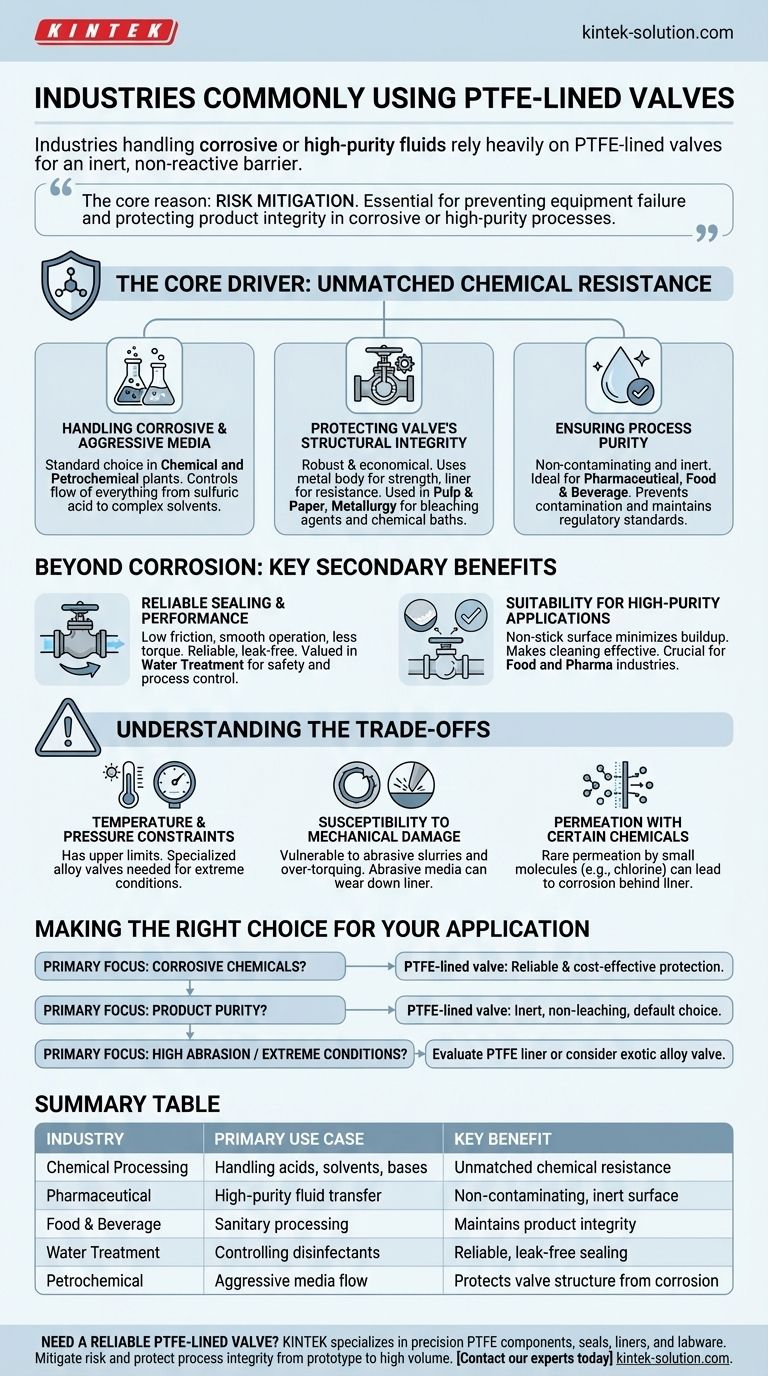
In short, industries that handle corrosive or high-purity fluids rely heavily on PTFE-lined valves. This includes chemical processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, petrochemicals, water treatment, and the food and beverage sectors. These valves are chosen because the PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) lining creates an inert, non-reactive barrier that protects both the valve's structure from aggressive media and the media itself from contamination.
The core reason for using PTFE-lined valves is risk mitigation. Any process involving corrosive chemicals or requiring absolute purity uses them to prevent equipment failure and protect the final product's integrity.

The Core Driver: Unmatched Chemical Resistance
The primary reason engineers specify PTFE-lined valves is their extraordinary ability to withstand chemical attack. This single property makes them essential in a wide range of demanding industrial environments.
Handling Corrosive and Aggressive Media
Many standard metal valves would quickly corrode and fail when exposed to strong acids, solvents, or bases. PTFE is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals.
This makes PTFE-lined valves the standard choice in chemical and petrochemical plants, where they are used to control the flow of everything from sulfuric acid to complex organic solvents.
Protecting the Valve's Structural Integrity
A PTFE-lined valve uses a common, cost-effective metal body (like cast iron or carbon steel) for strength and pressure containment. The liner then provides the chemical resistance.
This composite design offers a robust and economical solution for industries like pulp and paper or metallurgy, which handle bleaching agents and corrosive chemical baths.
Ensuring Process Purity
In many applications, the fluid being transported must remain completely pure. PTFE is an ideal material because it is non-contaminating and does not leach chemicals into the media.
This property is critical in the pharmaceutical and food and beverage industries, where even trace amounts of contamination can ruin a batch or violate regulatory standards.
Beyond Corrosion: Key Secondary Benefits
While chemical inertness is the main advantage, other properties of PTFE make these valves highly effective and reliable in operation.
Reliable Sealing and Performance
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, which allows valve components to operate smoothly with less torque. This results in reliable, leak-free performance over many cycles.
This is especially valued in water treatment facilities, which handle disinfectants and other chemicals where secure shutoff is essential for safety and process control.
Suitability for High-Purity Applications
The non-stick surface of PTFE prevents media from adhering to the valve's internal surfaces. This minimizes buildup and makes cleaning processes, common in food and pharma, much more effective.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly useful, PTFE-lined valves are not a universal solution. Understanding their limitations is key to using them correctly.
Temperature and Pressure Constraints
PTFE has upper temperature and pressure limits. In extreme high-pressure or high-temperature services, a valve constructed entirely from a specialized metal alloy may be required.
Susceptibility to Mechanical Damage
The PTFE lining, while durable, can be damaged by highly abrasive slurries or improper installation (e.g., over-torquing bolts). Abrasive media can wear down the liner over time, leading to eventual failure.
Permeation with Certain Chemicals
While rare, extremely small molecules like chlorine can sometimes slowly permeate a PTFE liner at high temperatures, which can lead to corrosion of the metal body from behind the lining. This must be considered in highly specialized applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct valve depends entirely on your process conditions and primary goal.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals: A PTFE-lined valve is often the most reliable and cost-effective solution for protecting your equipment.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute product purity: The inert, non-leaching nature of PTFE makes it the default choice for pharmaceutical, food, and beverage processes.
- If your primary focus is operating in high-abrasion or extreme temperature/pressure conditions: You must carefully evaluate if a PTFE liner meets your specifications or if a solid exotic alloy valve is necessary.
Ultimately, choosing a PTFE-lined valve is a strategic decision to isolate a process from the corrosive and contaminating effects of the outside world.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Use Case | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Processing | Handling acids, solvents, bases | Unmatched chemical resistance |
| Pharmaceutical | High-purity fluid transfer | Non-contaminating, inert surface |
| Food & Beverage | Sanitary processing | Maintains product integrity |
| Water Treatment | Controlling disinfectants | Reliable, leak-free sealing |
| Petrochemical | Aggressive media flow | Protects valve structure from corrosion |
Need a reliable PTFE-lined valve for your corrosive or high-purity application? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom-fabricated seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We help you mitigate risk and protect your process integrity with solutions tailored from prototypes to high-volume orders. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What finishing techniques are effective for machined Teflon parts? Achieve Functional Performance and Dimensional Stability



















