In control valves, PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a high-performance fluoropolymer prized for its remarkable properties. It is not a type of valve, but rather a critical material used to construct or line valve components to handle highly aggressive or pure fluids.
The core problem that PTFE solves in valve applications is material failure. When dealing with highly corrosive or reactive media, standard metal or plastic valves can degrade, leading to dangerous leaks and system contamination. PTFE provides a chemically inert and non-stick barrier, ensuring the valve's integrity, safety, and reliability in the most demanding environments.

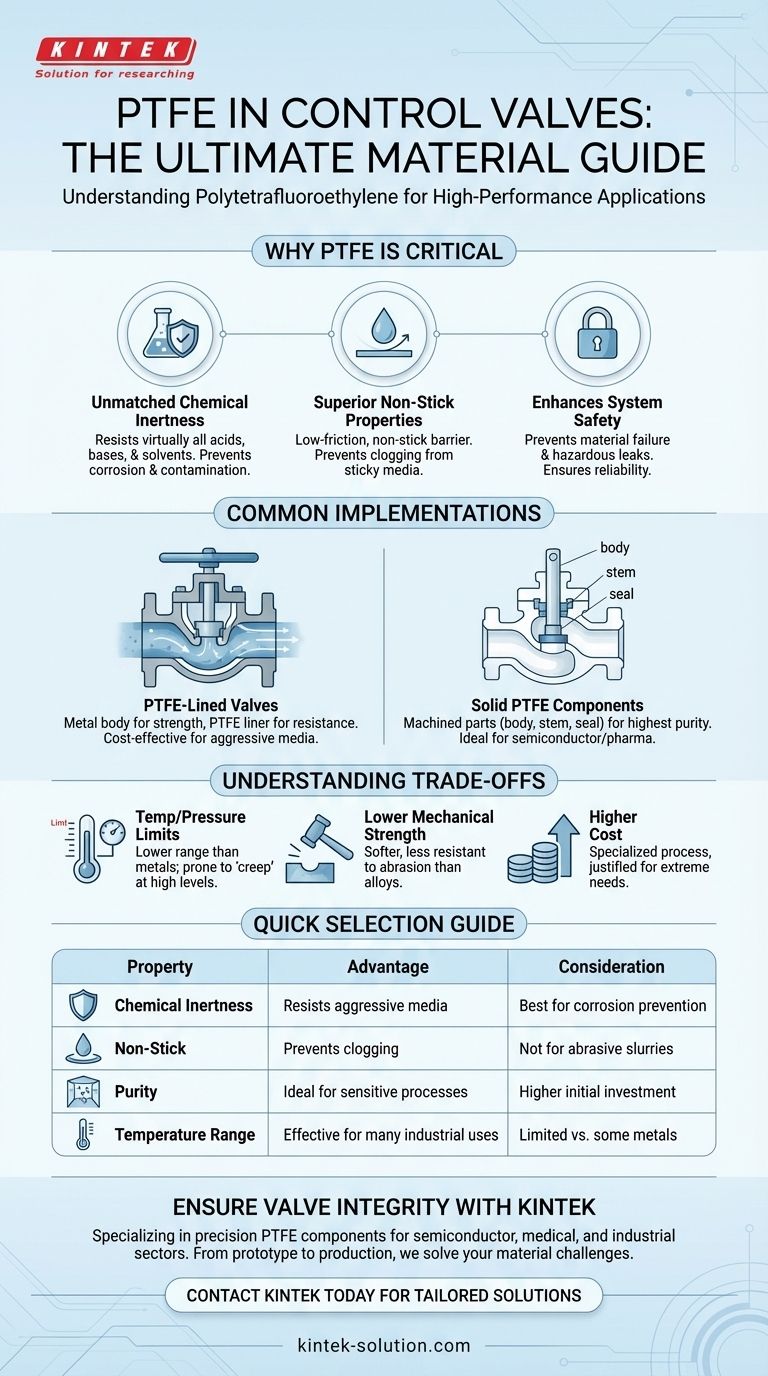
Why PTFE is a Critical Material in Valve Design
The selection of valve materials is dictated by the chemical and physical properties of the media flowing through it. PTFE has a unique combination of characteristics that makes it an indispensable choice for specific, challenging applications.
Unmatched Chemical Inertness
PTFE is renowned for its exceptional resistance to corrosion. It is virtually inert to almost all industrial chemicals, acids, bases, and solvents.
This property ensures that the valve components do not corrode, degrade, or react with the process media. This prevents contamination of the fluid and failure of the valve itself.
Superior Non-Stick Properties
The surface of PTFE is extremely low-friction and non-stick, similar to its common application in cookware.
In a control valve, this means that viscous or sticky media are less likely to adhere to and clog the valve's internal parts. This ensures smooth, reliable operation and helps maintain a pure, unobstructed flow path.
Enhancing System Safety and Reliability
The use of PTFE directly contributes to a safer and more reliable plant operation.
By resisting chemical attack, PTFE-lined or solid PTFE valves prevent material failure that could lead to leaks of hazardous substances. This prevention of unforeseen accidents is critical in chemical processing, manufacturing, and other industrial settings.
Common Implementations of PTFE in Valves
PTFE can be incorporated into valve design in several ways, depending on the application's specific requirements for purity, pressure, and cost.
PTFE-Lined Valves
A common and cost-effective method is to line the wetted parts of a standard metal valve (e.g., ductile iron or stainless steel) with a thick layer of PTFE.
This provides the structural strength and pressure-handling capability of the metal body while offering the complete chemical resistance of the PTFE liner where it matters most—in contact with the fluid.
Solid PTFE Components
For applications demanding the highest purity or facing extremely aggressive media, key valve components can be machined from solid PTFE.
This includes parts like the valve body, ball, stem, and seats. These are common in industries like semiconductor manufacturing or pharmaceuticals, where preventing even trace amounts of contamination is paramount.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While its chemical properties are exceptional, PTFE is not the solution for every application. Understanding its limitations is key to proper valve selection.
Temperature and Pressure Limits
Compared to metals, PTFE has a more limited operating temperature and pressure range. At higher temperatures, it can lose some of its mechanical strength, and under high pressure, it can be susceptible to "creep," or slow deformation.
Lower Mechanical Strength
PTFE is a relatively soft material. It is not as rigid or resistant to physical abrasion as stainless steel or other alloys. In systems with highly abrasive slurries, a PTFE lining can eventually wear down, requiring maintenance or replacement.
Cost Considerations
Due to the specialized manufacturing process, PTFE-lined or solid PTFE valves are typically more expensive than standard all-metal valves. Their use is justified by the need for extreme corrosion resistance or purity that other materials cannot provide.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting a valve with the right material is fundamental to the safety and efficiency of your process. Your decision should be guided by the specific demands of the media you are handling.
- If your primary focus is handling highly corrosive chemicals (like strong acids, bases, or solvents): A PTFE-lined valve is often the most reliable and cost-effective choice for ensuring long-term integrity.
- If your primary focus is maintaining absolute media purity (e.g., in pharmaceutical or semiconductor applications): A valve with solid PTFE wetted parts is essential to prevent any leaching or contamination.
- If your primary focus is high-pressure service without extreme corrosion: A standard metal valve may be a more suitable and economical option, potentially using PTFE only for seals and packing.
Ultimately, understanding the role of PTFE allows you to specify a control valve that guarantees safety, prevents contamination, and delivers reliable performance.
Summary Table:
| Property | Advantage in Control Valves | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Resists almost all acids, bases, and solvents. | Justified for aggressive media. |
| Non-Stick Surface | Prevents clogging from viscous or sticky fluids. | Not ideal for highly abrasive slurries. |
| Purity | Ideal for pharmaceutical and semiconductor applications. | Higher cost than standard metal valves. |
| Temperature Range | Effective for many industrial processes. | Limited compared to some metals. |
Ensure Valve Integrity with Precision PTFE Components from KINTEK
When your application demands uncompromising chemical resistance or absolute purity, the right PTFE components are not just an option—they are a necessity for safety and reliability. KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-performance PTFE seals, liners, and custom labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
We combine precision production with custom fabrication expertise, guiding your project from initial prototype to high-volume production. Our components are engineered to solve the exact material failure challenges described in this article, protecting your systems from corrosion and contamination.
Ready to specify the right valve materials for your critical process?
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application requirements and discover how our tailored PTFE solutions can enhance your system's performance and safety.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? The 3 Pillars Driving Demand for High-Performance Parts
- What industrial benefits do PTFE-machined parts offer? Achieve Peak Performance in Demanding Applications
- What challenges arise when machining PTFE (Teflon)? Overcome Softness, Heat, and Instability
- What are the unique properties of PTFE? Unlock Unmatched Performance in Demanding Applications
- What fabrication services are available for PTFE? Shearing, Stamping, Laser Cutting, Molding & Machining



















