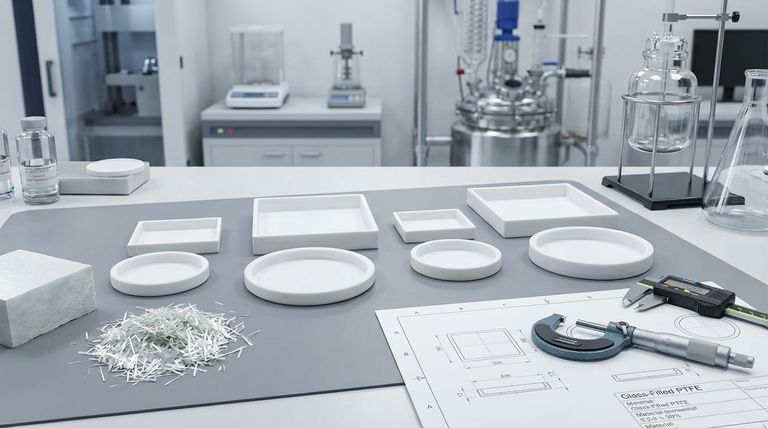
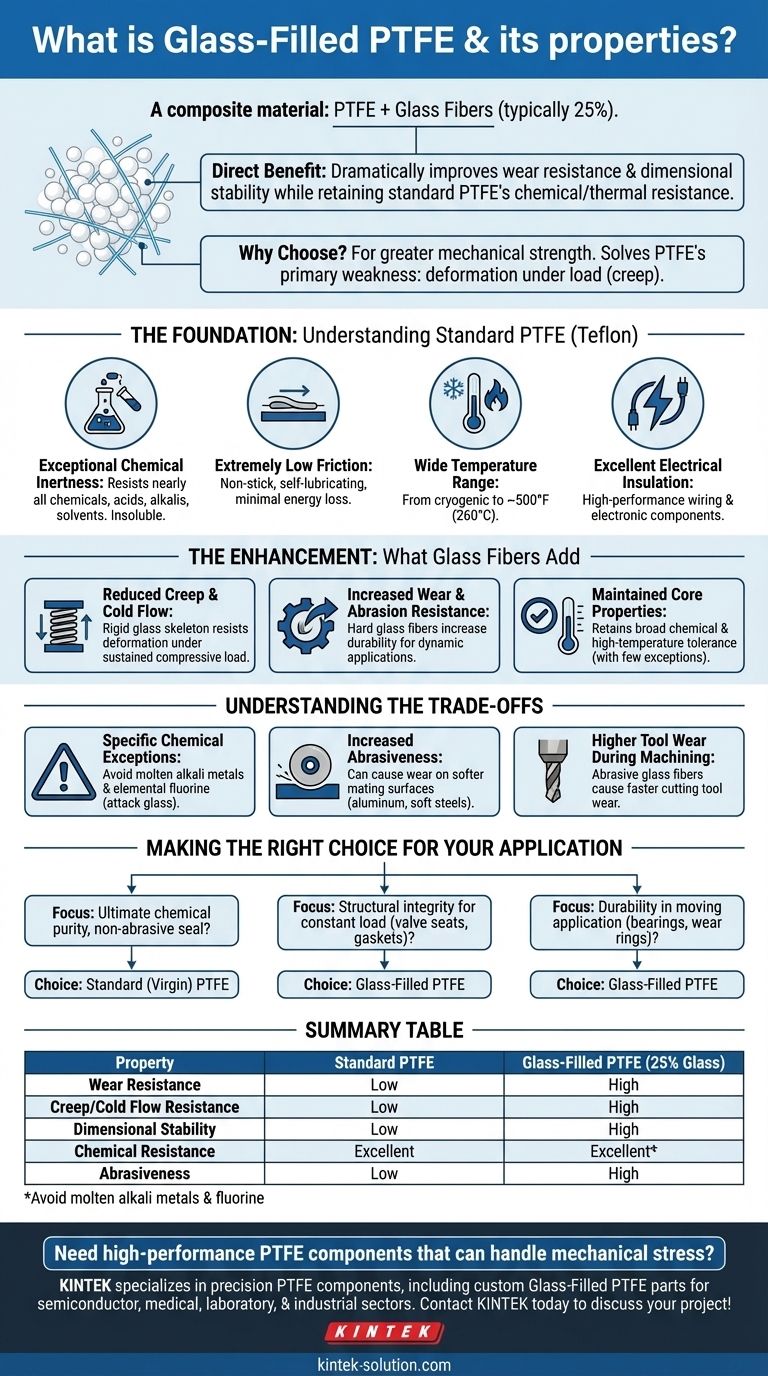
To be direct, Glass-Filled PTFE is a composite material created by adding glass fibers (typically 25% by weight) into a Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) base. This reinforcement dramatically improves key mechanical properties like wear resistance and dimensional stability while retaining the exceptional chemical and thermal resistance inherent to standard PTFE.
The core reason to choose Glass-Filled PTFE over standard PTFE is when your application demands greater mechanical strength. It solves PTFE's primary weakness—its tendency to deform under load (creep)—making it suitable for more demanding structural and dynamic roles.

The Foundation: Understanding Standard PTFE
To appreciate the role of the glass filler, we must first understand the remarkable properties of the base material, PTFE, commonly known by the brand name Teflon.
Exceptional Chemical Inertness
PTFE is renowned for its resistance to nearly all chemicals, including aggressive acids, alkalis, and organic solvents. It is almost completely insoluble, making it a default choice for handling corrosive fluids.
Extremely Low Friction
The material has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid. This results in a non-stick, self-lubricating surface ideal for components that need to slide easily with minimal energy loss.
Wide Temperature Range
PTFE performs reliably across a vast temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions up to approximately 500°F (260°C). This thermal stability allows it to be used in extreme environments where other plastics would fail.
Excellent Electrical Insulation
As a strong electrical insulator, PTFE is frequently used in high-performance wiring, connectors, and other electronic components where signal integrity is critical.
The Enhancement: What Glass Fibers Add
While standard PTFE is an excellent material, it is mechanically soft. The addition of glass fibers directly addresses this limitation.
Reduced Creep and Cold Flow
This is the most significant improvement. Creep, or cold flow, is the tendency of pure PTFE to slowly deform or "flow" when subjected to a sustained compressive load. The embedded glass fibers provide a rigid skeleton, dramatically increasing the material's resistance to this deformation.
Increased Wear and Abrasion Resistance
The hardness of the glass fibers substantially increases the material's durability. This makes Glass-Filled PTFE far superior for dynamic applications like bearings, seals, and piston rings where it will be subjected to friction and abrasion.
Maintained Core Properties
Crucially, Glass-Filled PTFE retains the broad chemical resistance and high-temperature tolerance of the virgin PTFE it is based on. It functions in the same chemical environments with only a few exceptions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material enhancement comes without compromise. Understanding the downsides is critical for proper application.
Specific Chemical Exceptions
While chemical resistance remains excellent, the glass filler is not as inert as the PTFE matrix. The material should not be used with molten alkali metals or elemental fluorine, which can attack the glass.
Increased Abrasiveness
The hardness that improves wear resistance can also be a liability. Glass-Filled PTFE is more abrasive than unfilled PTFE and can cause wear on softer mating surfaces, such as shafts made from aluminum or softer steels.
Higher Tool Wear During Machining
While still machinable, the abrasive nature of the glass fibers will cause significantly faster wear on cutting tools compared to machining standard, unfilled PTFE.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct material requires a clear understanding of your primary engineering goal.
- If your primary focus is ultimate chemical purity or a non-abrasive seal against a soft metal surface: Standard (virgin) PTFE is the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity for parts under constant load, like valve seats or gaskets: Glass-Filled PTFE is necessary to prevent cold flow and maintain the seal.
- If your primary focus is durability in a moving application, like bearings or wear rings: Glass-Filled PTFE provides the essential wear resistance for a long service life.
Ultimately, choosing the right variant is about balancing PTFE's exceptional chemical and thermal properties with the specific mechanical demands of your design.
Summary Table:
| Property | Standard PTFE | Glass-Filled PTFE (25% Glass) |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Low | High |
| Creep/Cold Flow Resistance | Low | High |
| Dimensional Stability | Low | High |
| Chemical Resistance | Excellent | Excellent* |
| Abrasiveness | Low | High |
| Avoid molten alkali metals & fluorine |
Need high-performance PTFE components that can handle mechanical stress?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom Glass-Filled PTFE parts for demanding applications in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We combine material expertise with custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—to deliver solutions that enhance durability and performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your project requirements and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some important physical property values for PTFE? Master Its Extreme Performance for Demanding Applications
- Why is PTFE considered a significant discovery? A Material That Revolutionized Industry
- What is the temperature range that PTFE can withstand? From -200°C to +260°C for Demanding Applications
- What is the working temperature range of PTFE? Master Extreme Heat and Cryogenic Applications
- How is PTFE used in industrial processes? Maximize Safety and Efficiency



















