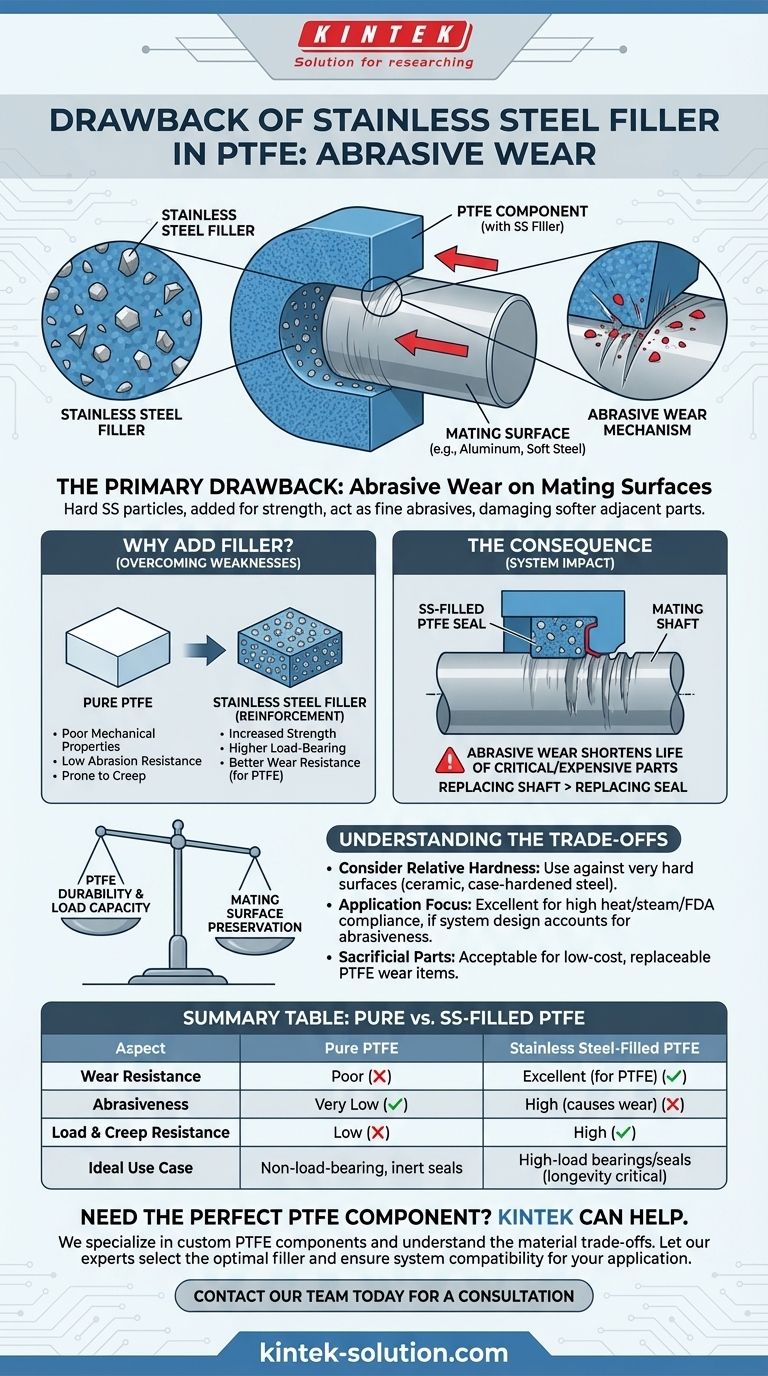
The primary drawback of using stainless steel filler in Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is its potential to cause abrasive wear on the mating surfaces it comes into contact with. While the filler dramatically improves the properties of the PTFE component itself, this hardness can damage softer, adjacent parts within a mechanical system.
The core issue is a fundamental trade-off: Fillers are added to PTFE to overcome its natural softness and low wear resistance. However, adding a hard material like stainless steel can make the resulting composite abrasive, potentially wearing down the very components it is designed to work with.

Why Fillers Are Added to PTFE
To understand the drawback, we must first understand the purpose of the filler. The decision to use filled PTFE is a direct response to the inherent limitations of the pure polymer.
The Weaknesses of Pure PTFE
Pure PTFE is exceptionally slick and chemically inert, but it has poor mechanical properties. It suffers from low abrasion resistance and is prone to creep, which is the tendency to slowly deform under a constant load.
This makes it unsuitable for demanding applications like high-load bearings or dynamic seals, where it would quickly fail or deform.
The Role of Stainless Steel Filler
Adding stainless steel powder to the PTFE matrix fundamentally changes its character. The filler acts as a reinforcing agent, significantly increasing strength, load-bearing capability, and the wear resistance of the PTFE part itself.
This makes it a robust material that performs well at high temperatures and in environments with steam or hot liquids.
The Primary Drawback: Abrasiveness
The very hardness that gives stainless steel-filled PTFE its strength is also the source of its main disadvantage.
Understanding the Wear Mechanism
The microscopic stainless steel particles embedded within the softer PTFE can act like a fine abrasive. As the filled PTFE part slides against another surface—such as a rotating shaft or a housing—these hard particles can scratch, score, and gradually wear away the material.
This effect is most pronounced when the mating surface is made of a softer material, such as aluminum, brass, or even unhardened steel.
Impact on System Longevity
This abrasive wear is not a failure of the PTFE component; in fact, the filled PTFE part will likely have a very long life. The problem is that it can shorten the life of other, often more critical or expensive, parts of the assembly.
Replacing a worn-out shaft is typically far more costly and difficult than replacing a simple seal or bearing.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a material is always about balancing competing properties. Stainless steel-filled PTFE is an excellent material when its trade-offs are understood and managed.
Durability vs. Mating Surface Preservation
The central choice is between maximizing the durability of the PTFE component and preserving the integrity of the surface it runs against. If the PTFE part is a low-cost, easily replaceable wear item, its abrasiveness might be an acceptable price for its own longevity.
Consider the Hardness of Mating Surfaces
The abrasive effect is highly dependent on the relative hardness of the two surfaces. If stainless steel-filled PTFE is used against a very hard surface, like a ceramic coating or a case-hardened steel shaft, the wear on that surface will be minimal. The problem arises when the mating surface is significantly softer.
Benefits in Demanding Environments
In applications subject to high heat, steam, or those requiring FDA compliance for the food industry, the unique benefits of stainless steel filler can make it the best option. The key is to ensure the complete system design accounts for its abrasive nature.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Ultimately, the decision depends on the goals and constraints of your specific design.
- If your primary focus is preserving an expensive or integrated mating surface (like a precision shaft): You must either use a non-abrasive filler or ensure the mating surface is significantly harder than the filler particles.
- If your primary focus is the longevity of the PTFE component in a high-load or high-temperature environment: Stainless steel-filled PTFE is an excellent choice, provided you have accounted for its effect on adjacent parts.
- If you are designing a system with a low-cost, sacrificial PTFE part: Its durability may be the most important factor, making stainless steel filler a logical option.
Choosing the right material requires you to think about the entire system, not just a single component.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Pure PTFE | Stainless Steel-Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Wear Resistance | Poor | Excellent (for the PTFE part) |
| Abrasiveness to Mating Surfaces | Very Low | High (can cause wear) |
| Load-Bearing & Creep Resistance | Low | High |
| Ideal Use Case | Non-load-bearing, chemically inert seals | High-load bearings/seals where PTFE longevity is critical |
Need the Perfect PTFE Component for Your System?
Choosing the right filler material is critical to your application's success and longevity. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware.
We understand the intricate trade-offs between material durability and system compatibility. Our experts will work with you to:
- Select the optimal filler (glass, carbon, or stainless steel) based on your specific load, temperature, and environmental requirements.
- Ensure compatibility with your mating surfaces to prevent premature wear and costly downtime.
- Deliver precision parts through custom fabrication, from prototypes to high-volume orders for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Let's optimize your design. Contact our team today for a consultation and quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the key benefits of PTFE in custom fabrication? Unlock Performance in Extreme Conditions
- What are some common applications of machined PTFE? Leverage its Unique Properties for Demanding Applications
- What is PTFE commonly known as and what are its unique properties? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are the primary applications of PTFE fasteners and custom parts? Critical Solutions for Extreme Environments
- What are the material advantages of machining Teflon? Unlock Unmatched Chemical & Thermal Resistance



















