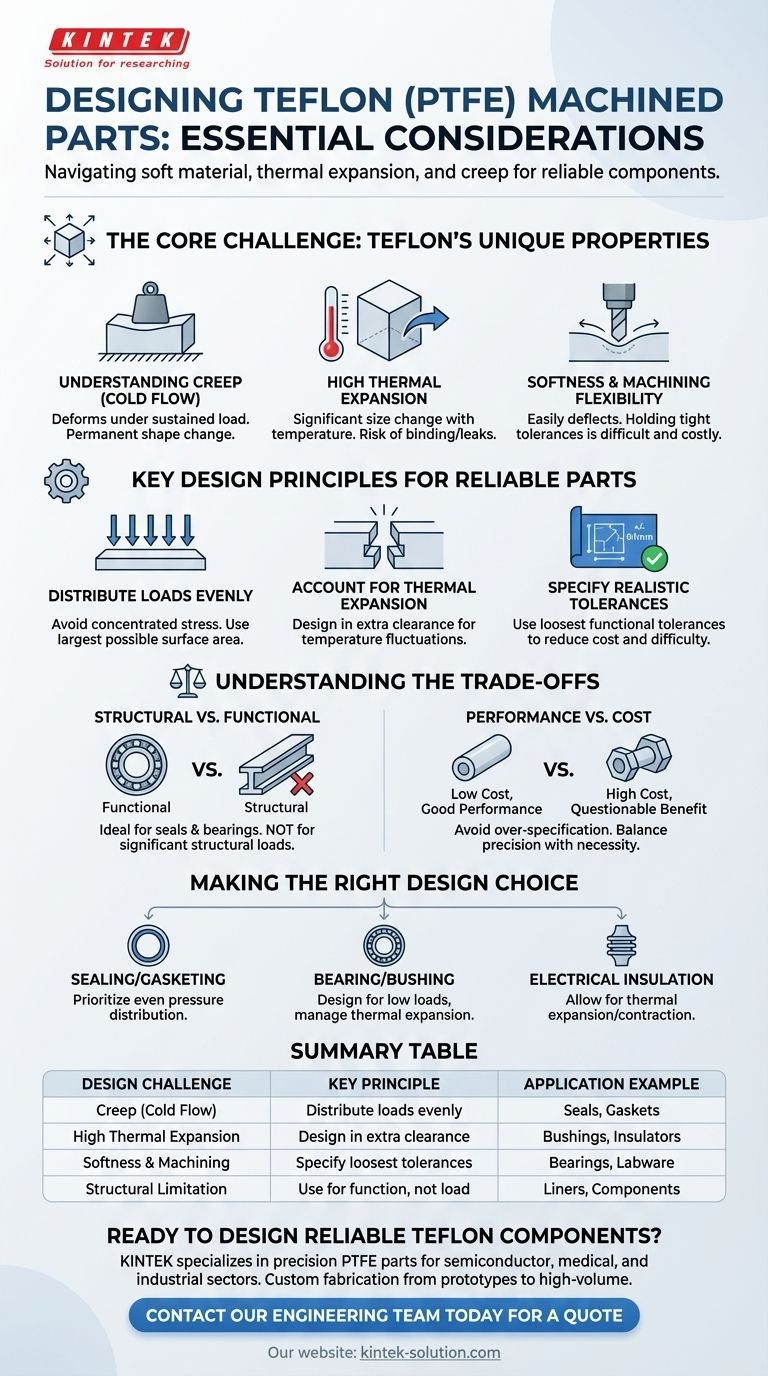
Designing machined parts with Teflon, or PTFE, requires a fundamentally different approach than designing with metals or harder plastics. Its unique combination of softness, high thermal expansion, and tendency to deform under pressure means that standard design practices can lead to component failure. A successful design must proactively account for these material characteristics from the very beginning.
The central challenge in Teflon part design is managing its inherent softness and high rate of thermal expansion. Successful designs must compensate for material creep under load, dimensional changes with temperature, and the material's flexibility during the machining process itself.
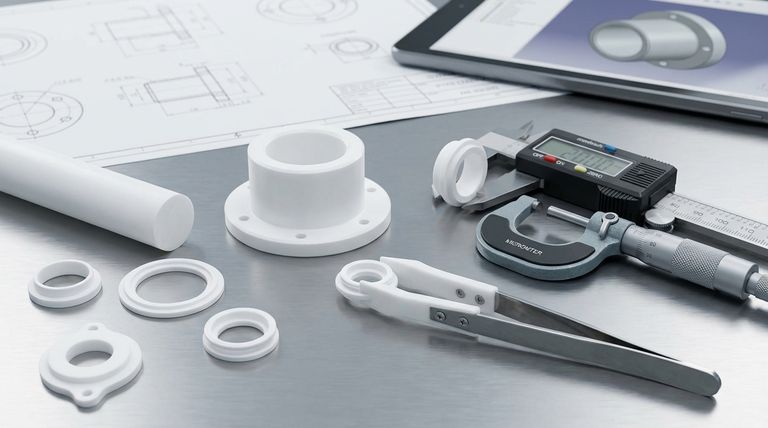

The Core Challenge: Teflon's Unique Properties
To design effective Teflon parts, you must first understand the material's behavior. Unlike rigid materials, Teflon is dynamic; it moves and changes shape in response to its environment.
Understanding Creep (Cold Flow)
Teflon has a tendency to slowly deform over time when subjected to a sustained load, a phenomenon known as creep or cold flow.
Even a moderate, constant pressure can cause the material to permanently change shape, which is a critical failure point for applications like seals and gaskets.
High Thermal Expansion
Teflon expands and contracts with temperature changes far more than most other engineering materials, especially metals.
A part designed to fit perfectly at room temperature may become too tight or too loose at its operating temperature, leading to binding, leaks, or complete failure.
Softness and Machining Flexibility
Teflon is a very soft material. During machining, it can easily deflect or compress under the pressure of the cutting tool.
This makes holding tight tolerances difficult and expensive. A design that calls for metal-like precision is often impractical and fails to account for the material's natural flexibility.
Key Design Principles for Reliable Teflon Parts
A successful Teflon part is one that is designed with the material's properties in mind, not against them. The following principles are essential.
Distribute Loads Evenly
To counteract creep, you must avoid concentrated points of stress. The primary strategy is to distribute mechanical loads over the largest possible surface area.
For example, when designing a Teflon gasket, ensure the clamping force is applied evenly across the entire face rather than at a few specific points.
Account for Thermal Expansion
Your design must accommodate the full operational temperature range of the part. This often means designing in extra clearance to allow the material to expand without being constrained.
Failing to do so can cause immense internal stress, leading to buckling or part failure.
Specify Realistic Tolerances
It is critical to specify the loosest possible tolerances that will still allow the part to function correctly.
Attempting to achieve extremely tight, metal-like tolerances on Teflon parts dramatically increases machining difficulty and cost, often with no real-world performance benefit.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Designing with Teflon involves balancing its unique benefits against its inherent limitations. Understanding these trade-offs is key to avoiding common pitfalls.
Structural vs. Functional Use
Teflon is an exceptional material for its low friction and chemical inertness, making it ideal for seals, bearings, and insulators.
However, it is not a structural material. It should never be used to bear significant, concentrated loads, as it will inevitably deform.
Performance vs. Cost
The cost of a machined Teflon part is heavily influenced by its complexity and tolerances.
Adding unnecessary features or demanding overly tight tolerances can increase the price exponentially due to higher machining time and scrap rates. Always question if that level of precision is truly necessary for the application.
Making the Right Design Choice
Apply these principles based on the primary function of your component.
- If your primary focus is sealing or gasketing: Prioritize even pressure distribution across the sealing face to prevent creep and ensure a long-lasting, effective seal.
- If your primary focus is a low-friction bearing or bushing: Design for low, evenly distributed loads and be especially mindful of thermal expansion that could cause the part to seize within its housing.
- If your primary focus is electrical insulation: Ensure the design allows for thermal expansion and contraction that could otherwise put stress on delicate connectors or surrounding components.
By designing with Teflon's unique properties in mind, you can leverage its distinct advantages to create exceptionally reliable and high-performing components.
Summary Table:
| Design Challenge | Key Principle | Application Example |
|---|---|---|
| Creep (Cold Flow) | Distribute loads evenly over large surface areas | Seals, Gaskets |
| High Thermal Expansion | Design in extra clearance for temperature changes | Bushings, Insulators |
| Softness & Machining | Specify the loosest functional tolerances | Bearings, Labware |
| Structural Limitation | Use for function, not for bearing concentrated loads | Liners, Components |
Ready to design reliable Teflon components?
KINTEK specializes in manufacturing precision PTFE parts (seals, liners, labware, and more) for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise in custom fabrication—from prototypes to high-volume orders—ensures your designs account for Teflon's unique properties, preventing failure and maximizing performance.
Contact our engineering team today to discuss your project and get a quote.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What are PTFE seals commonly known as? Discover Teflon® Seals for Extreme Performance
- What overall benefits do PTFE expansion joints provide to industrial systems? Enhance System Reliability and Longevity
- How does the compressibility of ePTFE gaskets benefit sealing applications? Achieve Superior, Leak-Free Seals
- What are the key advantages of choosing Teflon bearings for applications? Solve Extreme Environment Challenges
- What makes PTFE superior in terms of chemical resistance compared to rubber seals? The Key to Unmatched Reliability
- What role do Teflon PTFE sheets play in sewing projects? Achieve Flawless, Professional Results
- How is PTFE utilized in the electrical and electronics industry? Unlock Superior Performance & Reliability
- What are some modified PTFE materials and their properties? Enhance Strength and Wear Resistance for Demanding Applications



















