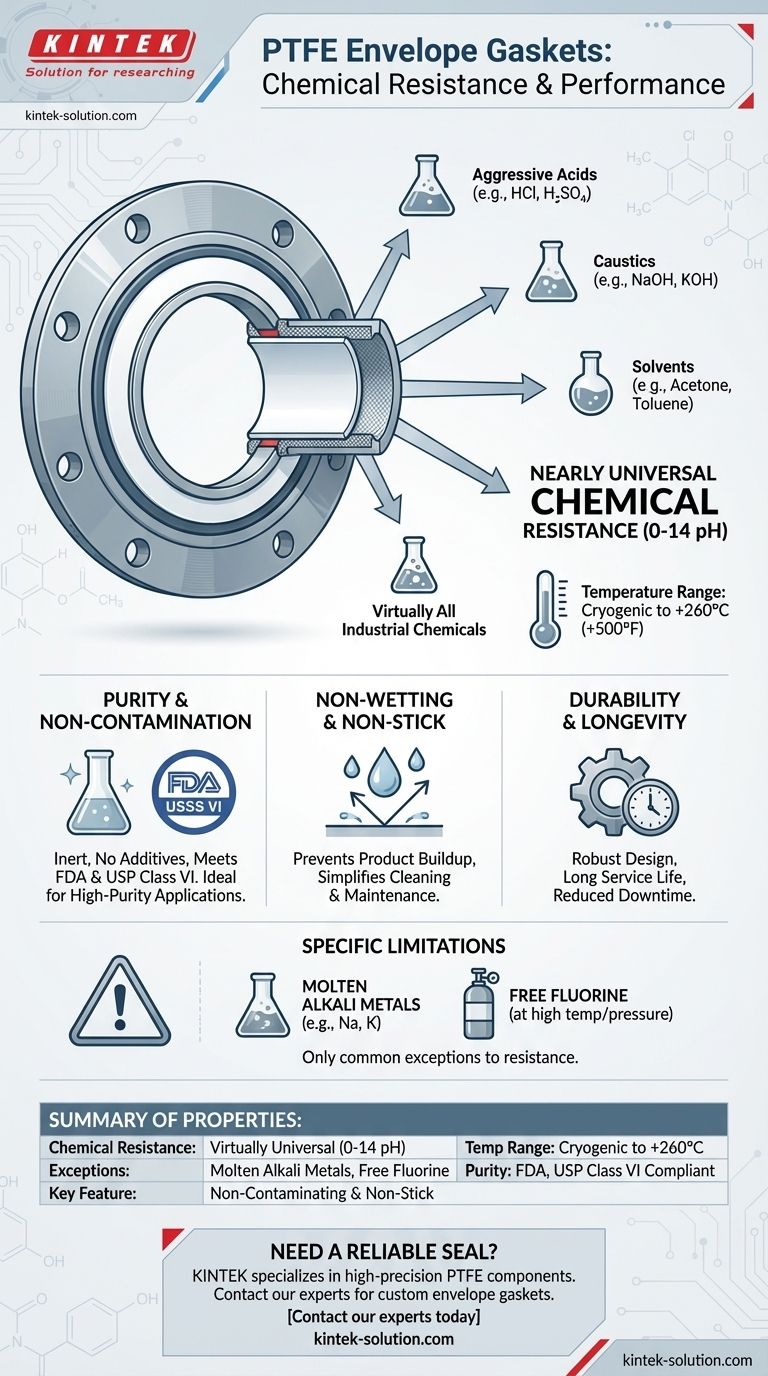
In short, PTFE envelope gaskets offer nearly universal chemical resistance. They are engineered to be chemically inert, allowing them to create a reliable seal for almost all industrial chemicals, including aggressive acids, caustics, and solvents across the entire 0-14 pH range.
A PTFE envelope gasket leverages the near-total chemical inertness of Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) to create a seal that is unaffected by virtually any process medium. Its primary limitation is not its broad chemical resistance but its reaction to a few highly specific substances, namely molten alkali metals and free fluorine.

The Foundation of PTFE's Chemical Inertness
A material's ability to resist chemical attack is the foundation of a reliable, long-lasting seal in corrosive environments. PTFE excels in this regard due to its fundamental molecular structure.
A Virtually Universal Seal
The primary chemical property of a PTFE envelope gasket is its ability to withstand media across the full pH scale (0-14). This makes it suitable for sealing everything from highly concentrated acids to potent caustics.
PTFE is virtually inert, meaning it does not react with the substances it contacts. It is unaffected by most corrosive liquids, vapors, and gases.
Purity and Non-Contamination
Because pure PTFE requires no additives, its chemical resistance is inherent to the material itself. This prevents the gasket from degrading, leaching, or otherwise contaminating the process media.
This non-contaminating property is why these gaskets often meet stringent FDA and USP Class VI standards, making them ideal for pharmaceutical, food and beverage, and other high-purity applications.
Non-Wetting and Non-Stick Surface
A direct result of PTFE's chemical nature is its non-wetting, non-stick surface. This prevents process materials from adhering to the gasket.
This feature simplifies cleaning and maintenance, reduces product buildup on the flange faces, and ensures a clean separation during disassembly.
Performance in Demanding Environments
Chemical resistance is not an isolated property. It works in conjunction with other characteristics to determine the gasket's overall performance and reliability.
Stability Across Temperature Ranges
PTFE maintains its exceptional chemical resistance across a very wide temperature spectrum, from cryogenic conditions up to +260°C (+500°F).
This stability is crucial in processes that involve significant temperature fluctuations, as the gasket's sealing integrity will not be compromised by chemical degradation.
Durability and Longevity
Because the gasket does not degrade when exposed to aggressive chemicals, it has a significantly longer service life.
This robust design reduces the need for frequent replacements, leading to less downtime and lower maintenance costs over the lifetime of the equipment.
Understanding the Practical Limitations
While its resistance is broad, no material is universally perfect. Understanding the specific, narrow limitations of PTFE is critical for ensuring safety and reliability in extreme applications.
The Few Chemical Exceptions
The only common industrial chemicals known to attack PTFE are molten alkali metals (like sodium and potassium) and free fluorine atoms at high temperatures and pressures. For all other applications, PTFE is considered fully resistant.
The Role of Temperature and Pressure
While chemically stable at high temperatures, the gasket's mechanical ability to hold a seal is still subject to its design pressure and temperature limits. The inner core material of the envelope gasket plays a significant role in its pressure resistance and creep relaxation properties.
Creep Relaxation
All PTFE materials can exhibit some degree of "creep," or deformation under a constant load. Envelope gaskets are engineered to minimize this effect, but it is a mechanical factor to consider in high-pressure or high-temperature applications that require consistent bolt torque over long periods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct gasket requires matching its properties to your primary operational goal.
- If your primary focus is handling aggressive chemicals: PTFE envelope gaskets are a default choice due to their near-universal resistance across the full 0-14 pH scale.
- If your primary focus is product purity: These gaskets are ideal, as their inert nature prevents process contamination and meets critical FDA and USP Class VI standards.
- If your primary focus is extreme conditions: You must verify that your process does not involve molten alkali metals or free fluorine, which are the few known chemical exceptions.
By understanding both its broad capabilities and its specific limitations, you can confidently deploy PTFE envelope gaskets in your most critical sealing applications.
Summary Table:
| Property | Performance |
|---|---|
| Chemical Resistance | Virtually universal (0-14 pH) |
| Temperature Range | Cryogenic to +260°C (+500°F) |
| Exceptions | Molten alkali metals, free fluorine |
| Purity Standards | FDA, USP Class VI compliant |
| Key Feature | Non-contaminating & non-stick surface |
Need a reliable seal for aggressive chemicals? KINTEK specializes in manufacturing high-precision PTFE components, including custom envelope gaskets for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors. Our expertise ensures your sealing solution offers superior chemical resistance and longevity. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application requirements, from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Customizable PTFE Seals Filter Holders for Versatile Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
- Custom PTFE Measuring Cylinders for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What is the main difference between bronze and PTFE bushings? Choose the Right Bushing for Your Application
- How does PTFE enhance baseball equipment? Unlock Faster Swings and Longer-Lasting Gear
- Can PTFE bushings operate without lubrication? Achieve maintenance-free performance in harsh environments.
- What are the cost implications of choosing PTFE over NBR for butterfly valve seats? A Guide to True Cost of Ownership
- Why is machined PTFE popular in the medical field? Unmatched Biocompatibility & Precision
- What is PTFE, and why is it used in expansion joints? Superior Chemical & Thermal Stability
- What are PTFE expansion joints and their primary function? Protect Piping Systems from Stress and Corrosion



















