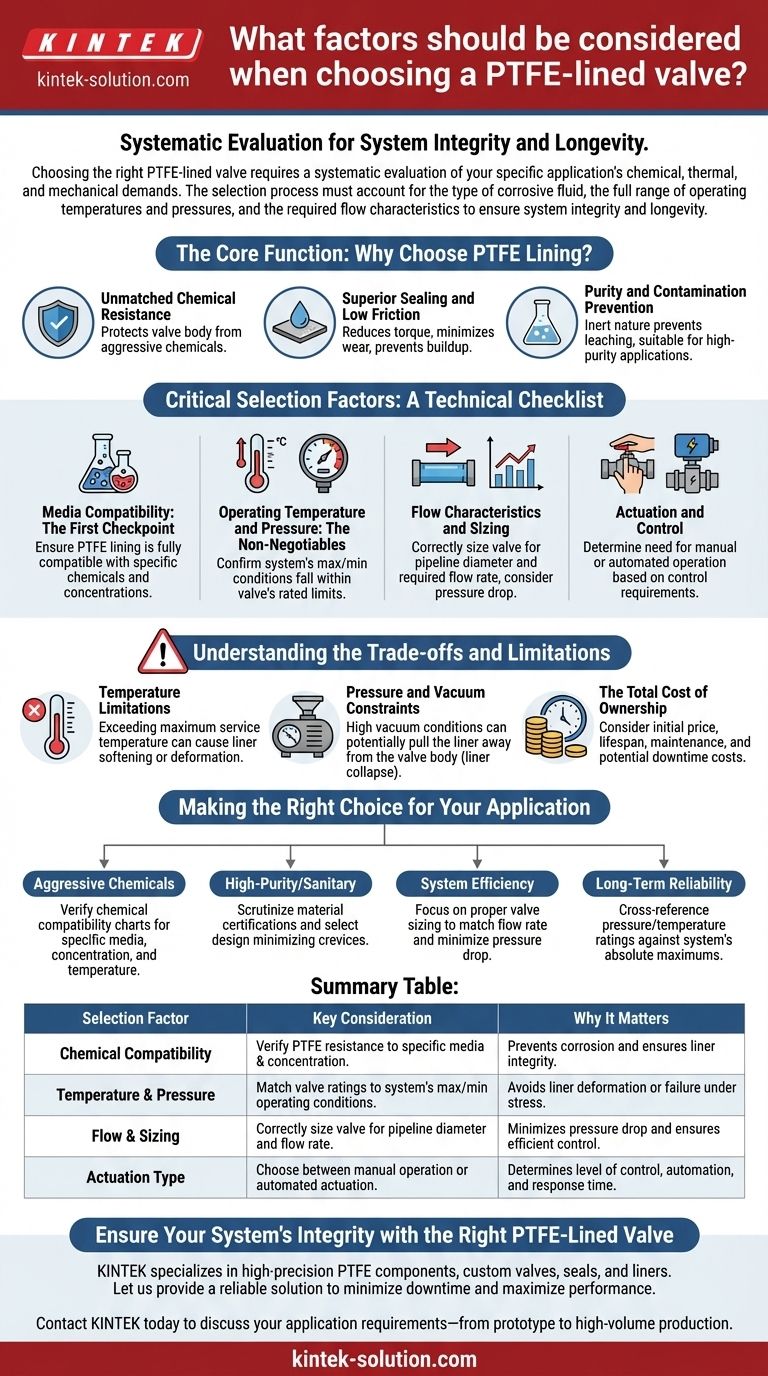
Choosing the right PTFE-lined valve requires a systematic evaluation of your specific application's chemical, thermal, and mechanical demands. The selection process must account for the type of corrosive fluid, the full range of operating temperatures and pressures, and the required flow characteristics to ensure system integrity and longevity.
The primary function of PTFE lining is to ensure chemical compatibility with corrosive or high-purity media. However, a successful selection hinges on verifying that the valve's core mechanical design—its pressure ratings, temperature limits, and size—can withstand the full range of your system's operating conditions.
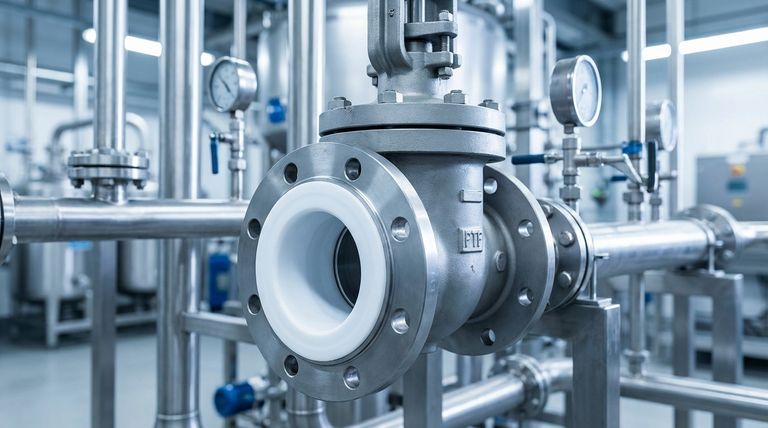

The Core Function: Why Choose PTFE Lining?
PTFE (Polytetrafluoroethylene) lining creates a protective barrier between the valve's metal components and the process media. Understanding its benefits clarifies why it is specified for demanding applications.
Unmatched Chemical Resistance
A PTFE liner acts as a chemically inert shield. It protects the structural metal parts of the valve body from aggressive or corrosive substances, dramatically extending the valve's lifespan in harsh chemical services.
Superior Sealing and Low Friction
PTFE has an extremely low coefficient of friction, resulting in a non-stick surface. This property reduces the torque needed for operation, minimizes wear on valve components, and helps prevent media buildup, which is critical for consistent sealing performance.
Purity and Contamination Prevention
In industries like pharmaceuticals and food processing, preventing contamination is paramount. The inert nature of PTFE ensures that the liner does not leach or react with the process media, preserving its purity.
Critical Selection Factors: A Technical Checklist
To select the appropriate valve, you must methodically match its specifications to your system's requirements. Use these factors as a definitive checklist.
Media Compatibility: The First Checkpoint
You must ensure the PTFE lining is fully compatible with the specific chemicals it will handle, including their concentrations. While PTFE is resistant to most chemicals, certain extreme conditions or specific compounds can pose a challenge.
Operating Temperature and Pressure: The Non-Negotiables
Every valve has a defined operating envelope for temperature and pressure. It is crucial to confirm that your system's maximum and minimum conditions fall safely within the valve's rated limits. The final rating is determined by the weakest component—either the valve body or the PTFE liner itself.
Flow Characteristics and Sizing
The valve must be sized correctly for the pipeline and the required flow rate. Consider factors like pipe diameter and desired pressure drop across the valve to ensure it provides efficient flow control without creating unnecessary system losses.
Actuation and Control
Determine whether the application requires manual operation (e.g., with a lever or handwheel) or automated operation via an electric or pneumatic actuator. This choice depends on the need for process automation, remote control, and response time.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
Objectivity requires acknowledging that even a high-performance material like PTFE has operational boundaries. Ignoring these can lead to premature failure.
Temperature Limitations of PTFE
While robust, PTFE has a maximum service temperature. Exceeding this limit can cause the liner to soften, deform, or lose its structural integrity, leading to valve failure and potential leakage.
Pressure and Vacuum Constraints
The valve's overall pressure rating is a function of both the metal body and the liner's design. Additionally, high vacuum conditions can potentially pull the liner away from the valve body, a phenomenon known as liner collapse, if the valve is not specifically designed for such service.
The Total Cost of Ownership
The initial purchase price is only part of the equation. A proper evaluation includes the total cost of ownership, factoring in expected lifespan, maintenance requirements, and the potential cost of downtime if an unsuitable valve fails.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary goal to prioritize the most critical selection criteria for your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is handling highly aggressive chemicals: Prioritize verifying chemical compatibility charts for your specific media, concentration, and temperature.
- If your primary focus is high-purity or sanitary processes: Scrutinize material certifications and select a valve design that minimizes crevices to prevent media entrapment.
- If your primary focus is system efficiency and control: Focus on proper valve sizing to match your flow rate requirements and minimize pressure drop.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Cross-reference the pressure and temperature ratings of both the PTFE liner and the valve body against your system's absolute maximum operational limits.
A methodical approach ensures your PTFE-lined valve becomes a reliable asset, not a potential point of failure.
Summary Table:
| Selection Factor | Key Consideration | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Compatibility | Verify PTFE resistance to specific media & concentration. | Prevents corrosion and ensures liner integrity. |
| Temperature & Pressure | Match valve ratings to system's max/min operating conditions. | Avoids liner deformation or failure under stress. |
| Flow & Sizing | Correctly size valve for pipeline diameter and flow rate. | Minimizes pressure drop and ensures efficient control. |
| Actuation Type | Choose between manual operation or automated actuation. | Determines level of control, automation, and response time. |
Ensure Your System's Integrity with the Right PTFE-Lined Valve
Selecting the correct valve is critical for the safety and efficiency of your operations in the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom-fabricated valves, seals, and liners.
We understand the demanding environments you operate in. Our expertise ensures that your PTFE-lined valve will be compatible with your specific media and rated for your exact temperature and pressure conditions.
Let us provide you with a reliable solution that minimizes downtime and maximizes performance.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application requirements—from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How do PTFE coated fasteners perform in marine and offshore environments? Superior Corrosion Protection for Critical Assets
- What are the design principles of PTFE radial lip seals? Mastering High-Performance Sealing
- What are some common applications of PTFE in CNC machining? Achieve Superior Performance in Demanding Industries
- In which industries are PTFE bellows commonly used due to their chemical resistivity? Essential for Corrosive & Pure Environments
- What are some applications of PTFE seals? Discover Their Critical Role in Demanding Industries
- What are the limitations of PTFE O-rings' media resistance? Avoid Common Application Traps
- What industries use PTFE piston rings? Key Applications for Oil-Free & Corrosive Environments
- What are the benefits of using PTFE liners in medical procedures? Enhance Safety & Performance



















