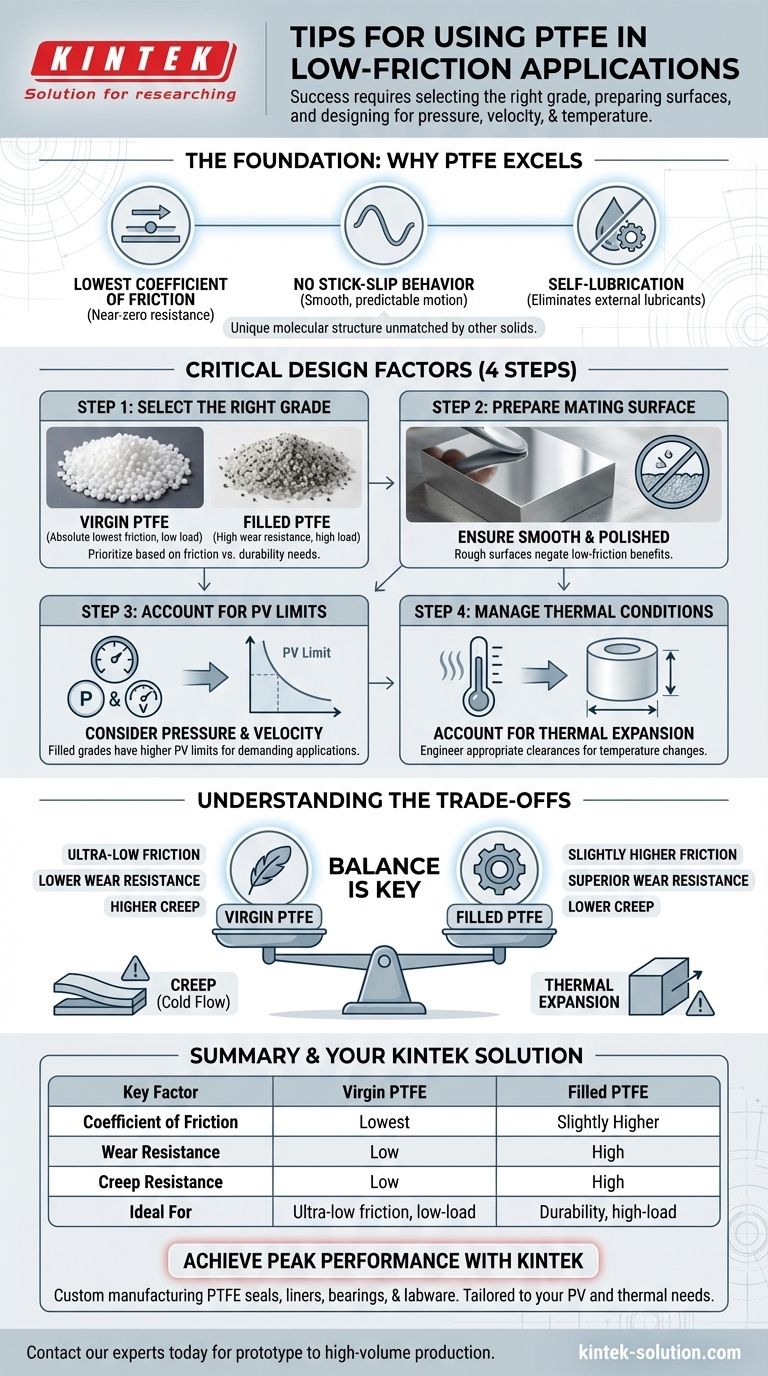
To effectively use PTFE for low-friction applications, you must go beyond simply choosing the material. Success requires selecting the correct PTFE grade for your load conditions, meticulously preparing the mating surface it will contact, and designing your system to account for pressure, velocity, and temperature.
PTFE offers the lowest coefficient of friction of any solid material, but achieving optimal performance is not automatic. Success hinges on a critical trade-off: balancing the ultra-low friction of virgin PTFE against the superior wear resistance of filled grades, tailored to your specific application's mechanical and thermal loads.

The Foundation: Why PTFE Excels at Low Friction
Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) is renowned as the "friction plastic" for a reason. Its unique molecular structure gives it properties that are unmatched by other polymers or even metals.
The Lowest Known Coefficient of Friction
PTFE has a lower coefficient of friction than any other known solid. This intrinsic property allows moving parts to slide against each other with minimal energy loss.
This is why it's the material of choice for applications demanding oil-free lubrication, from mechanical bearings to piston rings.
Eliminating Stick-Slip Behavior
The material’s non-stick surface prevents the jerky start-stop motion, known as stick-slip, that can occur in other systems. This ensures operations are consistently smooth and predictable.
The Benefit of Self-Lubrication
PTFE's low-friction nature means it can often function without any external liquid or grease lubricants. This simplifies designs, reduces maintenance costs, and prevents contamination in sensitive environments like medical or food processing equipment.
Critical Design Factors for Success
Harnessing PTFE's benefits requires careful attention during the design and implementation phase. Merely substituting PTFE for another material is not a complete solution.
Step 1: Select the Right PTFE Grade
The most important decision is choosing between virgin and filled PTFE.
Virgin PTFE offers the absolute lowest coefficient of friction. It is ideal for low-load applications where minimizing sliding resistance is the single most important goal.
Filled PTFE incorporates additives like glass, carbon, or bronze. These fillers dramatically increase wear resistance, compressive strength, and stability under load, making it suitable for more demanding applications.
Step 2: Prepare the Mating Surface
The surface that slides against the PTFE component is just as important as the PTFE itself. A rough or abrasive mating surface will quickly wear down the PTFE, negating its low-friction benefits.
For optimal performance and longevity, ensure the mating surface is smooth and polished.
Step 3: Account for Pressure and Velocity (PV)
Every material has a limit on the pressure (P) and velocity (V) it can withstand before it begins to fail rapidly. This is known as the PV limit.
You must consider the combined load and speed of your application. Filled PTFE grades have significantly higher PV limits than virgin PTFE, making them essential for high-load or high-speed systems.
Step 4: Manage Thermal Conditions
PTFE has a wide operating temperature range, but its properties can change with temperature. It is critical to account for thermal expansion and ensure the material remains stable within the specific thermal environment of your application.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect, and a trusted advisor must highlight the limitations. Understanding PTFE's trade-offs is key to preventing design failures.
Friction vs. Wear Resistance
This is the central trade-off. While adding fillers to PTFE increases wear resistance by orders of magnitude, it also slightly increases the coefficient of friction.
Your choice must be a deliberate one: prioritize ultra-low friction with virgin PTFE or prioritize durability under load with a filled grade.
Creep (Cold Flow)
A known characteristic of PTFE is its tendency to creep, or slowly deform over time when under a sustained compressive load. This is especially true for virgin PTFE.
Fillers significantly reduce creep. If your component—such as a seal or gasket—will be under constant pressure, a filled grade is almost always the correct choice.
Thermal Expansion
PTFE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion than most metals. In designs with tight tolerances, temperature fluctuations can cause a PTFE part to expand or contract significantly.
Designers must account for this by engineering appropriate clearances to avoid binding or failure when temperatures change.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific goal should dictate your material selection and design strategy.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest possible friction: Use virgin PTFE with a highly polished mating surface in a low-load, controlled temperature environment.
- If your primary focus is durability and long service life under load: Choose a filled PTFE grade (e.g., glass or carbon-filled) and ensure the design accounts for the material's PV limit.
- If your primary focus is chemical resistance and smooth valve operation: Virgin PTFE is excellent, but for seals under pressure, ensure the design accommodates for potential material creep.
By strategically balancing these factors, you can harness PTFE's unique properties to create exceptionally efficient and durable mechanical systems.
Summary Table:
| Key Factor | Virgin PTFE | Filled PTFE |
|---|---|---|
| Coefficient of Friction | Lowest | Slightly Higher |
| Wear Resistance | Low | High |
| Creep Resistance | Low | High |
| Ideal For | Ultra-low friction, low-load applications | Durability, high-load applications |
Achieve peak performance in your low-friction application with precision-engineered PTFE components from KINTEK.
Whether you require the ultra-low friction of virgin PTFE or the enhanced durability of filled grades for high-load scenarios, KINTEK delivers. We specialize in custom manufacturing PTFE seals, liners, bearings, and labware for the semiconductor, medical, laboratory, and industrial sectors.
Our expertise ensures your components are perfectly tailored to your specific pressure, velocity, and temperature requirements, maximizing efficiency and service life.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs—from prototype to high-volume production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
- Custom PTFE Square Trays for Industrial and Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- What tips can improve Teflon machining results? Master Sharp Tools, Heat Control, and Rigid Support
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What industries use PTFE machined parts and for what applications? Critical Components for Demanding Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments



















