At its most basic level, PTFE stands for Polytetrafluoroethylene. It is a synthetic polymer composed entirely of carbon and fluorine atoms, arranged into a long, repeating chain with the chemical formula (CF₂)n.
The true significance of PTFE lies not just in its name, but in how its simple two-element composition creates one of the strongest chemical bonds in organic chemistry. This carbon-fluorine bond is the source of its legendary non-reactivity, thermal stability, and low-friction surface.
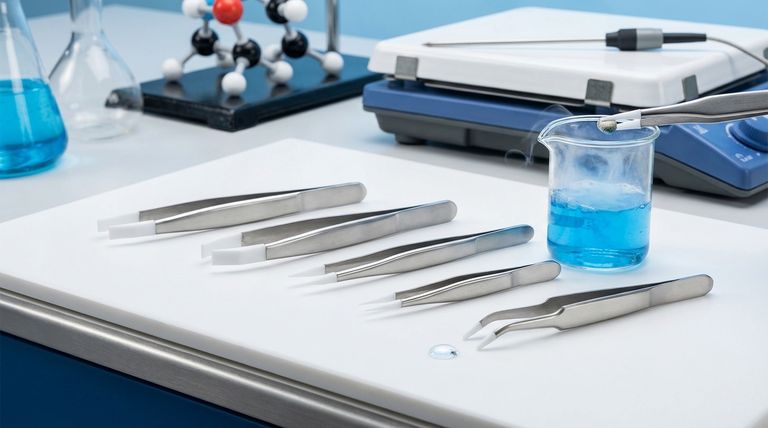
Deconstructing the Chemical Structure
To understand why PTFE behaves the way it does, we must break down its structure and the meaning behind its name.
The Carbon "Backbone"
The foundation of PTFE is a long, stable chain of carbon atoms bonded to one another. This chain structure is common to many polymers, but what's attached to it is what makes PTFE unique.
The Fluorine "Shield"
Each carbon atom in the chain is bonded to two fluorine atoms. These fluorine atoms are relatively large and effectively form a tight, protective sheath around the entire carbon backbone.
The Carbon-Fluorine Bond
The bond between each carbon and fluorine atom is exceptionally strong and stable. This powerful connection is the single most important feature of PTFE's chemistry and the primary reason for its extraordinary properties.
The Source of PTFE's Unique Properties
The molecular architecture—a carbon chain perfectly shielded by strongly bonded fluorine atoms—directly translates into the material's famous characteristics.
Consequence 1: Extreme Chemical Inertness
The fluorine sheath prevents other chemicals from reaching and reacting with the vulnerable carbon backbone. Combined with the strength of the C-F bond itself, this makes PTFE almost completely inert and resistant to nearly all corrosive chemicals, acids, and bases.
Consequence 2: Low-Friction Surface (Non-Stick)
The surface of PTFE is composed entirely of fluorine atoms. This creates a very low surface energy, meaning other substances have virtually nothing to "grab onto." This is the principle behind its non-stick behavior in cookware and its use as a dry lubricant.
Consequence 3: Hydrophobicity and Thermal Stability
This same low-energy surface repels both water and oils, making PTFE highly hydrophobic. Furthermore, the immense strength of its chemical bonds requires a great deal of thermal energy to break, giving it a high melting point and excellent performance across a wide range of temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. While its chemical properties are elite, PTFE has important physical limitations that must be considered.
Mechanical Weakness
In its pure form, PTFE is a relatively soft material. It can be prone to "creep" (deforming under load) and has poor abrasion resistance. For this reason, it is often mixed with fillers like glass, carbon, or graphite to enhance its mechanical strength and wear resistance.
Processing Challenges
PTFE has an extremely high melting point and melt viscosity, which means it cannot be processed using conventional thermoplastic methods like injection molding or extrusion. Instead, it requires more complex and costly techniques like compression molding and sintering, similar to how metal parts are made.
How This Composition Dictates Its Use
Understanding PTFE's chemical makeup allows you to select it for the right application.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance: PTFE is an unmatched choice for seals, gaskets, and vessel linings in the chemical processing and pharmaceutical industries due to its non-reactive nature.
- If your primary focus is low friction: Its non-stick surface makes it the standard for high-performance cookware coatings, cable insulation, and low-friction bearings.
- If your primary focus is mechanical load: Be aware that pure PTFE may be unsuitable and that a filled or reinforced grade will likely be necessary to prevent failure.
Ultimately, knowing that PTFE is a simple carbon-fluorine polymer is the key to unlocking why it is one of the most versatile and valuable materials in modern engineering.
Summary Table:
| Property | Consequence of PTFE's Chemical Structure |
|---|---|
| Chemical Inertness | Excellent resistance to corrosive chemicals, acids, and bases. |
| Low-Friction Surface | Non-stick behavior and dry lubricant capabilities. |
| Hydrophobicity | Repels water and oils. |
| Thermal Stability | High melting point and performance across a wide temperature range. |
| Mechanical Weakness | Pure PTFE is soft and can creep; often requires fillers for strength. |
Need high-precision PTFE components that leverage these unique properties?
At KINTEK, we specialize in manufacturing custom PTFE seals, liners, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in precision production and custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures you get components that deliver on PTFE's promise of superior chemical resistance, low friction, and thermal stability.
Contact us today to discuss your specific application and get a quote!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Bottles for Diverse Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How was Teflon discovered and when was it commercialized? The Accidental Invention of a Wonder Polymer
- What makes PTFE an ideal material for corrosion-resistant applications? Unmatched Chemical Inertness for Harsh Environments
- What chemicals can degrade Teflon? A Guide to PTFE's Chemical Limits
- What are some common uses of PTFE? Unlock Extreme Performance for Your Industry
- What customization options are available for PTFE materials? Tailor Performance for Your Application
- What medical applications benefit from PTFE? A Guide to Its Critical Role in Healthcare
- Is Teflon used in clothing or textiles? Discover the Hidden Coating That Repels Stains and Water
- What are the applications of PTFE dispersion? A Guide to Non-Stick, Chemical-Resistant Coatings & More



















