Thanks to its unique molecular structure and adaptable manufacturing processes, Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) can be manufactured into an exceptionally wide range of forms. These include basic stock shapes like sheets, tubes, and blocks; precision-machined components such as gears, seals, and bearings; protective coatings and linings; and advanced materials like porous membranes.
PTFE’s true value lies not just in its renowned chemical inertness and low friction, but in its profound manufacturing versatility. This allows the raw polymer to be transformed into nearly any geometry required, from simple washers to complex, high-performance mechanical parts.

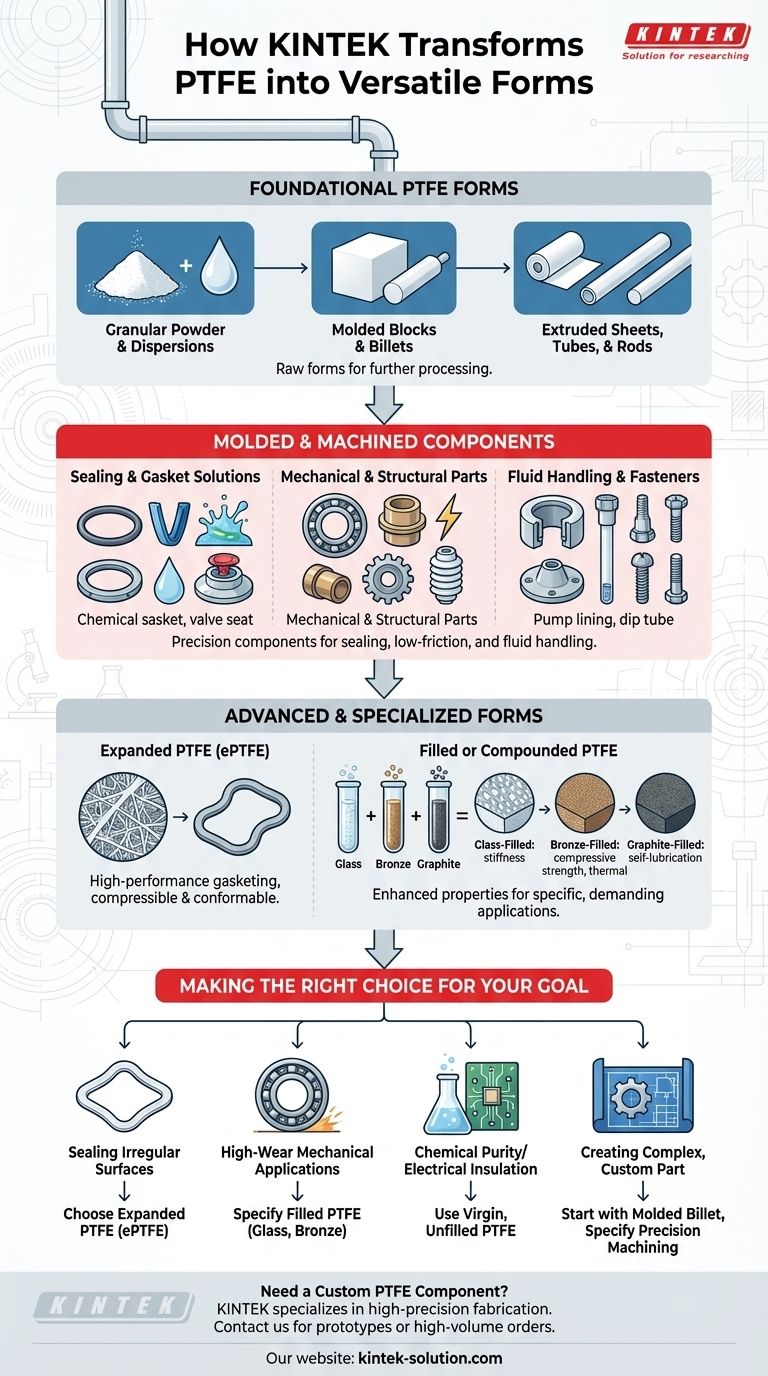
Foundational PTFE Forms
The manufacturing process for most PTFE components begins with one of a few foundational forms. These serve as the raw material for more complex parts or are used directly in applications.
Granular Powder and Dispersions
The journey begins with PTFE in its rawest form: a granular white powder or a fine-powder dispersion. This is the base material created during the polymerization process, which is then used to create all other solid forms.
Molded Blocks and Billets
The raw powder is often processed using compression molding. This involves pressing the grains under immense pressure and heat to create solid stock shapes like blocks, billets, and rods. These are ideal for subsequent machining.
Extruded Sheets, Tubes, and Rods
PTFE can be mixed with a lubricant and extruded through a die to create continuous lengths of a specific profile. This process is used to manufacture standard-sized tubes, rods, and thin sheets.
Common Molded & Machined Components
From basic stock shapes, an enormous variety of finished components can be created through molding or precision machining. This is where PTFE's versatility truly serves engineering needs.
Sealing and Gasket Solutions
PTFE's chemical resistance and compressibility make it a premier sealing material.
- Gaskets, Seals, and Washers: Cut or machined from sheets for flanges and joints.
- O-Rings, V-Rings, and Piston Rings: Molded or machined for dynamic and static sealing in pumps and valves.
- Valve Seats and Balls: Critical components in ball valves, providing a chemically resistant, leak-proof seal.
Mechanical and Structural Parts
The material's low-friction "non-stick" property is leveraged in many moving parts.
- Bearings and Bushings: Allows for smooth, unlubricated motion in mechanical assemblies.
- Gears and Slide Plates: Used where self-lubrication and chemical resistance are paramount.
- Insulators: PTFE's excellent dielectric properties make it a top choice for electrical insulators.
Fluid Handling and Fasteners
Because PTFE is nearly universally inert, it is ideal for components handling corrosive fluids.
- Pump Linings and Dip Tubes: Protects equipment from aggressive chemicals.
- Nozzles: Provides a durable, non-contaminating orifice for fluid transfer.
- Fasteners: PTFE screws, nuts, and bolts are used in environments where metal corrosion is a concern.
Advanced and Specialized Forms
Beyond standard shapes, PTFE can be processed into advanced materials with enhanced properties tailored for specific, demanding applications.
Expanded PTFE (ePTFE)
By physically stretching PTFE under specific conditions, a strong, microporous material called ePTFE is created. It has a multi-directional fibrous structure, making it exceptionally compressible and conformable. This is primarily used for high-performance gasketing on irregular or damaged surfaces.
Filled or Compounded PTFE
To enhance specific mechanical properties, PTFE can be blended with other materials.
- Glass-Filled PTFE: Increases stiffness and wear resistance.
- Bronze-Filled PTFE: Significantly improves compressive strength and thermal conductivity.
- Graphite-Filled PTFE: Enhances self-lubricating properties and lowers the coefficient of friction further.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a PTFE form is not just about the final shape; the manufacturing method and composition directly impact performance and cost.
Machining vs. Molding
Molding is cost-effective for producing large quantities of relatively simple, standard parts like O-rings or basic seals. Machining from stock billets provides high precision and is ideal for complex geometries, prototypes, or low-volume production runs, but it comes at a higher per-unit cost.
Virgin PTFE vs. Filled Grades
Virgin PTFE offers the highest chemical purity and best electrical insulation properties. However, it is susceptible to "creep" or deformation under load. Filled grades dramatically improve mechanical strength, wear resistance, and stability, but these additives may slightly reduce the material's overall chemical resistance and alter its frictional properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct PTFE form is critical to the success of your project. Your primary objective should guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is sealing irregular surfaces: Choose expanded PTFE (ePTFE) for its superior compressibility and adaptability.
- If your primary focus is high-wear mechanical applications: Specify a filled PTFE grade (e.g., glass or bronze) machined into a bearing, bushing, or gear.
- If your primary focus is chemical purity or electrical insulation: Use components machined from virgin, unfilled PTFE stock.
- If your primary focus is creating a complex, custom part: Start with a molded billet or rod of the appropriate PTFE grade and specify a precision machining process.
Ultimately, PTFE's adaptability from a simple powder into countless finished forms makes it one of the most versatile problem-solving materials in modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| PTFE Form Category | Key Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Foundational Forms | Granular Powder, Molded Blocks, Extruded Tubes/Rods | Raw material for further processing, stock shapes |
| Molded & Machined Components | Seals, Gaskets, Bearings, Bushings, Insulators | Sealing solutions, low-friction mechanical parts, electrical insulation |
| Advanced & Specialized Forms | Expanded PTFE (ePTFE), Glass/Bronze/Graphite-Filled PTFE | High-performance gasketing, enhanced wear resistance, improved lubrication |
Need a Custom PTFE Component?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components—from seals and liners to complex labware and mechanical parts. Whether you require prototypes or high-volume orders, our expertise in custom fabrication ensures your parts meet exact specifications for chemical resistance, low friction, and durability.
Let's discuss your project requirements: Contact our team today to get a quote and see how our PTFE solutions can enhance your application in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, or industrial sectors.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are some common applications of Teflon bushings in machinery? Solve Friction in Harsh Environments
- How do PTFE and NBR oil seals compare in terms of flexibility and installation? Choose the Right Seal for Your Application
- What is PTFE and why is it used in mechanical seals? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Low Friction
- How does a PTFE rotary lip seal work? Unlock Low-Friction Sealing for Demanding Applications
- What other factors influence the CNC machining quality of PTFE parts? Master Material, Environment & Skill
- What is the basic structure and working principle of PTFE O-ring seals? Unlock Superior Sealing Performance
- How does the wide temperature range of PTFE gaskets benefit industrial applications? Achieve Reliable Sealing from -200°C to +260°C
- What are the five outstanding characteristics of PTFE seals? Engineered for Extreme Performance



















