friction surface, bonding PTFE to other materials can be challenging. It often requires special surface treatments like chemical etching to achieve proper adhesion.
Cost Considerations
As a high-performance polymer, PTFE is generally more expensive than commodity plastics like polyethylene or polypropylene. Its use is typically justified by the demanding nature of the application where other materials would fail.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct form of PTFE depends entirely on the problem you need to solve.
- If your primary focus is surface performance (non-stick, low friction): A PTFE coating system is the most effective solution.
- If your primary focus is preventing leaks in a static joint: Use a custom-cut PTFE gasket for superior chemical and thermal resistance.
- If your primary focus is sealing a moving part (like a pump shaft): PTFE packing provides a durable, low-friction dynamic seal.
- If your primary focus is creating custom components or electrical insulation: PTFE sheets provide a versatile base material for fabrication.
By understanding PTFE's fundamental properties, you can confidently select the right form to ensure reliability and performance in your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Property | Key Characteristic | Common Application Forms |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to nearly all chemicals, acids, and bases | Coatings, Liners, Gaskets |
| Thermal Stability | Performs from cryogenic temps up to 327°C (620°F) | Seals, Insulators, Labware |
| Low Friction | Extremely low coefficient of friction (non-stick) | Coatings, Bearings, Packing |
| Electrical Resistance | Excellent electrical insulator | Wire Insulation, Components |
| Biocompatibility | Non-toxic and biocompatible | Medical Implants, Devices |
Need a reliable PTFE component for your demanding application?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—including seals, liners, gaskets, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine expert material knowledge with custom fabrication capabilities, from prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring your components meet exact performance requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project and leverage our expertise in high-performance polymer solutions.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why is Teflon considered an exceptional material choice? Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the key properties that make PTFE commercially valuable? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- What are the chemical compatibility characteristics of PTFE? Unmatched Chemical Resistance for Demanding Applications
- What automotive application benefits from PTFE coating? Enhance Vehicle Reliability and Performance
- What is PTFE and what are its key characteristics? Discover the High-Performance Polymer
- What are the benefits of adding fillers to PTFE? Enhance Wear, Strength, and Performance
- How does expanded PTFE differ from virgin PTFE? Unlock Superior Sealing Performance
- What is the chemical name for Teflon? Unpacking PTFE's Versatile Properties



















