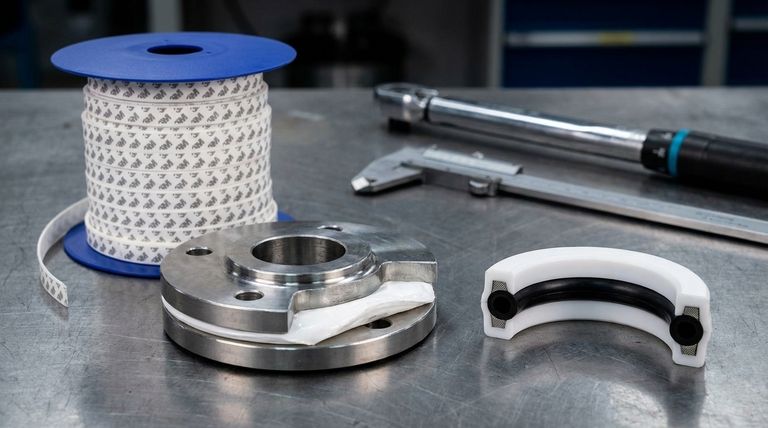
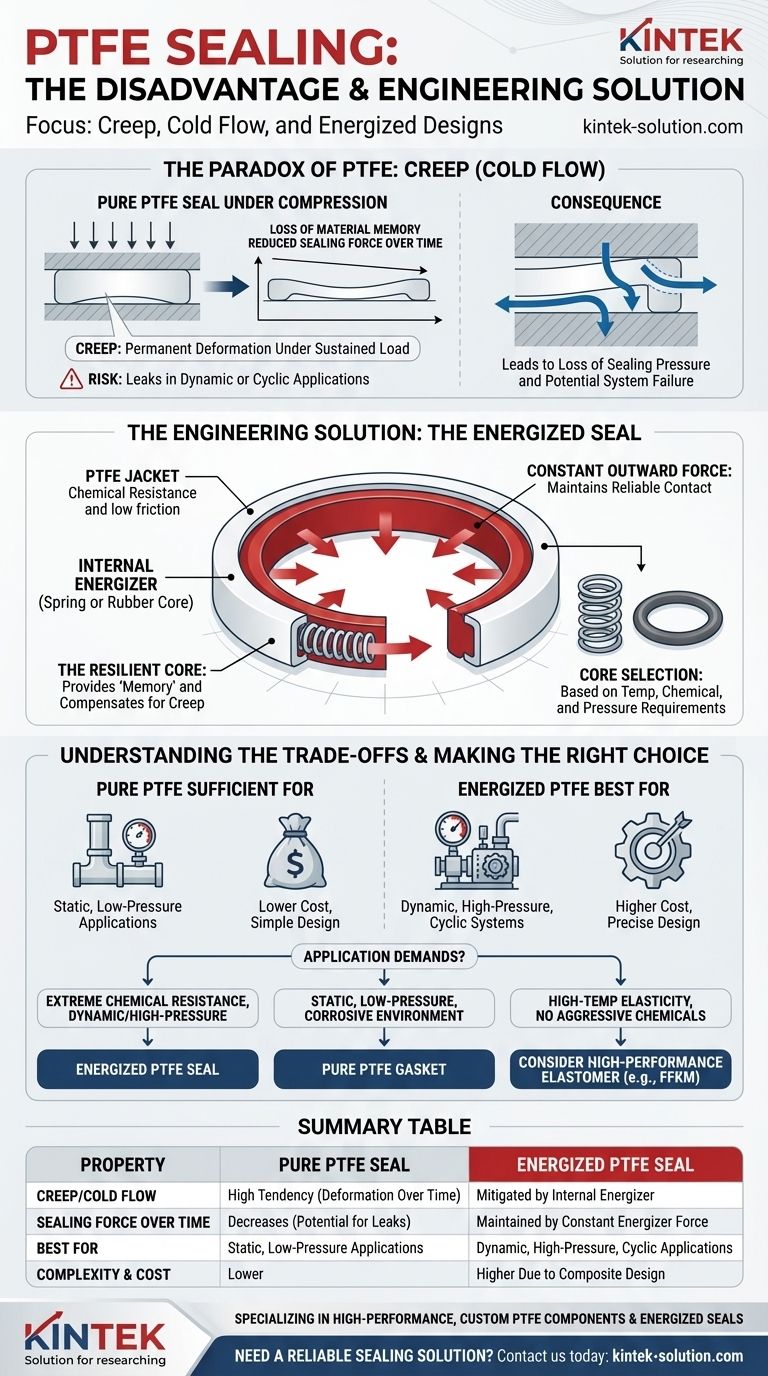
The primary disadvantage of PTFE as a sealing material is its tendency to creep, also known as cold flow, when placed under sustained compression. This means that over time, the material can deform and lose its sealing force. This critical issue is addressed by incorporating a bonded rubber core or a spring energizer inside the PTFE, which provides the constant outward force needed to maintain a reliable seal.
PTFE offers an almost unmatched combination of chemical inertness and low friction, but it lacks the material "memory" of rubber. The central challenge is therefore not avoiding PTFE, but understanding when to use an energized design to compensate for its natural tendency to creep.

The Paradox of PTFE: Understanding Creep
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) has a unique molecular structure that gives it incredible properties, but also this inherent weakness. Understanding this paradox is key to using it effectively.
What is Creep (or Cold Flow)?
Creep is the tendency of a solid material to deform permanently under the influence of persistent mechanical stress. Unlike a rubber O-ring that snaps back to its original shape when pressure is released, PTFE lacks this elastic memory.
Under compression, a pure PTFE seal will slowly flow into the micro-imperfections of a mating surface. This can lead to a loss of the initial sealing pressure.
A Strength and a Weakness
This same lack of memory is what allows a PTFE seal to conform exceptionally well to a surface, creating an excellent initial seal. It effectively "molds" itself into the application.
However, over time and with thermal cycling or pressure fluctuations, this inability to "push back" becomes its primary failure mode. The seal loses its resilience, and leaks can develop.
The Impact on Sealing Performance
The direct consequence of creep is a reduction in the sealing force over time. This can lead to equipment downtime, product contamination, and safety hazards, especially in critical applications.
For this reason, pure, un-energized PTFE gaskets are typically limited to applications where pressure is low and consistent.
The Engineering Solution: The Energized Seal
To harness PTFE's benefits while mitigating its weakness, engineers developed the energized seal. This composite design combines the best properties of multiple materials.
How an Energizer Works
An energized seal consists of a PTFE jacket and an internal energizing element, which is typically a specialized spring or a rubber elastomer core.
The PTFE jacket provides the chemical resistance, low friction, and temperature stability. The internal energizer provides the constant mechanical force, pushing the PTFE jacket outwards against the sealing surfaces.
The Role of the Resilient Core
The rubber core or spring acts as the "memory" for the seal. It ensures that even if the PTFE material begins to creep slightly, there is a continuous and active force maintaining contact and preventing leaks.
This design transforms PTFE from a passive gasket material into a dynamic, highly reliable sealing component suitable for a vast range of demanding conditions.
Selecting the Right Core Material
The core material is chosen based on the specific application's requirements. For example, the temperature and chemical environment dictate whether an NBR, FKM, or silicone rubber core is appropriate. This ensures the energizer itself does not become the point of failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While energized PTFE seals are a powerful solution, they are not a universal replacement for all other seal types. Acknowledging the trade-offs is crucial for proper material selection.
When Pure PTFE is Sufficient
For many static, low-pressure applications, a simple, pure PTFE gasket or washer is perfectly adequate and highly cost-effective. If the compressive load is minimal and consistent, significant creep may not occur.
Cost and Design Complexity
An energized seal is a more complex and therefore more expensive component than a standard O-ring or a simple flat gasket. The design of the hardware gland it fits into is also more precise.
Chemical and Thermal Limitations
While PTFE itself is exceptionally resistant, the energizer can have its own limitations. The overall performance of the seal is dictated by the weakest component. For instance, a seal with a standard NBR rubber core cannot be used in a high-temperature application, even though the PTFE jacket could handle it.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct sealing solution requires you to analyze your system's demands against the properties of the material.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance in a dynamic or high-pressure system: An energized PTFE seal is the optimal choice, combining PTFE's inertness with the resilience needed to maintain a leak-free seal.
- If your primary focus is a static, low-pressure seal in a corrosive environment: A pure, unfilled PTFE gasket is likely sufficient and will be far more cost-effective.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature elasticity without aggressive chemicals: You might investigate a high-performance elastomer like FFKM, as the rubber core in an energized seal could be the limiting factor.
By understanding the principle of creep and its engineered solutions, you can confidently leverage PTFE's remarkable benefits while mitigating its inherent risks.
Summary Table:
| Property | Pure PTFE Seal | Energized PTFE Seal |
|---|---|---|
| Creep/Cold Flow | High tendency | Mitigated by internal energizer |
| Sealing Force Over Time | Decreases | Maintained by constant energizer force |
| Best For | Static, low-pressure applications | Dynamic, high-pressure, or cyclic applications |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher due to composite design |
Need a reliable sealing solution for demanding environments? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components, including advanced energized seals designed to overcome creep. Our expertise in precision fabrication ensures your seals maintain integrity under pressure, temperature fluctuations, and harsh chemicals. Whether you need prototypes or high-volume orders for semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial applications, we deliver the precision and reliability you require. Contact us today to discuss your specific needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PTFE seals in terms of prototyping and production? Accelerate R&D and Ensure Elite Performance
- What are PTFE seals and why are they considered a reliable solution for extreme environments? Engineered for Harsh Conditions
- What are the benefits of using PTFE seals in demanding industries? Solve Extreme Sealing Challenges
- What are the key properties of PTFE that make it suitable for sealing applications? | High-Performance Seals for Extreme Conditions
- What is the overall operating temperature range for PTFE seals, gaskets, and O-rings? Achieve Sealing Integrity from -200°C to +260°C



















