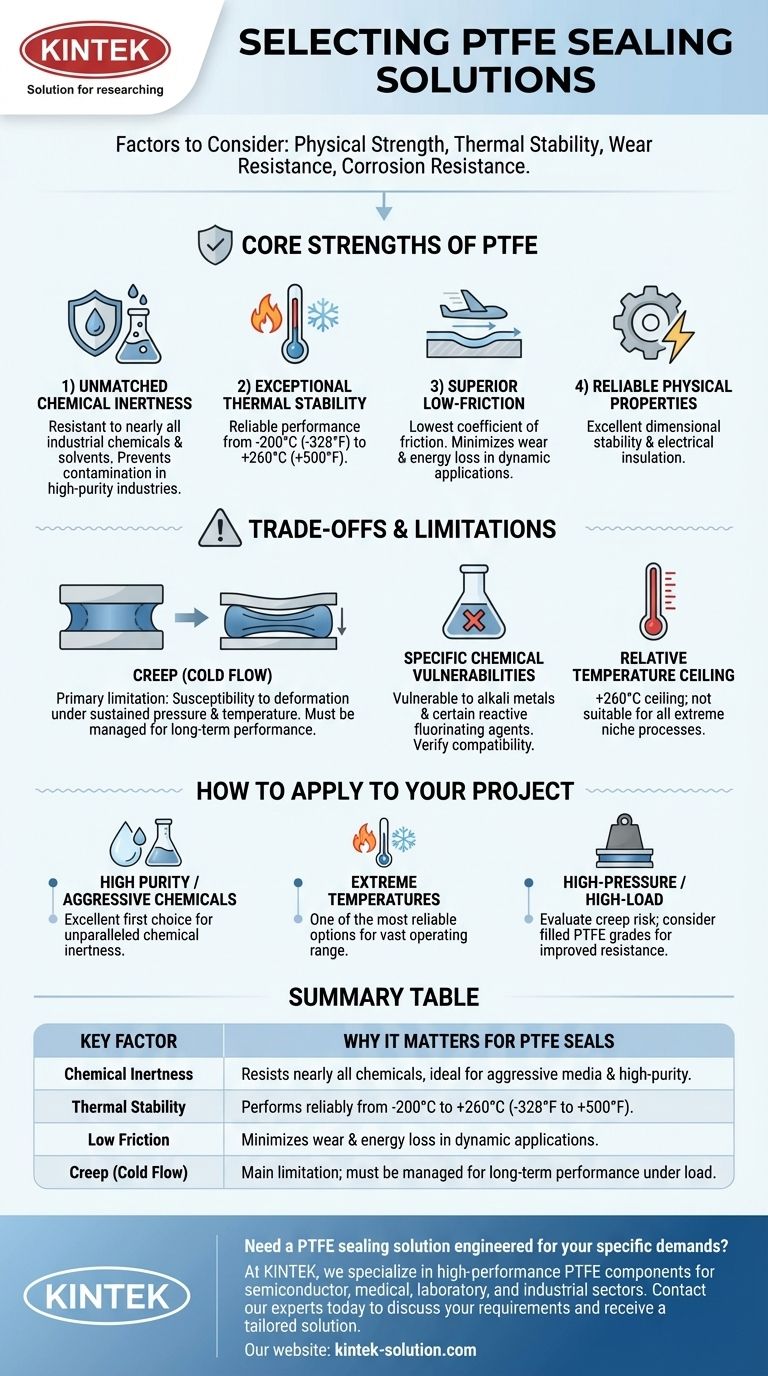
To select the right PTFE sealing solution, you must evaluate four primary factors: its physical strength, thermal stability across your operating temperature range, wear resistance, and its corrosion resistance against the specific media being sealed. A detailed assessment of these properties against your application's demands is essential for ensuring operational efficiency and preventing costly equipment failure.
While Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is an exceptionally versatile and reliable sealing material, its primary limitation is a susceptibility to creep, or cold flow, under pressure. Understanding this trade-off is the key to selecting the right seal for long-term performance.

The Core Strengths of PTFE Seals
PTFE is a default choice for many demanding industrial applications because of its unique combination of beneficial properties. It provides a level of performance that few other materials can match across such a wide range of conditions.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is resistant to nearly all industrial chemicals and solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for aggressive chemical processing.
Its inert nature also prevents it from contaminating the media it contacts. This is critical for high-purity industries like pharmaceuticals, food and beverage, and electronics manufacturing.
Exceptional Thermal Stability
PTFE seals perform reliably across an incredibly broad temperature spectrum, from cryogenic lows of -200°C (-328°F) up to high-heat applications of +260°C (+500°F).
This wide operating window allows it to maintain its key properties, like stiffness and strength, in conditions where many other materials would fail.
Superior Low-Friction Performance
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid material, often compared to wet ice on wet ice.
This characteristic minimizes wear and energy loss in dynamic sealing applications, such as in rotating shafts or pistons, contributing to a longer service life and greater efficiency.
Reliable Physical Properties
Beyond its primary benefits, PTFE offers excellent dimensional stability, meaning it holds its shape well under stress. It also serves as a fantastic electrical insulator, adding to its versatility in complex equipment.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
No material is perfect. Acknowledging PTFE's specific limitations is crucial for avoiding misapplication and potential seal failure. Being aware of these trade-offs allows you to make a more informed decision.
The Challenge of Creep (Cold Flow)
The most significant drawback of pure PTFE is its tendency to creep, also known as cold flow.
Under sustained pressure and temperature, the material can slowly deform and "flow" away from the compressive load. This can cause the sealing force to decrease over time, potentially leading to leaks.
Specific Chemical Vulnerabilities
While highly resistant, PTFE is not completely immune to all substances. It can be attacked by some alkali metals and certain highly reactive fluorinating agents.
You must always verify its compatibility with the specific chemicals in your system, especially if harsh alkalis are present.
Relative Temperature Ceiling
The operational ceiling of +260°C is suitable for a vast number of applications. However, some specialized industrial processes may require materials with even higher temperature resistances.
In these niche cases, other materials might be a more appropriate, albeit more expensive, choice.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your final decision should be guided by the most critical demand of your specific application. Use these points as a starting framework for your evaluation.
- If your primary focus is high purity or aggressive chemicals: PTFE is an excellent first choice due to its unparalleled chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is performance across extreme temperatures: PTFE's vast operating range makes it one of the most reliable options available.
- If your primary focus is a high-pressure or high-load static seal: You must carefully evaluate the risk of creep; consider filled PTFE grades, which add materials like glass or carbon to improve resistance to cold flow.
Ultimately, matching the unique properties of a material to the specific demands of its environment is the foundation of reliable engineering.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Why It Matters for PTFE Seals |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists nearly all chemicals, ideal for aggressive media and high-purity applications. |
| Thermal Stability | Performs reliably from -200°C to +260°C (-328°F to +500°F). |
| Low Friction | Minimizes wear and energy loss in dynamic applications. |
| Creep (Cold Flow) | The main limitation; must be managed for long-term performance under load. |
Need a PTFE sealing solution engineered for your specific demands?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-performance PTFE components—including seals, liners, and custom labware—for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We prioritize precision and offer custom fabrication from prototypes to high-volume orders to ensure your seals deliver unmatched chemical resistance, thermal stability, and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss your application requirements and receive a tailored solution that enhances your operational efficiency and prevents costly downtime.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of choosing PTFE washers? Unlock Superior Sealing in Extreme Conditions
- What factors affect PTFE seal performance? Optimize Your System for Reliability & Longevity
- How do PTFE coated washers enhance sealing applications? Ensure Leak-Free Performance in Demanding Environments
- What role does PTFE play in the printing and packaging industry? Enhancing Efficiency and Quality
- How can tight tolerances be achieved in CNC-machined PTFE parts? Master Precision Machining for Stable Components
- How often should PTFE sliding bearings be lubricated? A 3-Year Guide to Structural Integrity
- Is ePTFE gasket material safe for food and pharmaceutical applications? Ensuring Purity and Compliance
- In which industries are Teflon backup rings commonly used? Prevent Seal Failure in High-Pressure Systems



















