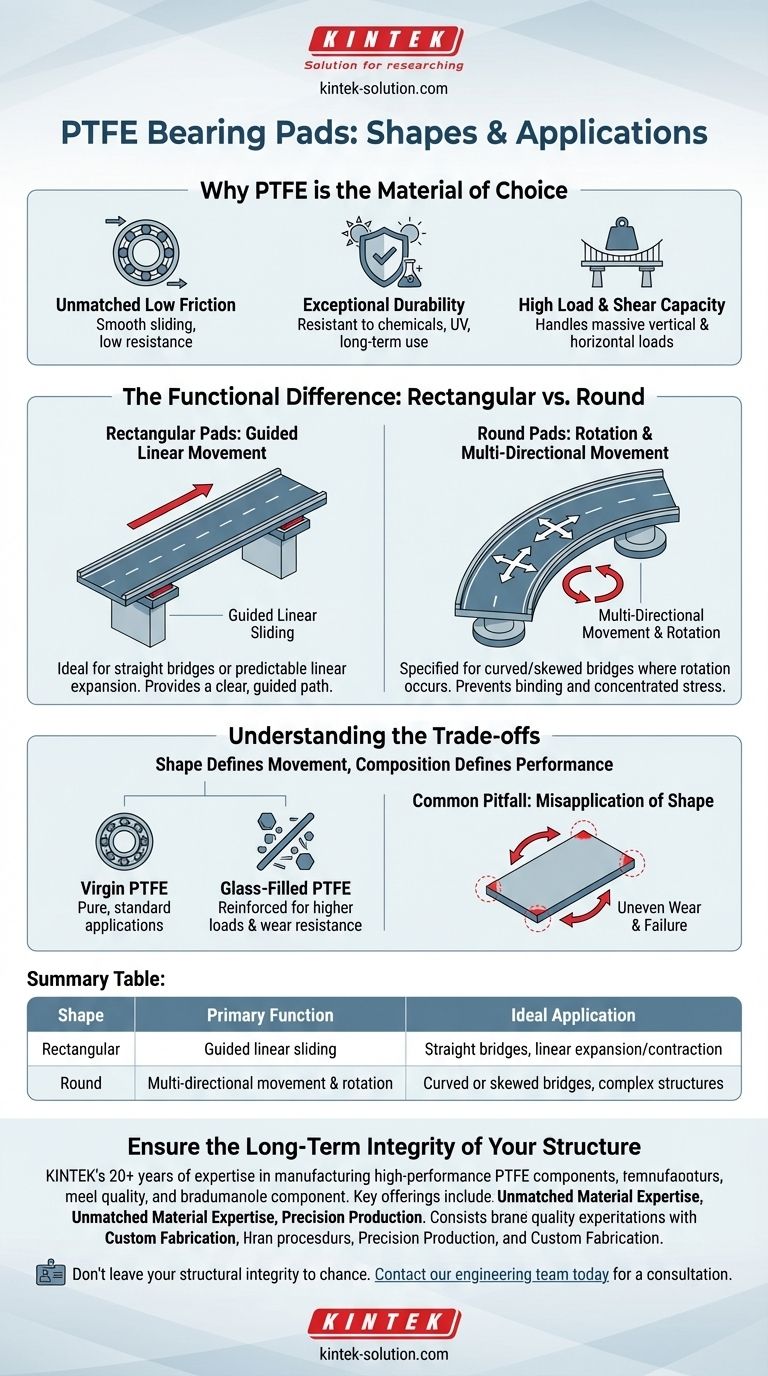
The two primary shapes for PTFE bearing pads are rectangular and round. Rectangular pads are the standard choice for straight bridges, accommodating linear expansion and contraction. Round pads, however, are specifically used for curved or skewed bridges where the structure must also be able to rotate safely.
The decision between a rectangular and a round PTFE bearing pad is not about aesthetics; it is a critical engineering choice determined by the type of movement the structure must accommodate. Rectangular pads are for linear sliding, while round pads are for multi-directional movement, including rotation.

Why PTFE is the Material of Choice
Before analyzing the shape, it's essential to understand why Polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), often known by the brand name Teflon, is the dominant material for high-load structural bearings.
Unmatched Low Friction
PTFE has one of the lowest coefficients of friction of any known solid material. This allows massive structural elements, like a bridge deck, to slide smoothly over their supports with minimal resistance.
This property is critical for managing the natural expansion and contraction caused by temperature changes, preventing immense stress from building up in the structure.
Exceptional Durability
Structural bearings are exposed to harsh environmental conditions for decades. PTFE is highly resistant to chemical degradation, weathering, and UV radiation, ensuring its performance and integrity over the long term.
High Load and Shear Capacity
Despite its low friction, PTFE can withstand enormous vertical loads. More importantly, it has a high shear capacity, meaning it can handle the horizontal forces generated by movement and braking loads without failing.
The Functional Difference: Rectangular vs. Round
The geometry of the bearing pad directly dictates how it controls structural movement.
Rectangular Pads: For Guided Linear Movement
Rectangular pads are ideal for straight bridges or structures where movement is predictable and occurs primarily along a single axis.
Their shape provides a clear, guided path for sliding. This ensures the structure expands and contracts in a controlled, linear fashion.
Round Pads: For Rotation and Multi-Directional Movement
Round pads are specified for curved bridges, skewed bridges, or complex structures where rotational movement occurs alongside linear expansion.
Because a circle has no preferential direction, a round pad allows the structure to rotate from a central point without binding or creating concentrated stress at corners. This is essential for preventing damage in structures that twist or shift in multiple directions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
Choosing the right pad involves more than just its shape. The material composition itself is a critical factor in its performance.
Shape Defines Movement, Composition Defines Performance
The shape dictates the type of movement allowed, but the specific grade of PTFE determines its load capacity and wear resistance.
The Role of Fillers
Pure, or virgin, PTFE is used in many applications, but for high-demand structural bearings, it is often reinforced.
Glass-filled PTFE, for example, contains glass fibers that significantly increase compressive strength and wear resistance, making it suitable for higher loads than virgin PTFE. Other fillers can be used to achieve specific properties.
Common Pitfall: Misapplication of Shape
Using a rectangular pad in an application that requires rotation is a critical design flaw. As the structure attempts to twist, the corners of the rectangular pad will resist the movement, leading to extreme point-loading, uneven wear, and potential bearing failure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Structure
Your selection must be based on the specific movements your design needs to accommodate.
- If your primary focus is a straight bridge with predictable linear expansion: A rectangular PTFE pad provides the most stable and cost-effective solution for guided movement.
- If your primary focus is a curved or skewed bridge requiring rotation: A round PTFE pad is non-negotiable to accommodate complex, multi-directional movements and prevent binding.
- If your structure is subject to exceptionally high loads or abrasive conditions: Specify a filled PTFE grade, such as glass-filled, in the appropriate shape to enhance strength and durability.
Choosing the correct bearing shape is fundamental to ensuring the long-term health and integrity of your structure.
Summary Table:
| Shape | Primary Function | Ideal Application |
|---|---|---|
| Rectangular | Guided linear sliding | Straight bridges, linear expansion/contraction |
| Round | Multi-directional movement & rotation | Curved or skewed bridges, complex structures |
Ensure the Long-Term Integrity of Your Structure
Choosing the wrong PTFE bearing pad shape can lead to premature wear, binding, and even structural failure. For over 20 years, KINTEK has been a trusted partner to engineers and project managers in the bridge and construction industry, manufacturing high-performance, custom PTFE components that meet exacting specifications.
We understand that your project's success depends on precision and reliability. Whether you need standard rectangular pads for a straightforward span or custom-fabricated round pads for a complex curved bridge, we deliver:
- Unmatched Material Expertise: From virgin to glass-filled PTFE, we help you select the optimal material grade for your load and environmental conditions.
- Precision Production: Our components are manufactured to the tightest tolerances, ensuring smooth, predictable movement and long service life.
- Custom Fabrication: We provide solutions from prototypes to high-volume production runs, tailored to your unique design requirements.
Don't leave your structural integrity to chance. Contact our engineering team today for a consultation on the right PTFE bearing solution for your project.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Parts and PTFE Tweezers
- Custom PTFE Parts Manufacturer for Teflon Containers and Components
- Customizable PTFE Rods for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Balls for Advanced Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Sleeves and Hollow Rods for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- How does PTFE contribute to low friction and wear resistance? Achieve Superior Performance with Advanced Materials
- What are the key considerations when machining Teflon? Master Precision Machining for Soft Polymers
- What are the best practices for achieving tight tolerances in Teflon (PTFE) machining? Master Precision for Demanding Applications
- What are the key advantages of PTFE? Unmatched Performance for Extreme Environments
- Why is CNC machining preferred for Teflon parts over other methods? Unlock Precision & Complex Designs



















