Ultimately, the performance of a PTFE seal depends on more than just the seal itself; it is determined by the interplay between the seal's material and design, the hardware it's installed in, and the specific operating conditions it must endure. Success requires a holistic view of the entire sealing system, not just the component.
A PTFE seal is not a simple drop-in replacement for a rubber O-ring. Its success hinges on a systems-engineering approach where the seal material, energizer, and hardware geometry are all precisely matched to the application's temperature, pressure, and motion.
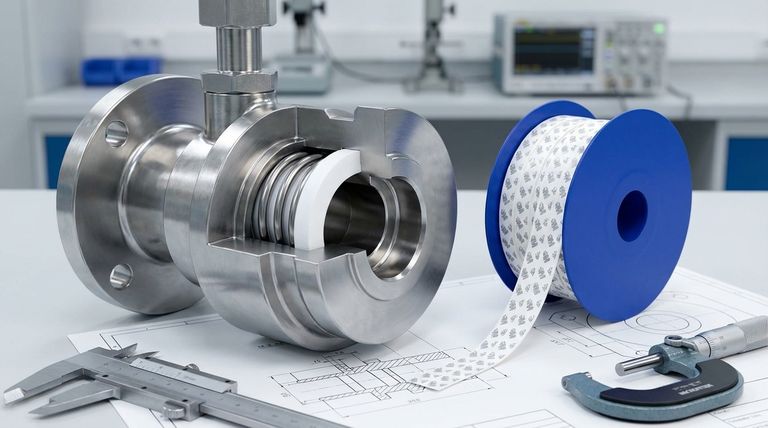

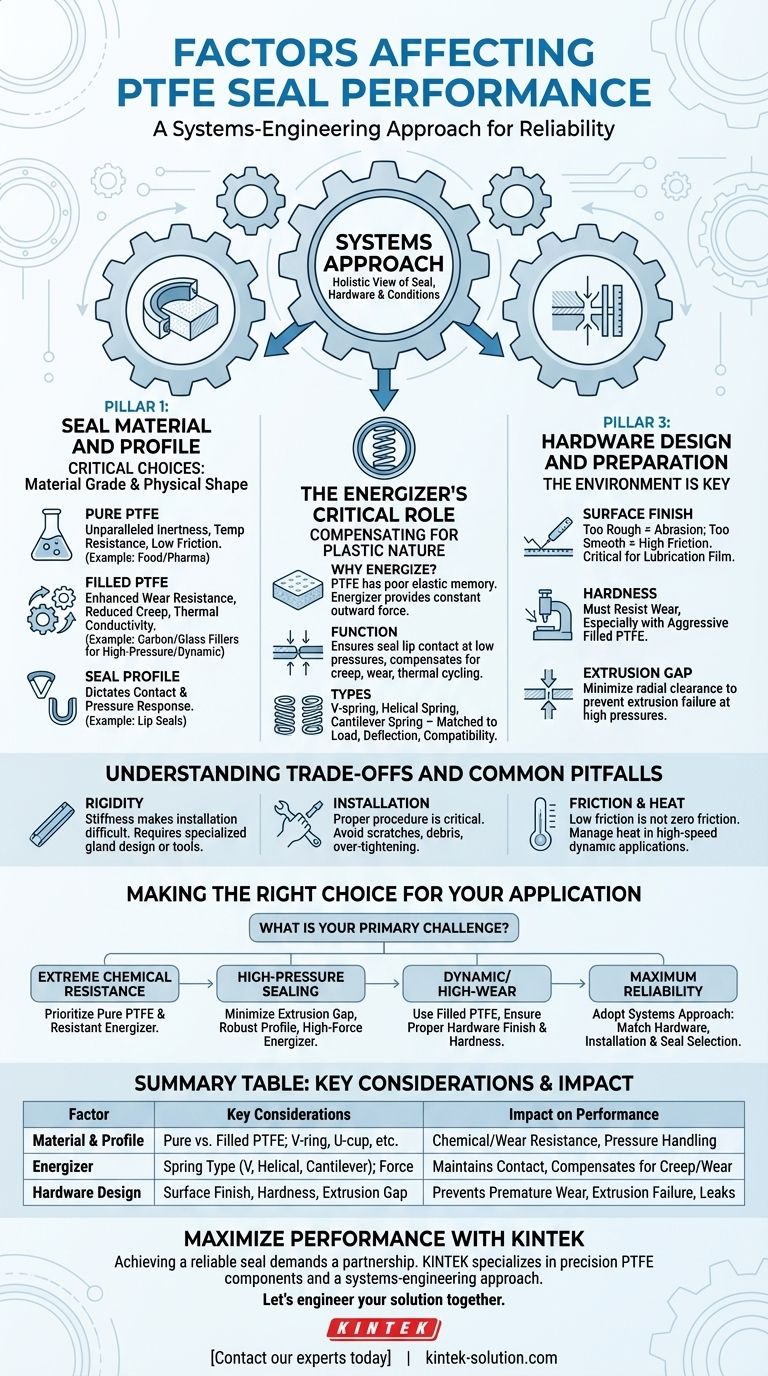
The Three Pillars of PTFE Seal Performance
A reliable sealing solution is built upon three foundational elements. Neglecting any one of these areas will compromise the integrity of the entire system.
Pillar 1: Seal Material and Profile
The specific grade of PTFE and the physical shape of the seal are the first critical choices.
Pure (virgin) PTFE is chosen for its unparalleled chemical inertness and is common in pharmaceutical or food-grade applications. It provides a baseline of excellent temperature resistance and low friction.
Filled PTFE enhances specific properties. Fillers like carbon, glass, or bronze are added to the PTFE matrix to dramatically improve wear resistance, reduce deformation under load (creep), and increase thermal conductivity, making them essential for demanding dynamic or high-pressure service.
The seal profile (e.g., a V-ring, U-cup, or specialized lip seal) must match the application. The shape dictates how the seal makes contact and responds to pressure, directly affecting its efficiency and lifespan.
Pillar 2: The Energizer's Critical Role
Unlike rubber, PTFE is a plastic—it has poor elastic memory and will not rebound to its original shape after being compressed. This is why most high-performance PTFE seals are energized.
An internal spring (or sometimes a rubber O-ring) provides a constant outward force. This energizer ensures the seal lips maintain contact with the hardware surfaces, even at low pressures or during thermal cycling. It compensates for material creep, minor hardware imperfections, and wear over the seal's life.
The choice of energizer—such as a V-spring, helical spring, or cantilever spring—is dictated by the required load, deflection range, and material compatibility needed for the application.
Pillar 3: Hardware Design and Preparation
A perfect seal will fail in poorly designed hardware. The mating components are just as critical as the seal itself.
Surface finish is paramount. A surface that is too rough will abrade the seal lip, causing premature wear. A surface that is too smooth can prevent a microscopic film of lubricating media from forming, increasing friction and heat.
Hardware hardness must be sufficient to resist wear from the seal, especially when using aggressive filled PTFE compounds in dynamic applications.
The extrusion gap (or radial clearance) is the small space between the moving and static hardware components. If this gap is too large, high pressure can physically push the seal material into the gap, destroying it. This is a leading cause of seal failure in high-pressure systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Common Pitfalls
While PTFE offers exceptional performance, its unique properties create specific challenges that must be managed during design and installation.
The Challenge of Rigidity
PTFE's plastic nature and relative stiffness can make installation difficult compared to flexible rubber seals. The hardware grooves and pockets must be designed to facilitate easy, damage-free installation, sometimes requiring multi-part glands or special installation tools.
The Criticality of Installation
Proper installation is not optional. Common failure modes include scratching the seal on sharp edges or threads, failing to clean the hardware of debris, or improperly sizing the seal. Over-tightening retaining hardware can also deform the soft PTFE material, creating a leak path.
Low Friction is Not Zero Friction
While PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any solid, friction still generates heat. In high-speed dynamic applications, this heat must be managed to prevent the seal from exceeding its temperature limits. The presence of system media (lubrication) is a key factor in managing this frictional heat.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Use your primary operational challenge to guide your design and selection process.
- If your primary focus is extreme chemical resistance: Prioritize pure PTFE or a compatible filled grade, and ensure the metal energizer (e.g., stainless steel, Hastelloy) is also resistant to the media.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure sealing: Pay meticulous attention to minimizing the extrusion gap and select a robust seal profile with a high-force energizer.
- If your primary focus is dynamic or high-wear applications: Use a filled PTFE compound and ensure the hardware surface finish and hardness are specified to create a durable, low-friction pairing.
- If your primary focus is maximum reliability and service life: Adopt a systems approach where hardware design, installation procedures, and seal selection are all given equal and thorough consideration.
Treating the seal as one part of an integrated mechanical system is the key to unlocking its full performance potential.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Key Considerations | Impact on Performance |
|---|---|---|
| Material & Profile | Pure vs. filled PTFE; V-ring, U-cup, etc. | Chemical resistance, wear resistance, pressure handling |
| Energizer | Spring type (V, helical, cantilever); force | Maintains seal contact, compensates for creep and wear |
| Hardware Design | Surface finish, hardness, extrusion gap | Prevents premature wear, extrusion failure, and leaks |
Maximize the performance and lifespan of your PTFE seals
Achieving a reliable seal requires more than just a component—it demands a partnership. KINTEK specializes in designing and manufacturing precision PTFE components (seals, liners, labware) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. We bring a systems-engineering approach to every project, from custom prototypes to high-volume production, ensuring your seals are perfectly matched to your application's unique temperature, pressure, and chemical challenges.
Let's engineer your solution together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Sealing Tapes for Industrial and High Tech Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the self-lubricating properties of PTFE rod? Achieve Low-Friction, Maintenance-Free Performance
- Why is it important to consider PTFE lining standards when selecting a supplier? Avoid Costly Failures
- What are the advantages of using Teflon lip seals? Achieve Unmatched Reliability in Extreme Conditions
- What are PTFE seals commonly known as? Discover Teflon® Seals for Extreme Performance
- What are the advantages of mechanical seals with PTFE rings? Superior Chemical & Thermal Resistance
- What are important installation tips for PTFE butterfly valves? Ensure a Leak-Free, Long-Lasting Seal
- What are the disadvantages of PTFE lined butterfly valves? Understanding Key Operational Limits
- What quality certification standards are important for Teflon gland packing? Ensure Long-Term Reliability



















