When selecting a Teflon O-ring, you must evaluate the fundamental trade-off between the two primary types: solid and encapsulated. The decision hinges on your application's specific requirements for chemical resistance, temperature range, and mechanical flexibility. A proper choice involves analyzing the working environment and ensuring the O-ring's material properties can provide a reliable, long-lasting seal.
The core decision in selecting a Teflon O-ring is not just about the material, but its form. You must choose between the absolute chemical and thermal resistance of a rigid, solid O-ring and the balanced flexibility and resilience of an encapsulated one.

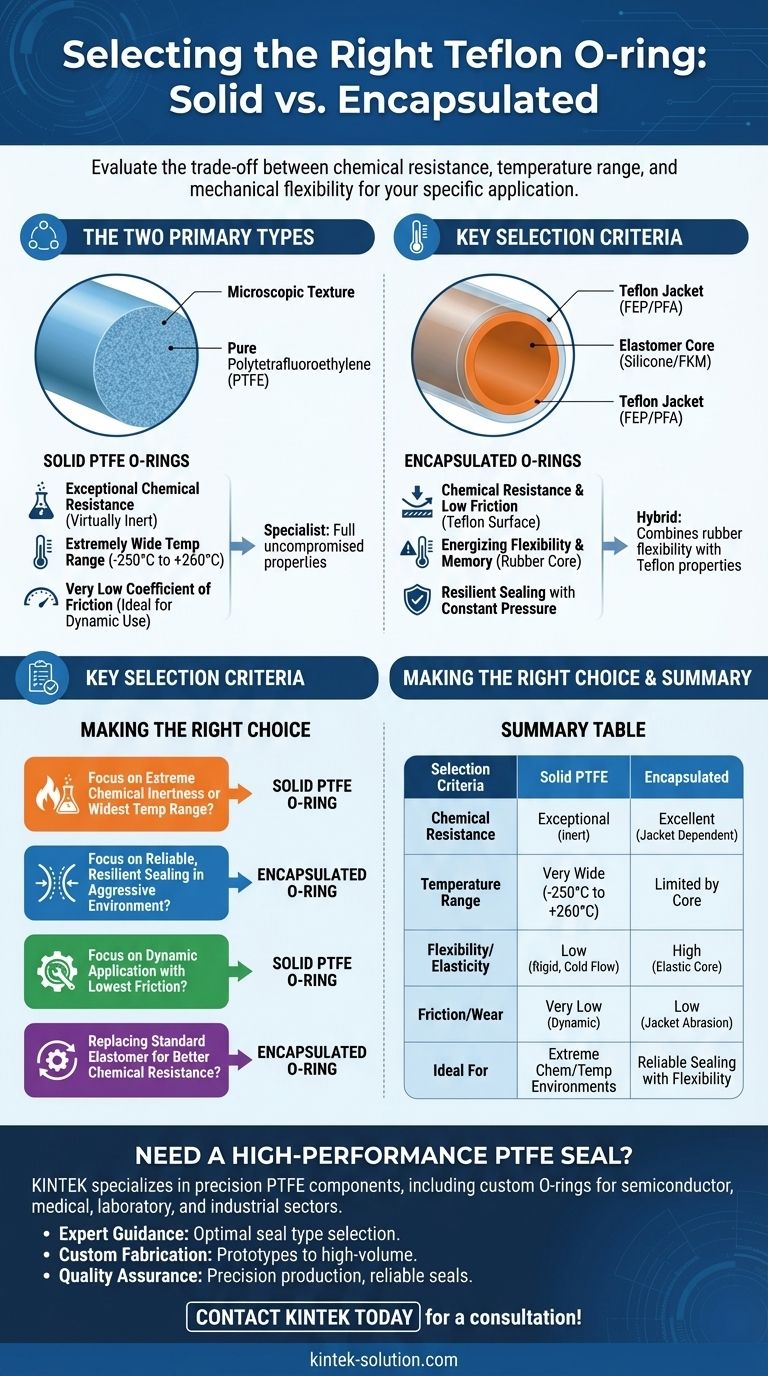
The Two Primary Types of Teflon O-Rings
Understanding the construction of each type is the first step in making an informed decision. Their differences in design directly translate to significant differences in performance.
Solid PTFE O-Rings: The Specialist
A solid Teflon O-ring is machined from pure Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE). This gives it the full, uncompromised properties of the material.
These O-rings offer exceptional chemical resistance, making them virtually inert to most industrial chemicals. They also operate across an extremely wide temperature range, typically from -250°C to +260°C.
Furthermore, their very low coefficient of friction makes them ideal for dynamic applications where minimal wear and non-stick properties are critical.
Encapsulated O-Rings: The Hybrid
An encapsulated O-ring features a dual-material construction. It consists of an elastomer core, usually Silicone or FKM (Viton®), which is seamlessly enclosed within a thin jacket of Teflon FEP or PFA.
This design combines the best of both worlds: the energizing flexibility and memory of a rubber O-ring with the chemical resistance and low friction of a Teflon surface. The core provides the constant outward pressure needed for a reliable seal.
Key Selection Criteria: Matching the O-Ring to the Application
Once you understand the two types, you can evaluate them against the specific demands of your system.
Chemical Compatibility
Both types offer excellent chemical resistance. However, a solid PTFE O-ring is superior for the most extreme chemical environments, as the entire component is chemically inert. The resistance of an encapsulated O-ring depends on the integrity of its thin outer jacket.
Temperature Range
For the broadest possible operating temperature range, solid PTFE is the clear choice. An encapsulated O-ring's temperature limits are dictated by its elastomer core, which is generally less tolerant of extreme heat and cold than solid PTFE.
Mechanical Performance and Elasticity
This is the most critical point of distinction. Encapsulated O-rings behave much like traditional rubber seals. Their elastic core allows them to compress, conform to surface imperfections, and rebound, ensuring a tight, resilient seal.
Solid PTFE is a rigid material with poor elastic memory. It does not spring back well after being compressed and can be prone to "cold flow," or permanent deformation under sustained pressure.
Friction and Wear
For dynamic seals where parts slide against the O-ring, the low friction of solid PTFE provides a distinct advantage, minimizing drag and wear. While encapsulated rings also have a low-friction surface, the thin jacket is more susceptible to abrasive damage.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
Choosing the wrong type of O-ring can lead to premature failure, leaks, and costly downtime.
The Rigidity of Solid PTFE
The primary drawback of solid PTFE is its inflexibility. This can make installation difficult, often requiring special care to avoid scratching or deforming the ring. Its lack of elasticity means it is less forgiving of imperfections in the sealing surfaces.
The Vulnerability of Encapsulated Jackets
The main weakness of an encapsulated O-ring is its outer jacket. If this thin Teflon layer is scratched during installation or damaged by abrasive media in the system, the less-resistant elastomer core can be exposed, leading to chemical attack and seal failure.
Cost Considerations
Due to their more complex, multi-material manufacturing process, encapsulated O-rings are typically more expensive than their solid PTFE counterparts. This cost must be weighed against their superior sealing flexibility in many applications.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be guided by the single most important factor for your system's success.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical inertness or the widest possible temperature range: A solid PTFE O-ring is the most robust choice.
- If your primary focus is reliable, resilient sealing in a chemically aggressive environment: An encapsulated O-ring provides the necessary flexibility that solid PTFE lacks.
- If your primary focus is a dynamic application requiring the lowest possible friction: The inherent non-stick properties of a solid PTFE O-ring offer superior performance.
- If you are replacing a standard elastomer O-ring for better chemical resistance: An encapsulated O-ring will provide a similar sealing feel and performance with upgraded protection.
By correctly identifying your application's most critical demand, you can select a seal that ensures operational reliability and minimizes costly maintenance.
Summary Table:
| Selection Criteria | Solid PTFE O-Ring | Encapsulated O-Ring |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Exceptional (fully inert) | Excellent (depends on jacket integrity) |
| Temperature Range | Very Wide (-250°C to +260°C) | Limited by elastomer core |
| Flexibility / Elasticity | Low (rigid, prone to cold flow) | High (elastic core for resilient seal) |
| Friction / Wear | Very Low (ideal for dynamic seals) | Low (but jacket can be abraded) |
| Ideal For | Extreme chemical/temperature environments | Reliable sealing with flexibility |
Need a High-Performance PTFE Seal for Your Application?
Choosing between solid and encapsulated Teflon O-rings is critical for your system's reliability. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE components, including custom O-rings, for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Help you select the optimal seal type for your specific chemical, temperature, and mechanical requirements.
- Custom Fabrication: From prototypes to high-volume orders, ensuring a perfect fit and performance.
- Quality Assurance: Precision production for reliable, long-lasting seals that minimize downtime.
Let our experts help you solve your sealing challenges. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What environmental factors should be considered when choosing PTFE sheets? Ensure Long-Term Performance
- Why are PTFE envelope gaskets preferred in pharmaceutical and food industries? Ensure Absolute Product Purity
- What is a PTFE coating thrust washer? Achieve Low-Friction, High-Performance Axial Load Management
- What factors should be considered when choosing PTFE packings? Select the Right Packing for Optimal Sealing
- What types of PTFE processing machines are commonly used? From Extrusion to Precision Machining
- What are the properties and uses of bronze-filled PTFE? A Guide to High-Performance Mechanical Components
- In which applications are PTFE O-rings commonly used? Critical Seals for Extreme Environments
- What are the advantages of PTFE in chemically aggressive environments? Unmatched Chemical Resistance & Reliability



















